Type II Error
... Type II Error in Two-Tailed Test of Population Mean with Unknown Variance In a two-tailed test of the population mean, the null hypothesis claims that the true population mean μ is equal to a given hypothetical value μ0. μ=μ o A type II error occurs if the hypothesis test based on a random sample f ...
... Type II Error in Two-Tailed Test of Population Mean with Unknown Variance In a two-tailed test of the population mean, the null hypothesis claims that the true population mean μ is equal to a given hypothetical value μ0. μ=μ o A type II error occurs if the hypothesis test based on a random sample f ...
0 - CA Sri Lanka
... This is a lower-tail test since the alternative hypothesis is focused on the lower tail below the mean of 3 This is an upper-tail test since the alternative hypothesis is focused on the upper tail above the mean of 3 ...
... This is a lower-tail test since the alternative hypothesis is focused on the lower tail below the mean of 3 This is an upper-tail test since the alternative hypothesis is focused on the upper tail above the mean of 3 ...
Estimation-Confidence intervals
... determine the likelihood of obtaining sample outcomes if the null hypothesis were true. The value of the test statistic is used to make a decision regarding the null hypothesis. The test statistic is a random variable because is a function of random variables. For instance, consider hypothesis tes ...
... determine the likelihood of obtaining sample outcomes if the null hypothesis were true. The value of the test statistic is used to make a decision regarding the null hypothesis. The test statistic is a random variable because is a function of random variables. For instance, consider hypothesis tes ...
P-Value Approximations for T-Tests of Hypothesis
... null hypothesis. That is the smaller a p-value, the more evidence exists to support the alternative hypothesis. This p-value determination enables a researcher to make decisions, regarding whether the data collected indicates significant differences or not in the population. Usually for alpha, the s ...
... null hypothesis. That is the smaller a p-value, the more evidence exists to support the alternative hypothesis. This p-value determination enables a researcher to make decisions, regarding whether the data collected indicates significant differences or not in the population. Usually for alpha, the s ...
Z - El Camino College
... Zdata is an extreme value. Unusual and extreme values of the sample mean, and therefore of Zdata will have a small p-value. Assuming H0 is true: Unusual and extreme values of sample mean and Zdata •Small p-value (close to 0) Values of sample mean and Zdata near center •Large p-value (greater than, s ...
... Zdata is an extreme value. Unusual and extreme values of the sample mean, and therefore of Zdata will have a small p-value. Assuming H0 is true: Unusual and extreme values of sample mean and Zdata •Small p-value (close to 0) Values of sample mean and Zdata near center •Large p-value (greater than, s ...
Inference for one sample
... is what we are trying to conclusively demonstrate–for the journalist, the alternative hypothesis (representing the case that the election can be ’called’) is p 6= 0.5. For the campaign manager of candidate A, a different alternative might be of interest–he would like to know if his candidate will wi ...
... is what we are trying to conclusively demonstrate–for the journalist, the alternative hypothesis (representing the case that the election can be ’called’) is p 6= 0.5. For the campaign manager of candidate A, a different alternative might be of interest–he would like to know if his candidate will wi ...
Inferences on a Population Mean
... Example: Suppose I toss a coin 10 times and get 9 heads. If we assume the coin is fair, what is the probability that I get 9 or 10 heads (the data observed or something more extreme)? Is that probability small enough to convince you that the coin is not fair? What if I toss the coins 100 times and g ...
... Example: Suppose I toss a coin 10 times and get 9 heads. If we assume the coin is fair, what is the probability that I get 9 or 10 heads (the data observed or something more extreme)? Is that probability small enough to convince you that the coin is not fair? What if I toss the coins 100 times and g ...
t–test - Bioinformatics.ca
... what is a p–value? a) A measure of how much evidence we have against the alternative hypothesis. b) The probability of making an error. c) Something that biologists want to be below 0.05 . ...
... what is a p–value? a) A measure of how much evidence we have against the alternative hypothesis. b) The probability of making an error. c) Something that biologists want to be below 0.05 . ...
Significance Testing
... contribution is the device used to quantify the distance between the data and what would be expected if the null hypothesis were true. That device is called the P-value. Fisher (1956) put it this way: “The logical basis of these scientific applications was the elementary one of excluding, at an assi ...
... contribution is the device used to quantify the distance between the data and what would be expected if the null hypothesis were true. That device is called the P-value. Fisher (1956) put it this way: “The logical basis of these scientific applications was the elementary one of excluding, at an assi ...
Hypothesis Testing: Example
... C. Probability and Critical Cutoff Approaches: Really the Same Thing D. How do we do hypothesis tests on small samples (n = 30 or less). E. How do we do hypothesis testing when we have information on population standard deviation? On sample standard deviations? F. How do we test a statement ...
... C. Probability and Critical Cutoff Approaches: Really the Same Thing D. How do we do hypothesis tests on small samples (n = 30 or less). E. How do we do hypothesis testing when we have information on population standard deviation? On sample standard deviations? F. How do we test a statement ...
Document
... Note: This CI contains only positive values. => “pA > pB” (at the 99% confidence level 99%). That is, the resin mix employed on building B seems to be better than the resin mixture employed on buildings A. In fact, we are 99% confident that the resin mixture on building A has a probability of causin ...
... Note: This CI contains only positive values. => “pA > pB” (at the 99% confidence level 99%). That is, the resin mix employed on building B seems to be better than the resin mixture employed on buildings A. In fact, we are 99% confident that the resin mixture on building A has a probability of causin ...
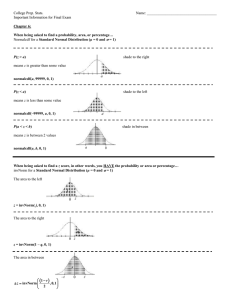
College Prep. Stats. Name: Important Information for Final Exam
... For right-tailed tests: P(t > test statistic) *To find this probability in your calculator, type: tcdf(t test statistic, 99999999, df) For left-tailed tests: P(t < –test statistic) *To find this probability in your calculator, type: tcdf(–99999999, t test statistic , df) ***Don’t forget if your test ...
... For right-tailed tests: P(t > test statistic) *To find this probability in your calculator, type: tcdf(t test statistic, 99999999, df) For left-tailed tests: P(t < –test statistic) *To find this probability in your calculator, type: tcdf(–99999999, t test statistic , df) ***Don’t forget if your test ...
8: Introduction to Statistical Inference
... Significance Level • α ≡ threshold for “significance” • If we choose α = 0.05, we require evidence so strong that it would occur no more than 5% of the time when H0 is true • Decision rule P-value ≤ α evidence is significant P-value > α evidence not significant • For example, let α = 0.01 P-val ...
... Significance Level • α ≡ threshold for “significance” • If we choose α = 0.05, we require evidence so strong that it would occur no more than 5% of the time when H0 is true • Decision rule P-value ≤ α evidence is significant P-value > α evidence not significant • For example, let α = 0.01 P-val ...
![[MSM04]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008529088_2-3ce1cce4ea32dddeeb96e74b738216a4-300x300.png)