Islam -primarily located in the Middle East/North Africa
... -the creation of these two branches goes back hundreds of years and was over who should take over and rule the Muslim nation after Mohammed’s death ...
... -the creation of these two branches goes back hundreds of years and was over who should take over and rule the Muslim nation after Mohammed’s death ...
Islam
... began in city of Mecca located on the Arabian Peninsula near the Byzantine Empire Arabians were polytheistic & came to visit Mecca to pray to the Kabba, a shrine containing idols of ...
... began in city of Mecca located on the Arabian Peninsula near the Byzantine Empire Arabians were polytheistic & came to visit Mecca to pray to the Kabba, a shrine containing idols of ...
Rise of Islam
... expanding Islam; Muslims were willing to sacrifice for their religion • The Muslim armies were well disciplined and expertly commanded; Byzantine and Sassanid empires were exhausted militarily from battles • People within the Byzantine and Sassanid empires welcomed Islam because many didn’t agree wi ...
... expanding Islam; Muslims were willing to sacrifice for their religion • The Muslim armies were well disciplined and expertly commanded; Byzantine and Sassanid empires were exhausted militarily from battles • People within the Byzantine and Sassanid empires welcomed Islam because many didn’t agree wi ...
CSM – Fall Introduction Biblical Worldview Series ISLAM
... 4. The Fast (Siyam) – Fast from dawn to dusk everyday during the ninth month of the Islamic lunar calendar, RAMADAN, which is sacred. 5. The Pilgrimage (Al-Hajj) – Expected to journey to Mecca at least once during their lifetime What Makes Christianity Unique? Basic concept of god within Hinduism ...
... 4. The Fast (Siyam) – Fast from dawn to dusk everyday during the ninth month of the Islamic lunar calendar, RAMADAN, which is sacred. 5. The Pilgrimage (Al-Hajj) – Expected to journey to Mecca at least once during their lifetime What Makes Christianity Unique? Basic concept of god within Hinduism ...
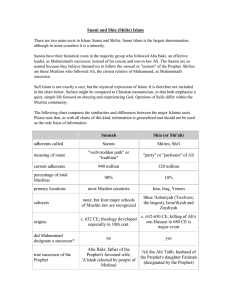
Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam
... Sufi Islam is not exactly a sect, but the mystical expression of Islam. It is therefore not included in the chart below. Sufism might be compared to Christian monasticism, in that both emphasize a quiet, simple life focused on obeying and experiencing God. Opinions of Sufis differ within the Muslim ...
... Sufi Islam is not exactly a sect, but the mystical expression of Islam. It is therefore not included in the chart below. Sufism might be compared to Christian monasticism, in that both emphasize a quiet, simple life focused on obeying and experiencing God. Opinions of Sufis differ within the Muslim ...
Behrman movie recommendation
... o fundamentalist – i.e. Al Wahhab; Southsiders (Ammerman) o Islamic modernist – a more liberal interpretation Mohammed M. Saud embraced Al-Wahhab’s doctrine - extreme interpretation leads to things like: claiming that anyone who says they’re “doing” something is polytheistic, b/c only God “does thin ...
... o fundamentalist – i.e. Al Wahhab; Southsiders (Ammerman) o Islamic modernist – a more liberal interpretation Mohammed M. Saud embraced Al-Wahhab’s doctrine - extreme interpretation leads to things like: claiming that anyone who says they’re “doing” something is polytheistic, b/c only God “does thin ...
WR Study Guide - Davis` World Studies Class
... 1. Which two groups (civilizations/groups of people? most affected Hinduism? ________________________ & __________________________ 2. Hindu’s occupation and social status have historically been determined by the family into which they were born. This system of classifying social classes is known as ...
... 1. Which two groups (civilizations/groups of people? most affected Hinduism? ________________________ & __________________________ 2. Hindu’s occupation and social status have historically been determined by the family into which they were born. This system of classifying social classes is known as ...
The Muslim World, 600-1250
... The Hijrah • Muhammad’s followers are attacked; together they leave Mecca in 622 • Hijrah—the Muslim migration from Mecca to Yathrib (renamed Medina) • Muhammad attracts many more followers, becomes great leader: • political leader—joins Jews and Arabs of Medina as a single community • religious lea ...
