Chapter 11 - Glasgow Independent Schools
... to accept the National Assembly’s declaration. – A delegation of women met with the king on October 5th to describe the horrible conditions their children were suffering from. – The king was forced to accept the new decrees and to move back to Paris to show his support of the National Assembly. • Th ...
... to accept the National Assembly’s declaration. – A delegation of women met with the king on October 5th to describe the horrible conditions their children were suffering from. – The king was forced to accept the new decrees and to move back to Paris to show his support of the National Assembly. • Th ...
The French Revolution of 1789 PowerPoint Presentation
... Established a nationwide system of public education ...
... Established a nationwide system of public education ...
Chapter 6 notes Sections 1 - 2
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
... Estate; the nobility, or Second Estate; and the rest of the population, or Third Estate. • In 1789, France faced social discontent, a severe financial crisis, and serious food shortages. • Louis XVI called on the Estates General to carry out reforms, but members of the Third Estate defied the king a ...
Chapter 11 - Glasgow Independent Schools
... to accept the National Assembly’s declaration. – A delegation of women met with the king on October 5th to describe the horrible conditions their children were suffering from. – The king was forced to accept the new decrees and to move back to Paris to show his support of the National Assembly. • Th ...
... to accept the National Assembly’s declaration. – A delegation of women met with the king on October 5th to describe the horrible conditions their children were suffering from. – The king was forced to accept the new decrees and to move back to Paris to show his support of the National Assembly. • Th ...
French Rev Review - Lakeland Regional High School
... Who? 5 man Directory, Robespierre, Marat again=exiled to St. Helena, battle of Waterloo, Battle What? Robespierre killed, Marat killed, Not effective, of the Nations, creation of an empire, invasion of ...
... Who? 5 man Directory, Robespierre, Marat again=exiled to St. Helena, battle of Waterloo, Battle What? Robespierre killed, Marat killed, Not effective, of the Nations, creation of an empire, invasion of ...
The French Revolution
... of the French Revolution: it lasted from March to July 1793. After the ruler of Mainz had fled in October 1792, citizens of Mainz founded a Jacobin club; they promoted the Enlightenment and the French revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity, aiming for a German republic to be estab ...
... of the French Revolution: it lasted from March to July 1793. After the ruler of Mainz had fled in October 1792, citizens of Mainz founded a Jacobin club; they promoted the Enlightenment and the French revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity, aiming for a German republic to be estab ...
Chapter 18—The French Revolution Outline
... ! In Paris, many small shopkeepers, tradesmen, artisans, and wage earners marched to the Bastille to get weapons for the militia. ! Due to poor leadership, the royal troops stationed at the Bastille fired ...
... ! In Paris, many small shopkeepers, tradesmen, artisans, and wage earners marched to the Bastille to get weapons for the militia. ! Due to poor leadership, the royal troops stationed at the Bastille fired ...
french revolution reading guide
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: 1. It has been said that France was a rich nation with an impoverished government. Explain this statement. 2. A motto of the French Revolution was “equality, liberty, and fraternity.” How did the revolution both support and violate this motto? Did French women benefit from the revo ...
... REVIEW QUESTIONS: 1. It has been said that France was a rich nation with an impoverished government. Explain this statement. 2. A motto of the French Revolution was “equality, liberty, and fraternity.” How did the revolution both support and violate this motto? Did French women benefit from the revo ...
Convention and Terror
... The city was near to Versailles and therefore the king was at arm’s length. He could easily try to overawe Parisians; they usually knew what he was up to at court and were within reach of royal forces. ...
... The city was near to Versailles and therefore the king was at arm’s length. He could easily try to overawe Parisians; they usually knew what he was up to at court and were within reach of royal forces. ...
The French Revolution
... ing the French model. A democratically elected parliament met in March 1793, declaring the represented territory (which extended to Bingen in the west and to Landau in the south) to be free and democratic, denying any ties to the Holy Roman Empire,* and joining France. The same day, Mainz was besieg ...
... ing the French model. A democratically elected parliament met in March 1793, declaring the represented territory (which extended to Bingen in the west and to Landau in the south) to be free and democratic, denying any ties to the Holy Roman Empire,* and joining France. The same day, Mainz was besieg ...
