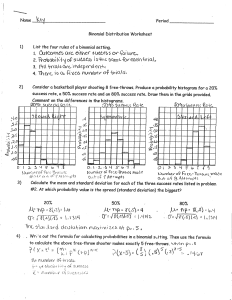
1) How many possible outcomes would there be if three coins were
... 1) How many possible outcomes would there be if three coins were tossed once? A) ...
... 1) How many possible outcomes would there be if three coins were tossed once? A) ...
Class 23_270_11
... will produce an interference pattern, like a wave. • However, each electron makes a single impact on a phosphorescent screen‐like a particle. • Electrons have indivisible (as far as we know) mass and electric charge, so if you suddenly closed one of the slits, you couldn’t chop the electron in ...
... will produce an interference pattern, like a wave. • However, each electron makes a single impact on a phosphorescent screen‐like a particle. • Electrons have indivisible (as far as we know) mass and electric charge, so if you suddenly closed one of the slits, you couldn’t chop the electron in ...
Sigma Notation - Books in the Mathematical Sciences
... The sign 3, called sigma, is a glorified symbol for addition that can be quite useful. It is utilized throughout mathematics, statistics, computer science and all other mathematical disciplines. With the 3 there is usually an index that typically is an i or j. Rather than define the 3 operation, I a ...
... The sign 3, called sigma, is a glorified symbol for addition that can be quite useful. It is utilized throughout mathematics, statistics, computer science and all other mathematical disciplines. With the 3 there is usually an index that typically is an i or j. Rather than define the 3 operation, I a ...
MATH-138: Objectives
... Recognize the difference between an experiment and an observational study. ...
... Recognize the difference between an experiment and an observational study. ...
Probability (Chapter 6)
... Knowing the make-up of a population allows us to infer the likely characteristics of samples from the same population (population to sample inference) This, however, is backwards from what we do in inferential statistics In inferential statistics, we make inferences from a known sample to what ...
... Knowing the make-up of a population allows us to infer the likely characteristics of samples from the same population (population to sample inference) This, however, is backwards from what we do in inferential statistics In inferential statistics, we make inferences from a known sample to what ...
Document
... e. The probability that an individual value will be more than 1.5 S.D. below the mean in the data set is 6.68% At home: What is the probability of getting less than 500 mm of rainfall in any one year in Edinburgh, Scotland given a mean annual rainfall of 664 mm and a S.D. of 120 mm? ...
... e. The probability that an individual value will be more than 1.5 S.D. below the mean in the data set is 6.68% At home: What is the probability of getting less than 500 mm of rainfall in any one year in Edinburgh, Scotland given a mean annual rainfall of 664 mm and a S.D. of 120 mm? ...
MSc Regulation and Competition
... What are the main sources of data errors? What can be done to reduce errors in data you did not collect yourself? ...
... What are the main sources of data errors? What can be done to reduce errors in data you did not collect yourself? ...
Math 302.102 Fall 2010 The Binomial Distribution Suppose that we
... Suppose that we are considering repeated trials where in each trial we might observe one of only two possible results. We can label these results as success or failure. (Or, in applications, they might be on/off, zero/one, yes/no, left/right, male/female, shows improvement/does not show improvement, ...
... Suppose that we are considering repeated trials where in each trial we might observe one of only two possible results. We can label these results as success or failure. (Or, in applications, they might be on/off, zero/one, yes/no, left/right, male/female, shows improvement/does not show improvement, ...
Assignment 2
... Bonus question: We are given n (n > 5) points in three dimensional space (R3 ) that are in general position, i.e., no four of them lie on the same plane. Let Ω denote the set of the planes determined by any three of these points and assume that no two planes in Ω are parallel so that any two planes ...
... Bonus question: We are given n (n > 5) points in three dimensional space (R3 ) that are in general position, i.e., no four of them lie on the same plane. Let Ω denote the set of the planes determined by any three of these points and assume that no two planes in Ω are parallel so that any two planes ...
to the wave function
... wave function or state function (r, t) that depends on the coordinates of the particle(s) and on time. – a mathematical description of a physical system • The probability to find the particle in the volume element d = dr dt located at r at time t is given by (r, t)(r, t) d . – Born interpretat ...
... wave function or state function (r, t) that depends on the coordinates of the particle(s) and on time. – a mathematical description of a physical system • The probability to find the particle in the volume element d = dr dt located at r at time t is given by (r, t)(r, t) d . – Born interpretat ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.