... The Hijrah • Muhammad’s followers are attacked; together they leave Mecca in 622 • Hijrah—the Muslim migration from Mecca to Yathrib (renamed Medina) • Muhammad attracts many more followers, becomes great leader: • political leader—joins Jews and Arabs of Medina as a single community • religious lea ...
File
... In the 7th century CE the angel Gabriel appeared to Muhammad, in the city of Mecca, who persuaded him to begin reciting the word of God and to act as a Prophet. Muslims believe that God sent Muhammad as the final prophet (much like he had sent Moses or Jesus) to help bring people back to the one tru ...
... In the 7th century CE the angel Gabriel appeared to Muhammad, in the city of Mecca, who persuaded him to begin reciting the word of God and to act as a Prophet. Muslims believe that God sent Muhammad as the final prophet (much like he had sent Moses or Jesus) to help bring people back to the one tru ...
File
... • Sunnis believe that a caliph (Head of State) should be elected by the whole community • Shi’ites assert that only Allah himself can choose a leader, and that Muhammad’s only rightful successors are his descendants • Sunni and Shia Muslims also accept different sets of Hadith (moral guidence and La ...
... • Sunnis believe that a caliph (Head of State) should be elected by the whole community • Shi’ites assert that only Allah himself can choose a leader, and that Muhammad’s only rightful successors are his descendants • Sunni and Shia Muslims also accept different sets of Hadith (moral guidence and La ...
Islamic Art Reading
... Muslims, produced for Muslim patrons, or created by Muslim artists. The basic components of Islamic ornament are calligraphy, vegetal patterns, and geometric patterns. ...
... Muslims, produced for Muslim patrons, or created by Muslim artists. The basic components of Islamic ornament are calligraphy, vegetal patterns, and geometric patterns. ...
Islam Powerpoint
... The Five Pillars of Islam 1. Faith: There is only one God, and Muhammad is the Prophet 2. Prayer: Five times a day ...
... The Five Pillars of Islam 1. Faith: There is only one God, and Muhammad is the Prophet 2. Prayer: Five times a day ...
Arabia and Islam Graphical Review
... 5. Based on this map why do you think Mecca was such an important city? I think Mecca is an important city because maybe it was the capital of Arabia History Close-up P. 57 6. Do you think the man in the bottom-right corner is a townsperson or a nomad? Why? I think that he is a townsperson because i ...
... 5. Based on this map why do you think Mecca was such an important city? I think Mecca is an important city because maybe it was the capital of Arabia History Close-up P. 57 6. Do you think the man in the bottom-right corner is a townsperson or a nomad? Why? I think that he is a townsperson because i ...
The Prophet - mrconnerseasterncivs
... ◊ Shift from Judaism because of Jewish treatment to him and his followers ◊ Face Mecca rather than Jerusalem ◊ Muhammad married women from powerful families and was able to influence people to his beliefs ...
... ◊ Shift from Judaism because of Jewish treatment to him and his followers ◊ Face Mecca rather than Jerusalem ◊ Muhammad married women from powerful families and was able to influence people to his beliefs ...
Islam-Submission to Allah - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... • Abu Bakr was followed by three more caliphs, the last of which was Alī ibn Abī Tālib. It is with his succession that a division in Islam became more defined. • Sunni Muslims believe that Ali was the fourth caliph, a position chosen based on ability to lead. The Shi’a (Shiites) supported Ali; howev ...
... • Abu Bakr was followed by three more caliphs, the last of which was Alī ibn Abī Tālib. It is with his succession that a division in Islam became more defined. • Sunni Muslims believe that Ali was the fourth caliph, a position chosen based on ability to lead. The Shi’a (Shiites) supported Ali; howev ...
ISLAM, ALLAH, AND MUHAMMAD
... ISLAM, ALLAH, AND MUHAMMAD Building upon the beliefs Judaism, Christianity (“the people of the book”) and local Arabian religion, Muhammad became the prophet of a new faith, Islam. After ultimately overcoming the opposition of his fellow Arabs in Mecca, Muhammad focused the energies of the Arabs int ...
