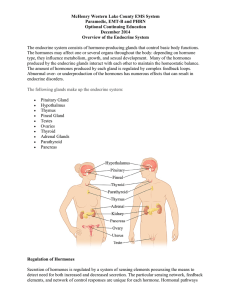
Unit P: Endocrine System
... d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
... d. When blood level of hormone increases, brain hormones stop 2. Nervous control – in some cases, sympathetic nervous system causes direct release of hormone from gland (for example, when stress causes the adrenal medulla to secrete adrenalin) ...
Endocrine System
... 1. Main hormone, thyroxine, is controlled by secretion of TSH 2. Thyroxine controls the rate of metabolism 3. Calcitonin, another hormone that controls calcium ion concentration in the body, prevents hypercalcemia Parathyroid glands – produce parathormone which helps control blood calcium, prevents ...
... 1. Main hormone, thyroxine, is controlled by secretion of TSH 2. Thyroxine controls the rate of metabolism 3. Calcitonin, another hormone that controls calcium ion concentration in the body, prevents hypercalcemia Parathyroid glands – produce parathormone which helps control blood calcium, prevents ...
hormones
... The hormones that guide reproductive processes come from the anterior pituitary and the gonads. During pregnancy, the placenta also makes hormones. The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetical ...
... The hormones that guide reproductive processes come from the anterior pituitary and the gonads. During pregnancy, the placenta also makes hormones. The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetical ...
The Endocrine System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system. The respective functions of the testes are: producing sperm producing male sex hormones of which testosterone is the bestknown. Testosterone is responsible for the appearance of secondary sex characteristics in m ...
... testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system. The respective functions of the testes are: producing sperm producing male sex hormones of which testosterone is the bestknown. Testosterone is responsible for the appearance of secondary sex characteristics in m ...
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland
... thyrotropin-releasing hormone atrial natriuretic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormone Amino acid derivatives – consists of: ...
... thyrotropin-releasing hormone atrial natriuretic hormone gonadotropin-releasing hormone Amino acid derivatives – consists of: ...
Biology 416K Summer 2002
... b. stored in vesicles in the cytoplasm c. secreted by an active transport mechanism requiring ATP d. short-half life after secretion e. composed of a chain of amino acids 29. This hormone is not made in the anterior pituitary: a. FSH b. ADH c. LH d. TSH e. prolactin 30. An increase in epinephrine se ...
... b. stored in vesicles in the cytoplasm c. secreted by an active transport mechanism requiring ATP d. short-half life after secretion e. composed of a chain of amino acids 29. This hormone is not made in the anterior pituitary: a. FSH b. ADH c. LH d. TSH e. prolactin 30. An increase in epinephrine se ...
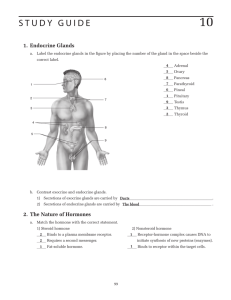
S T U D Y G U I D E
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
... lular respiration. This produces hyperglycemia and forces cells to use fats for cellular respiration which _____________________________________________________________________________________________ results in acidosis. b. A new mother is informed that her baby has severe hypothyroidism. How would ...
The Endocrine System
... for producing the ova or egg and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. *Estrogen – stimulates the development of the reproductive organs, including the breast, and secondary sex characteristics such as pubic and axillary hair, prepares for menstruation. Progesterone – works with estrogen to build ...
... for producing the ova or egg and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. *Estrogen – stimulates the development of the reproductive organs, including the breast, and secondary sex characteristics such as pubic and axillary hair, prepares for menstruation. Progesterone – works with estrogen to build ...
The Endocrine System
... for producing the ova or egg and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. *Estrogen – stimulates the development of the reproductive organs, including the breast, and secondary sex characteristics such as pubic and axillary hair, prepares for menstruation. Progesterone – works with estrogen to build ...
... for producing the ova or egg and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. *Estrogen – stimulates the development of the reproductive organs, including the breast, and secondary sex characteristics such as pubic and axillary hair, prepares for menstruation. Progesterone – works with estrogen to build ...
02. Role of the central nervous system and endocrine glands
... secrete chemical signals into the circulatory system. • The secretory products of endocrine glands are called hormones (hoЇrmoЇnz), a term derived from the Greek word hormon, meaning to set into motion. • Traditionally, a hormone is defined as a chemical signal, or ligand, that (1) is produced in mi ...
... secrete chemical signals into the circulatory system. • The secretory products of endocrine glands are called hormones (hoЇrmoЇnz), a term derived from the Greek word hormon, meaning to set into motion. • Traditionally, a hormone is defined as a chemical signal, or ligand, that (1) is produced in mi ...
Biochemistry, Secretion, and Transport of Hormones
... _______ (hormone) and stimulation of the __________ nervous system also increase plasma insulin levels. ...
... _______ (hormone) and stimulation of the __________ nervous system also increase plasma insulin levels. ...
Study Guide for Endocrine
... 45. Where is the adrenal gland located? 46. What are the two regions of the adrenal gland? 47. What hormone signals the hormones of the adrenal cortex? 48. Where is that hormone released from? 49. What are the three classifications of corticoid hormones? 50. What precursor is required for the manufa ...
