The sum of the interior (=vertex) angles in a polygon
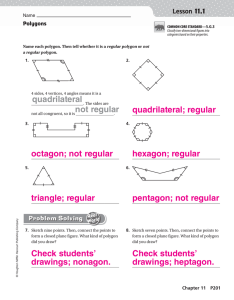
... A polygon is regular when all the sides and interior angles are equal. We call a regular three-sided polygon an equilateral triangle, a regular four-sides polygon is a square, a regular five-sided polygon is a regular pentagon, etc. We can use the general formula you found above to find the sum of t ...
... A polygon is regular when all the sides and interior angles are equal. We call a regular three-sided polygon an equilateral triangle, a regular four-sides polygon is a square, a regular five-sided polygon is a regular pentagon, etc. We can use the general formula you found above to find the sum of t ...
Practice C - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... Determine if each conjecture is true. If not, write or draw a counterexample. 5. Three points that determine a plane also determine a triangle. ...
... Determine if each conjecture is true. If not, write or draw a counterexample. 5. Three points that determine a plane also determine a triangle. ...
The pigeonhole principle
... Let M1= (K1, Σ, δ1, s1, F1) accept L1. Proof: A construction for a new DFA M= (K, Σ, δ, s, F) which accepts the complement of L1. ...
... Let M1= (K1, Σ, δ1, s1, F1) accept L1. Proof: A construction for a new DFA M= (K, Σ, δ, s, F) which accepts the complement of L1. ...
1 Appendix to notes 2, on Hyperbolic geometry:
... De…nition: A “point” is a pair ( ; ) in this set. De…nition: A “line”is any diameter of this disk, or the set of points on a circle which intersects D and which meets the boundary of D in two places and at right angles to the boundary of D at both of these places. Notice that a diameter can be consi ...
... De…nition: A “point” is a pair ( ; ) in this set. De…nition: A “line”is any diameter of this disk, or the set of points on a circle which intersects D and which meets the boundary of D in two places and at right angles to the boundary of D at both of these places. Notice that a diameter can be consi ...
Regular Languages - Monash University
... • A language which can be described by a Regular Expression is called a Regular Language. • If a word belongs to the language described by a regular expression, then we say it is matched by the regular expression. ...
... • A language which can be described by a Regular Expression is called a Regular Language. • If a word belongs to the language described by a regular expression, then we say it is matched by the regular expression. ...
Section 22.1
... measure of 83. Find the defect of the quadrilateral. Why should the answer of this problem be exactly twice as much as the answer to the previous problem? ...
... measure of 83. Find the defect of the quadrilateral. Why should the answer of this problem be exactly twice as much as the answer to the previous problem? ...
List of regular polytopes and compounds
This page lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces.The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an n-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an n-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of a (n-1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example the cube has Schläfli symbol {4,3}, and with its octahedral symmetry, [4,3] or File:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png, is represented by Coxeter diagram File:CDel node 1.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png.The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconvex and infinite forms. Nonconvex forms use the same vertices as the convex forms, but have intersecting facets. Infinite forms tessellate a one-lower-dimensional Euclidean space.Infinite forms can be extended to tessellate a hyperbolic space. Hyperbolic space is like normal space at a small scale, but parallel lines diverge at a distance. This allows vertex figures to have negative angle defects, like making a vertex with seven equilateral triangles and allowing it to lie flat. It cannot be done in a regular plane, but can be at the right scale of a hyperbolic plane.A more general definition of regular polytopes which do not have simple Schläfli symbols includes regular skew polytopes and regular skew apeirotopes with nonplanar facets or vertex figures.