... ISLAM, ALLAH, AND MUHAMMAD Building upon the beliefs Judaism, Christianity (“the people of the book”) and local Arabian religion, Muhammad became the prophet of a new faith, Islam. After ultimately overcoming the opposition of his fellow Arabs in Mecca, Muhammad focused the energies of the Arabs int ...
Chapter 6 Powerpoint
... followers believe that the angel Gabriel transmitted them to him). The revelations were later written in the Qur’an. At first Muhammed had a small following but slowly as his following grew, the Umayyad notables who dominated Meccan life saw him as a threat to their own wealth and power. New faith t ...
... followers believe that the angel Gabriel transmitted them to him). The revelations were later written in the Qur’an. At first Muhammed had a small following but slowly as his following grew, the Umayyad notables who dominated Meccan life saw him as a threat to their own wealth and power. New faith t ...
Islam - WordPress.com
... • Arts, calligraphy, and arabesques in writing and on pottery • Architecture: buildings w/patios, mosques w/minarets • Literature: The Arabian Nights • Position of women decline (influenced by Persian culture) • Sufis – mystics who focused on an emotional union with Allah – become missionaries ...
... • Arts, calligraphy, and arabesques in writing and on pottery • Architecture: buildings w/patios, mosques w/minarets • Literature: The Arabian Nights • Position of women decline (influenced by Persian culture) • Sufis – mystics who focused on an emotional union with Allah – become missionaries ...
Islamic Empires
... • A conflict arose over who should be caliph among the Safavids, Ottomans, and other Muslims. • Islam split into two groups. 1. The Shia thought that only members of Muhammad’s family could become caliphs. 2. The Sunni thought it did not matter as long as they were good Muslims and strong leaders. ...
... • A conflict arose over who should be caliph among the Safavids, Ottomans, and other Muslims. • Islam split into two groups. 1. The Shia thought that only members of Muhammad’s family could become caliphs. 2. The Sunni thought it did not matter as long as they were good Muslims and strong leaders. ...
rise of islam
... • the Cave of Hira Revelation (Muhammad was 40) • Muhammad did not believe he was creating a new religion ...
... • the Cave of Hira Revelation (Muhammad was 40) • Muhammad did not believe he was creating a new religion ...
Muslim Civilizations
... carpets, fine glassware, furniture, and tapestries Social Mobility: Ability to move up in social class. People could improve their social rank through religious, scholarly, or military achievements. Slavery- Common in Muslim lands, but freeing slaves was an act of charity. Slaves worked in houses or ...
... carpets, fine glassware, furniture, and tapestries Social Mobility: Ability to move up in social class. People could improve their social rank through religious, scholarly, or military achievements. Slavery- Common in Muslim lands, but freeing slaves was an act of charity. Slaves worked in houses or ...
File
... In the harsh desert climate of Arabia, Muhammad, a merchant from Mecca, introduced a major world religion called Islam. Main Ideas ...
... In the harsh desert climate of Arabia, Muhammad, a merchant from Mecca, introduced a major world religion called Islam. Main Ideas ...
Islam in Indonesia

Indonesia is constitutionally a secular state (but the government officially recognizes only six formal religions), with Islam being the dominant religion in the country. Indonesia also has a larger Muslim population than any other country in the world, with approximately 202.9 million identifying themselves as Muslim (87.2% of Indonesia's total population in 2011).Based on demographical statistics, 99% of Indonesian Muslims mainly follow the Shafi'i school of Sunni jurisprudence, although when asked, 56% does not adhere to any specific denomination. There are around one million Shias (0.5%), who are concentrated around Jakarta, and about 400,000 Ahmadi Muslims (0.2%). The remaining 0.3% are adherents of other branches including Wahhabism/Salafism etc. In general, Muslims in Indonesia can be categorized in terms of two orientations: ""modernists"" who closely adhere to orthodox theology while embracing modern learning, ""traditionalists,"" who tend to follow the interpretations of local religious leaders and religious teachers at Islamic boarding schools (pesantren).