Document
... If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why does it rotate? It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolli ...
... If a wheel is placed on a flat surface and a force is applied at the center of the wheel what will it do? It will translate and rotate. Why does it rotate? It rotates due to the frictional force at the point of contact, that is in a direction opposite to the direction the wheel would slip. The rolli ...
Unit 8(Electromagnetic Waves)
... (i) Calculate the displacement current density inside the cable. (ii) Integrate the displacement current density across the crosssection of the cable to find the total displacement current Id. (iii) Compare the conduction current I0 with the dispalcement ...
... (i) Calculate the displacement current density inside the cable. (ii) Integrate the displacement current density across the crosssection of the cable to find the total displacement current Id. (iii) Compare the conduction current I0 with the dispalcement ...
Bohr vs. Correct Model of Atom
... • Don’t have definite electron position, only a probability function. Java • Each orbital can have 0 angular momentum! • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) Coming Soon! ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin ...
... • Don’t have definite electron position, only a probability function. Java • Each orbital can have 0 angular momentum! • Each electron state labeled by 4 numbers: n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) Coming Soon! ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin ...
Quantum Readiness
... 28. A researcher is studying a particle confined by a potential well between x positions -1 and +1. The well is in a material that has been cooled to a temperature near absolute zero, so the researcher is certain that the particle is in its ground state. The potential well is reasoned to be very de ...
... 28. A researcher is studying a particle confined by a potential well between x positions -1 and +1. The well is in a material that has been cooled to a temperature near absolute zero, so the researcher is certain that the particle is in its ground state. The potential well is reasoned to be very de ...
Unit 4 Study Guide - Key - Effingham County Schools
... 5. _Wavelength____________ (λ) is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. What is its unit? _m, cm, or nm_________ 6. _Frequency____________ (ν) is defined as the number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time. What is its unit? _waves/second or hertz(Hz)___________ ...
... 5. _Wavelength____________ (λ) is the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. What is its unit? _m, cm, or nm_________ 6. _Frequency____________ (ν) is defined as the number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time. What is its unit? _waves/second or hertz(Hz)___________ ...
SOME ASPECTS OF STRANGE MATTER : STARS AND
... Incidentally, issue of behaviour of radiation as particle – the photon – was finally settled in 1923 by A. H. Compton. Compton found that the light scattered from a particle at rest is shifted in wavelength as given by (1 cos ) c ...
... Incidentally, issue of behaviour of radiation as particle – the photon – was finally settled in 1923 by A. H. Compton. Compton found that the light scattered from a particle at rest is shifted in wavelength as given by (1 cos ) c ...
polarization of the allotropic hollow foms of carbon and its use in
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
powerpoint
... Atom Diffraction from a Crystal The Phenomenon A supersonic beam of He particles hitting a GaAs crystal splits ...
... Atom Diffraction from a Crystal The Phenomenon A supersonic beam of He particles hitting a GaAs crystal splits ...
Waves
... To form a pulse that is zero everywhere outside of a finite spatial range x requires adding together an infinite number of waves with continuously varying wavelengths and amplitudes. ...
... To form a pulse that is zero everywhere outside of a finite spatial range x requires adding together an infinite number of waves with continuously varying wavelengths and amplitudes. ...
Physics 200 Class #1 Outline
... So when the photon scatters, it loses energy and gives this energy to the electron. This means that it changes frequency (and wavelength) when it scatters. For example, green light hitting an electron may scatter off as red light, which has lower energy. Conservation of linear momentum: The calculat ...
... So when the photon scatters, it loses energy and gives this energy to the electron. This means that it changes frequency (and wavelength) when it scatters. For example, green light hitting an electron may scatter off as red light, which has lower energy. Conservation of linear momentum: The calculat ...
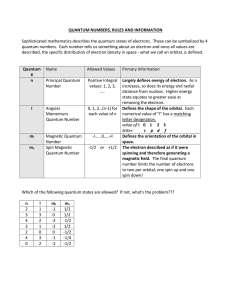
Quantum Number Table
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
... Largely defines energy of electron. As n increases, so does its energy and radial distance from nucleus. Higher energy state equates to greater ease at removing the electron. Defines the shape of the orbital. Each numerical value of "l" has a matching letter designation. value of l: 0 1 2 3 letter: ...
chapter40
... At long wavelengths, Planck’s equation reduces to the Rayleigh-Jeans expression At short wavelengths, it predicts an exponential decrease in intensity with ...
... At long wavelengths, Planck’s equation reduces to the Rayleigh-Jeans expression At short wavelengths, it predicts an exponential decrease in intensity with ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... ____________________________ developed the ________________________ principle which states that it is not possible to simultaneously determine the position and momentum of a particle, such as an electron. ...
... ____________________________ developed the ________________________ principle which states that it is not possible to simultaneously determine the position and momentum of a particle, such as an electron. ...
















![introduction [Kompatibilitätsmodus]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017596641_1-03cad833ad630350a78c42d7d7aa10e3-300x300.png)