... 45. Where is the adrenal gland located? 46. What are the two regions of the adrenal gland? 47. What hormone signals the hormones of the adrenal cortex? 48. Where is that hormone released from? 49. What are the three classifications of corticoid hormones? 50. What precursor is required for the manufa ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system
... hormone releasing hormone (GRH or GHRH) by the hypothalamus. GH stimulates growth in all body tissues. Helps assist amino acids into body tissues to build up proteins. d. Gonadotropin releasing hormone ( GnRH) causes the anterior pituitary to secrete two hormones called gonadotripins that stimulate ...
... hormone releasing hormone (GRH or GHRH) by the hypothalamus. GH stimulates growth in all body tissues. Helps assist amino acids into body tissues to build up proteins. d. Gonadotropin releasing hormone ( GnRH) causes the anterior pituitary to secrete two hormones called gonadotripins that stimulate ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system part 2
... growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH). Growth Hormone (GH) or Human Growth Hormone (hGH) is also called somatotropin and is produced and released from the anterior pituitary. This hormone is stimulated by the release of growth hormone releasing hormone (GRH or GHRH) by the hypothalamus. GH stimul ...
... growth hormone inhibiting hormone (GHIH). Growth Hormone (GH) or Human Growth Hormone (hGH) is also called somatotropin and is produced and released from the anterior pituitary. This hormone is stimulated by the release of growth hormone releasing hormone (GRH or GHRH) by the hypothalamus. GH stimul ...
Chapter 2, Introduction to the vertebrate endocrine system
... Minor structural differences yield major functional differences ...
... Minor structural differences yield major functional differences ...
chemical coordination and integration
... It is a primary sex organ. It also produces 2 hormones called estrogen and progesterone Estrogen is produced by ovarian follicles. It is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristic features in female. After ovulation the ruptured follicle is converted into a structure called c ...
... It is a primary sex organ. It also produces 2 hormones called estrogen and progesterone Estrogen is produced by ovarian follicles. It is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristic features in female. After ovulation the ruptured follicle is converted into a structure called c ...
Testosterone`s Effects on Anxiety
... Action of Enzymes in the CNS (especially the hypothalamus): • 5alpha-reductase amplifies T’s actions by conversion to DHT (a more potent form of T). • Aromatase differentiates T by conversion to oestrogen. These enzymes account for gender related differences in adult life (eg sexual and aggressive b ...
... Action of Enzymes in the CNS (especially the hypothalamus): • 5alpha-reductase amplifies T’s actions by conversion to DHT (a more potent form of T). • Aromatase differentiates T by conversion to oestrogen. These enzymes account for gender related differences in adult life (eg sexual and aggressive b ...
Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]
... Amines (derived from amino acids) Thyroxine, epinephrine (adrenaline) Steroids testosterone, estrogen, progesterone ...
... Amines (derived from amino acids) Thyroxine, epinephrine (adrenaline) Steroids testosterone, estrogen, progesterone ...
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT
... maintain the status quo. In addition, secretion and activity of a particular hormone may be adjusted upward or downward in response to challenges such as chronic stress, disease, or change in nutritional status. For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sen ...
... maintain the status quo. In addition, secretion and activity of a particular hormone may be adjusted upward or downward in response to challenges such as chronic stress, disease, or change in nutritional status. For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sen ...
Dear Notetaker:
... - Sending signals from one organ to elicit a response in other organs - A number of specialized glands to release hormones into circulation that can influence organs at distant tissues o Endocrine, influence tissue at a distant location o Paracrine, influence tissue at close vicinity (local tissue) ...
... - Sending signals from one organ to elicit a response in other organs - A number of specialized glands to release hormones into circulation that can influence organs at distant tissues o Endocrine, influence tissue at a distant location o Paracrine, influence tissue at close vicinity (local tissue) ...
Dr. AASHISH H. PANCHAL (M.PHARM., Ph.D.) GSEB, CBSE, ICSE
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
Estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen (see spelling differences) is the primary female sex hormone and is responsible for development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. Estrogen may also refer to any substance, natural or synthetic that mimics the effects of the natural hormone. The steroid 17β-estradiol is the most potent and prevalent endogenous estrogen, but several metabolites of estradiol also have estrogenic hormonal activity. Synthetic estrogens are used as part of some oral contraceptives, in estrogen replacement therapy for postmenopausal women, and in hormone replacement therapy for trans women.The name estrogen comes from the Greek οἶστρος (oistros), literally meaning ""verve or inspiration"" but figuratively sexual passion or desire, and the suffix -gen, meaning ""producer of"".Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ERs) which in turn modulate the expression of many genes. Additionally, estrogens bind to and activate rapid-signaling membrane estrogen receptors (mERs), such as GPER (GPR30).Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates as well as some insects. Their presence in both vertebrates and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient evolutionary history. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women.


















![Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016605577_1-a7aad459db07937df65df4f3a411aef9-300x300.png)