Maths Methods - Outcome 6 - Probability
... It is different to binomial and markov chain. Typically a question will ask: e.g. What is the probability that you have x failures before ...
... It is different to binomial and markov chain. Typically a question will ask: e.g. What is the probability that you have x failures before ...
Assist
... Complement, union, and intersection of events, Conditional probability, independent events, mutually exclusive events Counting techniques (Factorials, permutation, combination, multiplication rule) IV. Probability Distributions Discrete probability distributions Probability mass function, cumulative ...
... Complement, union, and intersection of events, Conditional probability, independent events, mutually exclusive events Counting techniques (Factorials, permutation, combination, multiplication rule) IV. Probability Distributions Discrete probability distributions Probability mass function, cumulative ...
midterm answers
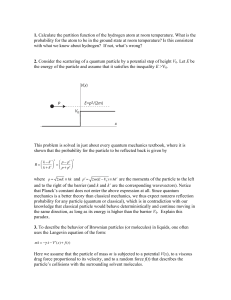
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
... the square of the wave function is the probability density, since the wave function is approaching zero without reaching it as long as x is finite, the square of the wave function will not reach zero either, this being the probability density in the barrier, the particle has a probability to be ther ...
Chapter 2
... No. Notice that a pair of events, A and B, are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur jointly, that is, P(AB) = 0. Independence, on the other hand, means that P(AB) = P(A) P(B). Consider this example. Let A = the card is a heart and B = the card is an ace. A card is drawn from a deck of 52 cards. W ...
... No. Notice that a pair of events, A and B, are mutually exclusive if they cannot occur jointly, that is, P(AB) = 0. Independence, on the other hand, means that P(AB) = P(A) P(B). Consider this example. Let A = the card is a heart and B = the card is an ace. A card is drawn from a deck of 52 cards. W ...
Click here for the word document of this reflection
... classroom. I feel his approach will not infer in any learning and too provide a greater understanding for my students. After reading this article I will be trying this setting in my classroom. I can see that the importance of variation to later subjects in statistics. As I teach my students in proba ...
... classroom. I feel his approach will not infer in any learning and too provide a greater understanding for my students. After reading this article I will be trying this setting in my classroom. I can see that the importance of variation to later subjects in statistics. As I teach my students in proba ...
Exam Tips File
... 7. Answers to experimental design questions should include clear evidence of blocking, randomization, control, and replication. Randomization should generally be clearly explained using a random # generator or random # table. 8. Confidence Interval explanations: Interpretation of the interval: We ca ...
... 7. Answers to experimental design questions should include clear evidence of blocking, randomization, control, and replication. Randomization should generally be clearly explained using a random # generator or random # table. 8. Confidence Interval explanations: Interpretation of the interval: We ca ...
Practice Quiz - Probability
... 1) Use the spinner below to answer the question. Assume that it is equally probable ...
... 1) Use the spinner below to answer the question. Assume that it is equally probable ...
Linear Circuit Analysis with Reactive Components
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
Problem set 9
... work in the momentum basis. So you need to know how x̂ acts in k -space. This was worked ...
... work in the momentum basis. So you need to know how x̂ acts in k -space. This was worked ...
K.K. Gan Physics 416 Problem Set 2 Due Thursday, May 6, 2003
... 6) Suppose a missile defense system destroys an incoming missile 95% of the time. a) If an evil country launches 20 missiles what is the probability that the missile defense system will destroy all of the incoming missiles? b) How many missiles have to be launched to have a 50% chance of at least on ...
... 6) Suppose a missile defense system destroys an incoming missile 95% of the time. a) If an evil country launches 20 missiles what is the probability that the missile defense system will destroy all of the incoming missiles? b) How many missiles have to be launched to have a 50% chance of at least on ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.