French Revolution
... are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. — That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, — That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abo ...
... are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness. — That to secure these rights, Governments are instituted among Men, deriving their just powers from the consent of the governed, — That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abo ...
Chapter 19 A Revolution in Politics
... – not even Robespierre’s fellow leaders felt safe Danton & other politicians were executed in early 1794 for trying to stop Terror ...
... – not even Robespierre’s fellow leaders felt safe Danton & other politicians were executed in early 1794 for trying to stop Terror ...
File
... they wanted a republic rather than a constitutional monarchy held the ideologies of the most radical thinkers of the Enlightenment, and, particularly the views of Rousseau who emphasized equality, popular sovereignty, and civic virtue o Girondists were a subgroup of the Jacobins and assumed lead ...
... they wanted a republic rather than a constitutional monarchy held the ideologies of the most radical thinkers of the Enlightenment, and, particularly the views of Rousseau who emphasized equality, popular sovereignty, and civic virtue o Girondists were a subgroup of the Jacobins and assumed lead ...
CHAPTER 20 The French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era, 1789
... toppled. In America, the 13 British colonies attained their independence from England. B. Political and Fiscal Crisis in Eighteenth Century France France under Louis XV was in a constant state of financial crisis. The crisis was made worse by the huge debts contracted to finance the Seven Years’ War ...
... toppled. In America, the 13 British colonies attained their independence from England. B. Political and Fiscal Crisis in Eighteenth Century France France under Louis XV was in a constant state of financial crisis. The crisis was made worse by the huge debts contracted to finance the Seven Years’ War ...
AP World History Chapter 22 Outline Chapter 22: Revolutionary
... countryside. The National Assembly was emboldened to set forth its position in the Declaration of the Rights of Man. 3. As the economic crisis grew worse, Parisian market women marched on Versailles and captured the king and his family. The National Assembly passed a new constitution that limited th ...
... countryside. The National Assembly was emboldened to set forth its position in the Declaration of the Rights of Man. 3. As the economic crisis grew worse, Parisian market women marched on Versailles and captured the king and his family. The National Assembly passed a new constitution that limited th ...
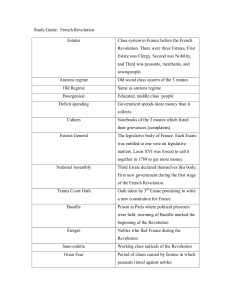
Study Guide: French Revolution Estates Class system in France
... 3 rd phase (radical): 1793 King & Queen are executed National Convention set up Committee of Public Safety. Reign of Terror July 1793 – July 1794 4 th phase (moderates): Directory – 5 man rule 17951799 5 th phase: Rule of Napoleon (17991815) coup d’etat –overthrow of government. ...
... 3 rd phase (radical): 1793 King & Queen are executed National Convention set up Committee of Public Safety. Reign of Terror July 1793 – July 1794 4 th phase (moderates): Directory – 5 man rule 17951799 5 th phase: Rule of Napoleon (17991815) coup d’etat –overthrow of government. ...
Key Individuals - This area is password protected
... revolution. the causes of tensions and conflicts generated in the old regime that many historians see as contributing to the revolution; for example, rising and unfulfilled class expectations; fluctuations in economic activity; failed attempts at economic, social or political reform; perceived soc ...
... revolution. the causes of tensions and conflicts generated in the old regime that many historians see as contributing to the revolution; for example, rising and unfulfilled class expectations; fluctuations in economic activity; failed attempts at economic, social or political reform; perceived soc ...
Chapter 21 Notes
... to impose new taxes or to prevent further westward settlement provoked protests in the colonies. 2. In the Great Lakes region, British policies undermined the Amerindian economy and provoked a series of Amerindian raids on the settled areas of Pennsylvania and Virginia. The Amerindian alliance that ...
... to impose new taxes or to prevent further westward settlement provoked protests in the colonies. 2. In the Great Lakes region, British policies undermined the Amerindian economy and provoked a series of Amerindian raids on the settled areas of Pennsylvania and Virginia. The Amerindian alliance that ...
C1: Revolution and Reaction in Europe, 1789-1848
... The city was near to Versailles and therefore the king was at arm’s length. He could easily try to overawe Parisians; they usually knew what he was up to at court and were within reach of royal forces. ...
