* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MATH-138: Objectives
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
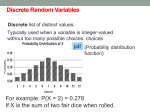
MATH-138: Objectives Intro Stats, by Richard D. De Veaux, Paul F. Velleman, and David E. Bock Unit II The student will be able to: Chapter 9: Understanding Randomness 1. 2. 3. Explain what it means to be random. Accurately model a situation through simulation. Discuss the results of a simulation study and draw conclusions about the questions being investigated. Chapter 10: Sample Surveys 4. 5. 6. 7. Classify samples, populations, parameters and statistics. Identify and explain the different sampling techniques: census, simple random samples, stratified, cluster, and systematic. Identify and explain possible sampling mistakes: convenience, voluntary response, bad sampling frame, and under coverage. Recognize different types of bias. Chapter 11: Experiments & Observational Studies 8. Recognize the difference between an experiment and an observational study. Chapter 12: From Randomness to Probability 9. 10. 11. 12. State the definition of trial, outcome, sample space, event and P(A). Apply the Law of Large Numbers. Recognize when events are disjoint and when events are independent. State the basic definitions and apply the rules of probability for disjoint and independent events. Chapter 13: Probability Rules! 13. 14. 15. Apply the General Addition and General Multiplication rules. Compute conditional probabilities and use the rule to test for independence. Use a tree diagram to understand conditional probabilities and to reverse conditioning. 1 Chapter 14: Random Variables and Probability Models 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. Distinguish between discrete and continuous random variables. Find the probability model for a discrete random variable. Find and interpret in context the mean (expected value) and the standard deviation of a random variable. Determine if a situation involves Bernoulli trials. Know the appropriate conditions for using a Binomial model. Calculate binomial probabilities. Find and interpret in context the mean and standard deviation of a Binomial model.