Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elaboration of thoughts to store on a short-term basis “working memories” that are used to analyze each new thought while it is entering the braine. The somatic, visual, and auditory association areas all meet one another in th ...
... The prefrontal association area is frequently described as important for elaboration of thoughts to store on a short-term basis “working memories” that are used to analyze each new thought while it is entering the braine. The somatic, visual, and auditory association areas all meet one another in th ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... Induction (i.e. learning) o High frequency stimulation → LTP o Low frequency stimulation → LTD Result in a decrease in AMPA receptors ...
... Induction (i.e. learning) o High frequency stimulation → LTP o Low frequency stimulation → LTD Result in a decrease in AMPA receptors ...
Flash Card Fever!
... approved answers to questions about oneself on a survey or questionnaire. experimenter control ...
... approved answers to questions about oneself on a survey or questionnaire. experimenter control ...
Shipp Visual memory Notes
... The recurrent anatomy of CA3 could allow it to function as an ‘attractor network’ (according to artificial intelligence, neural-network theories). The idea of such a network is that, after appropriate modification of connection weights (i.e. LTP), a previous pattern of network activity resulting fro ...
... The recurrent anatomy of CA3 could allow it to function as an ‘attractor network’ (according to artificial intelligence, neural-network theories). The idea of such a network is that, after appropriate modification of connection weights (i.e. LTP), a previous pattern of network activity resulting fro ...
05powerpoint
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Amnesia Cartoon
... • Lack of recall for biographical information from childhood through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory • able to sight-read ...
... • Lack of recall for biographical information from childhood through adulthood including professional events • unable to recall or recognize lyrics of well-known songs • could not recall any famous cellist and remembered the name of only one composer (Beethoven) • Musical memory • able to sight-read ...
Optical Stimulation of Engram-bearing Cells
... Here we have shown that optical activation of hippocampal cells that were active during fear conditioning is sufficient to elicit freezing behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and ma ...
... Here we have shown that optical activation of hippocampal cells that were active during fear conditioning is sufficient to elicit freezing behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and ma ...
PSYCHOLOGY Time-1 hour and 15 minutes 100 Questions
... The painful experience associated with termination of the use of an addictive substance is known as (A)discontinuance (B)tolerance (C)withdrawal (D)forced independence (E) transduction 2. When parents refuse to accept several psychologists’ diagnosis of a child’s mental illness, they are using which ...
... The painful experience associated with termination of the use of an addictive substance is known as (A)discontinuance (B)tolerance (C)withdrawal (D)forced independence (E) transduction 2. When parents refuse to accept several psychologists’ diagnosis of a child’s mental illness, they are using which ...
No Slide Title
... presented to HM and then some seconds later, the same or another cue was presented and he was asked to determine whether the two stimuli were the same or different. ...
... presented to HM and then some seconds later, the same or another cue was presented and he was asked to determine whether the two stimuli were the same or different. ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... forgetting emotional memories. ...
... forgetting emotional memories. ...
Lesson 7
... All Bobby wanted in the world was to be able to play wiffle ball with his friends. All Bobby’s neurotic mother wanted was for him to avoid injuries at all costs. Running the bases was going to be a ...
... All Bobby wanted in the world was to be able to play wiffle ball with his friends. All Bobby’s neurotic mother wanted was for him to avoid injuries at all costs. Running the bases was going to be a ...
Module 24 Powerpoint
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
... Karl Lashley (18901958) showed that rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
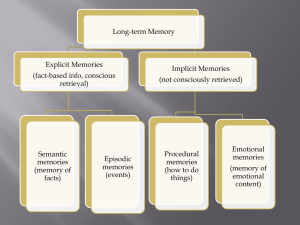
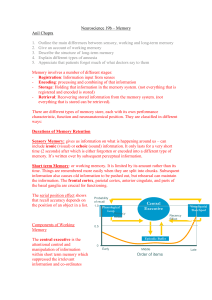
Neuroscience 19b – Memory
... include iconic (visual) or echoic (sound) information. It only lasts for a very short time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount ...
... include iconic (visual) or echoic (sound) information. It only lasts for a very short time (2 seconds) after which is either forgotten or encoded into a different type of memory. It’s written over by subsequent perceptual information. Short term Memory: or working memory. It is limited by its amount ...
Module 12 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time ...
... anxiety-producing information in the unconscious, from which repressed memories cannot be recalled voluntarily, but something may cause them to enter consciousness at a later time ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
Memory and Law
... semantic means (which all activate different parts of the brain). The most vivid autobiographical memories tend to be of emotional events, which are likely to be recalled more often and with more clarity than neutral events. One theory suggests that high levels of emotional arousal lead to atten ...
... semantic means (which all activate different parts of the brain). The most vivid autobiographical memories tend to be of emotional events, which are likely to be recalled more often and with more clarity than neutral events. One theory suggests that high levels of emotional arousal lead to atten ...
Readings
... frequency or recency, (2) weak or few associations with other information, and (3) interfering associations. (recall vs. recognition) Remembering is enhanced by frequent rehearsal in working memory and in conjunction with other information related in a meaningful way. Thinking involves activation of ...
... frequency or recency, (2) weak or few associations with other information, and (3) interfering associations. (recall vs. recognition) Remembering is enhanced by frequent rehearsal in working memory and in conjunction with other information related in a meaningful way. Thinking involves activation of ...
Memory kaleidoscope: enhancing memory to improve learning
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
... proteins, and electrical impulses. If the information does not receive sufficient attention or if it is not deemed necessary for the long-term,it will be encoded for short-term use only and ultimately discarded unless reclassified. The encoding process takes into consideration the emotional nature, ...
Memory
... • The circuit of neurons is called a “cell assembly” • Eventually, the neurons in the cell assembly change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
... • The circuit of neurons is called a “cell assembly” • Eventually, the neurons in the cell assembly change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
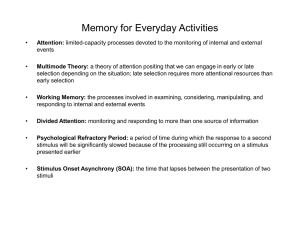
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Divided Attention: monitoring and responding to more than one source of information ...
... Divided Attention: monitoring and responding to more than one source of information ...