... The city was near to Versailles and therefore the king was at arm’s length. He could easily try to overawe Parisians; they usually knew what he was up to at court and were within reach of royal forces. ...
French Revolution
... the Reign of Terror. The most famous victim of Robespierre was the widowed queen, Marie Antoinette. Remaining calm and dignified she was forced to ride through the streets of Paris in a horse and cart to her demise. Along the way she was jeered by the crowds that gathered along the route. On the gui ...
... the Reign of Terror. The most famous victim of Robespierre was the widowed queen, Marie Antoinette. Remaining calm and dignified she was forced to ride through the streets of Paris in a horse and cart to her demise. Along the way she was jeered by the crowds that gathered along the route. On the gui ...
Civil Constitution of the Clergy
... A bourgeoisie Lockean value The nation is sovereign (Rousseau) Taxes are made by common consent Powers of government should be separated (Montesquieu) “man” refers to all human beings, even women ...
... A bourgeoisie Lockean value The nation is sovereign (Rousseau) Taxes are made by common consent Powers of government should be separated (Montesquieu) “man” refers to all human beings, even women ...
French Revolution WebQuest Worksheet
... Task 2 – Look over this PowerPoint on the French Revolution and answer the following question: If you had to pick, which estate would you choose to belong to, and why? Answer this question with a full paragraph and include at least three reasons that support your answer. ...
... Task 2 – Look over this PowerPoint on the French Revolution and answer the following question: If you had to pick, which estate would you choose to belong to, and why? Answer this question with a full paragraph and include at least three reasons that support your answer. ...
Jacobin

Jacobin is separate and distinct from Jacobite and Jacobian.The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (French: Société des amis de la Constitution), commonly known as the Jacobin Club (Club des Jacobins, pronounced: [ʒa.kɔ.bɛ̃]), was the most famous and influential political club in the development of the French Revolution. Initially founded by anti-Royalist deputies from Brittany, the Club grew into a nationwide republican movement, with a membership estimated at a half million or more. The Jacobin Club was heterogeneous and included both prominent parliamentary factions of the early 1790s, the radical Mountain and the more moderate Girondists.In 1792-3, the Girondists (led by Brissot and including Thomas Paine) dominated the Jacobin Club and led the country. Believing that revolutionary France would not be accepted by its neighbours, they called for an aggressive foreign policy and forced war on Austria. The Girondists were the dominant faction when the Jacobins overthrew the monarchy and created the republic. When the Republic failed to deliver the unrealistic gains that had been expected, they lost popularity. The Girondists sought to curb fanatical revolutionary violence, and were therefore accused by the Mountain of being royalist sympathisers. The National Guard eventually switched its support from the Girondists to the Mountain, allowing the Mountain to stage a coup d'etat.In May 1793, led by Maximilien de Robespierre, the leaders of the Mountain faction succeeded in sidelining the Girondist faction and controlled the government until July 1794. Their time in government was characterized by radically progressive legislation imposed with very high levels of political violence. In June 1793, they approved the Constitution of Year 1 which introduced universal male suffrage for the first time in history. In September 1793, twenty-one prominent Girondists were guillotined, beginning the Reign of Terror. In October, during the Terror, the new constitution was ratified in a referendum which most eligible voters avoided participating in. The Mountain executed tens of thousands of opponents nationwide, ostensibly to suppress the Vendée insurrection and the Federalist insurrections, and to prevent any other insurrections, during the War of the First Coalition.In 1794, the fall of Robespierre pushed the Mountain out of power. The Jacobin Club was closed and many of its remaining leaders, notably Robespierre, were themselves executed.Today, Jacobin and Jacobinism are used in a variety of senses. In Britain, where the term ""Jacobin"" has been linked primarily to the Mountain, it is sometimes used in Britain as a pejorative for radical, left-wing revolutionary politics, especially when it exhibits dogmatism and violent repression. In France, ""Jacobin"" now generally indicates a supporter of a centralized republican state and strong central government powers and/or supporters of extensive government intervention to transform society. It is also used in other related senses, indicating proponents of a state education system which strongly promotes and inculcates civic values, and proponents of a strong nation-state capable of resisting any undesirable foreign interference.