Exam - HomeworkForYou
... 35) In a sample of 88 children selected randomly from one town, it is found that 8 of them suffer from asthma. Find the P-value for a test of the claim that the proportion of all children in the town who suffer from asthma is equal to 11%. A) -0.2843 B) 0.2843 C) 0.5686 D) 0.2157 ...
... 35) In a sample of 88 children selected randomly from one town, it is found that 8 of them suffer from asthma. Find the P-value for a test of the claim that the proportion of all children in the town who suffer from asthma is equal to 11%. A) -0.2843 B) 0.2843 C) 0.5686 D) 0.2157 ...
Hypothesis Testing
... What does this result mean? Statistically, the researcher has enough evidence to reject the figure of $74,914 as the true national average net income for sole proprietor CPAs. Although the researcher conducted a two tailed test, the evidence gathered indicates that the national average may have incr ...
... What does this result mean? Statistically, the researcher has enough evidence to reject the figure of $74,914 as the true national average net income for sole proprietor CPAs. Although the researcher conducted a two tailed test, the evidence gathered indicates that the national average may have incr ...
Lecture 14: Hypothesis testing, continued
... question, we do an experiment. We expose 100 new plants and 100 old plants to fusarium, and found that the mean growth rate was 35 with standard deviation 10 for the new plants, and mean 33 and standard deviation 8 for the old plants. ...
... question, we do an experiment. We expose 100 new plants and 100 old plants to fusarium, and found that the mean growth rate was 35 with standard deviation 10 for the new plants, and mean 33 and standard deviation 8 for the old plants. ...
3 HYPOTHESIS TESTING: ONE SAMPLE TESTS
... Let p denote the actual proportion of Company B's shareholders who are in favour of the offer. Then H0: p = 0.50 (claim of Company B's Chief Executive) H1: p > 0.50 (claim of Company A's Chairman; one-tailed) Significance level, α = 0.01 If X denotes the number of Company B's shareholders in the sam ...
... Let p denote the actual proportion of Company B's shareholders who are in favour of the offer. Then H0: p = 0.50 (claim of Company B's Chief Executive) H1: p > 0.50 (claim of Company A's Chairman; one-tailed) Significance level, α = 0.01 If X denotes the number of Company B's shareholders in the sam ...
Ch11 - Qc.edu
... We can define a “rare event” arbitrarily by setting a threshold for our P-value. If our P-value falls below that point, we’ll reject the null hypothesis. ...
... We can define a “rare event” arbitrarily by setting a threshold for our P-value. If our P-value falls below that point, we’ll reject the null hypothesis. ...
PowerPoint slides
... computer statistical packages give a Pvalue for hypothesis tests, sometimes called sig. in SPSS. The P-value is the actual probability of getting the sample mean value or a more extreme sample mean value in the direction of the alternative hypothesis (> or <) if the null hypothesis is true. © The Mc ...
... computer statistical packages give a Pvalue for hypothesis tests, sometimes called sig. in SPSS. The P-value is the actual probability of getting the sample mean value or a more extreme sample mean value in the direction of the alternative hypothesis (> or <) if the null hypothesis is true. © The Mc ...
Psychology 2010 Lecture 10 Notes: Hypothesis Testing Ch 6
... test. This means that knowledgeable data analysts don’t even bother to compute p-values when they do a Z test. They remember that the Critical Z is 1.96 and after conducting their research, if their obtained Z is equal to or more negative than -1.96 or equal to or more positive than + 1.96, they rej ...
... test. This means that knowledgeable data analysts don’t even bother to compute p-values when they do a Z test. They remember that the Critical Z is 1.96 and after conducting their research, if their obtained Z is equal to or more negative than -1.96 or equal to or more positive than + 1.96, they rej ...
7.1 Statistical Hypotheses
... making a Type I Error to be small. (We’d rather actually be right and think we’re wrong than think we’re right and actually be wrong.) The maximum acceptable probability (of making a Type I error) is usually chosen at the beginning of the hypothesis test, and is called the level of significance for ...
... making a Type I Error to be small. (We’d rather actually be right and think we’re wrong than think we’re right and actually be wrong.) The maximum acceptable probability (of making a Type I error) is usually chosen at the beginning of the hypothesis test, and is called the level of significance for ...
mm lecture chapter 6
... really were no effect), then the magnitude of the sampled effect would be likely to occur by chance in no more than some specified percentage (typically 5%) of samples. ...
... really were no effect), then the magnitude of the sampled effect would be likely to occur by chance in no more than some specified percentage (typically 5%) of samples. ...
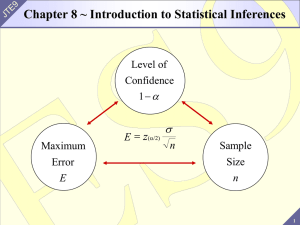
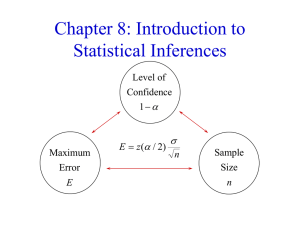
Chap 08
... b. If the decision is fail to reject Ho, then the conclusion should be worded something like, “There is not sufficient evidence at the level of significance to show that . . . (the meaning of the alternative hypothesis)” Notes: The decision is about Ho The conclusion is a statement about Ha ...
... b. If the decision is fail to reject Ho, then the conclusion should be worded something like, “There is not sufficient evidence at the level of significance to show that . . . (the meaning of the alternative hypothesis)” Notes: The decision is about Ho The conclusion is a statement about Ha ...