Unit3_Investigation4_overview
... Note to teachers: It is also possible to construct a regular pentagon with compass and straightedge. That construction is related to the Golden Ratio and is introduced as a special topic in Unit 8. However, there are many regular polygons that cannot be constructed with compass and straightedge. The ...
... Note to teachers: It is also possible to construct a regular pentagon with compass and straightedge. That construction is related to the Golden Ratio and is introduced as a special topic in Unit 8. However, there are many regular polygons that cannot be constructed with compass and straightedge. The ...
6.7 Regular Polygons
... Since regular polygons have lines of symmetry, we can use those lines of symmetry, and the center point to find out the magnitude of rotation and the interior angle. Using the figure at the right, draw the lines of symmetry and plot center point, C. Connect all vertices to center point C. The degree ...
... Since regular polygons have lines of symmetry, we can use those lines of symmetry, and the center point to find out the magnitude of rotation and the interior angle. Using the figure at the right, draw the lines of symmetry and plot center point, C. Connect all vertices to center point C. The degree ...
Assignment 4
... 3. Section 10.1, #18. There is a typo in the problem statement: the sequence X1 , X2 , . . . should be an infinite sequence, not a finite one. Hint: Theorem 10.2 in the text may be useful. 4. Let G = (V, E) be a finite graph (the number of vertices and edges, |V | and |E| respectively, are both fini ...
... 3. Section 10.1, #18. There is a typo in the problem statement: the sequence X1 , X2 , . . . should be an infinite sequence, not a finite one. Hint: Theorem 10.2 in the text may be useful. 4. Let G = (V, E) be a finite graph (the number of vertices and edges, |V | and |E| respectively, are both fini ...
Summary of lesson - Education TI
... congruent, and the angles are also congruent. In this activity, you will explore the interior angles of regular polygons by dividing the polygons into triangles. Move to page 1.2. The regular polygon is inscribed in a circle whose central angle measure is given. Change the number of sides in the reg ...
... congruent, and the angles are also congruent. In this activity, you will explore the interior angles of regular polygons by dividing the polygons into triangles. Move to page 1.2. The regular polygon is inscribed in a circle whose central angle measure is given. Change the number of sides in the reg ...
Summary of lesson
... congruent, and the angles are also congruent. In this activity, you will explore the interior angles of regular polygons by dividing the polygons into triangles. Move to page 1.2. The regular polygon is inscribed in a circle whose central angle measure is given. Change the number of sides in the reg ...
... congruent, and the angles are also congruent. In this activity, you will explore the interior angles of regular polygons by dividing the polygons into triangles. Move to page 1.2. The regular polygon is inscribed in a circle whose central angle measure is given. Change the number of sides in the reg ...
An Algorithm to Generate Repeating Hyperbolic Patterns
... used to replicate each of Escher’s four “Circle Limit” patterns. This was discussed in the paper Creating Repeating Hyperbolic Patterns [1]. Unfortunately there is an error in the Pascal pseudocode describing the algorithm. There is a correct algorithm given in the later paper Hyperbolic Symmetry [2 ...
... used to replicate each of Escher’s four “Circle Limit” patterns. This was discussed in the paper Creating Repeating Hyperbolic Patterns [1]. Unfortunately there is an error in the Pascal pseudocode describing the algorithm. There is a correct algorithm given in the later paper Hyperbolic Symmetry [2 ...
File - 6B Mrs. Bishop
... Explain how you remember how many equal sides each of these triangles have: o Equilateral triangle ...
... Explain how you remember how many equal sides each of these triangles have: o Equilateral triangle ...
Lesson 14
... Tessellations • A tessellation is a pattern of repeating figures in which there are no gaps between the figures. • A regular polygon can be used to create a tessellation IF the measure of each interior angle evenly divides 360°. • If the measure of the angle does not divide into 360°, there will be ...
... Tessellations • A tessellation is a pattern of repeating figures in which there are no gaps between the figures. • A regular polygon can be used to create a tessellation IF the measure of each interior angle evenly divides 360°. • If the measure of the angle does not divide into 360°, there will be ...
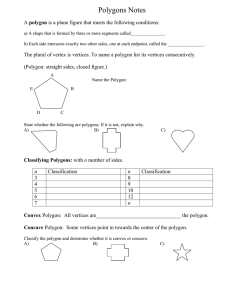
Polygons Notes
... A polygon is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: a) A shape that is formed by three or more segments called_______________. b) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint, called the ________________. ...
... A polygon is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: a) A shape that is formed by three or more segments called_______________. b) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint, called the ________________. ...
List of regular polytopes and compounds
This page lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces.The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an n-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an n-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of a (n-1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example the cube has Schläfli symbol {4,3}, and with its octahedral symmetry, [4,3] or File:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png, is represented by Coxeter diagram File:CDel node 1.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png.The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconvex and infinite forms. Nonconvex forms use the same vertices as the convex forms, but have intersecting facets. Infinite forms tessellate a one-lower-dimensional Euclidean space.Infinite forms can be extended to tessellate a hyperbolic space. Hyperbolic space is like normal space at a small scale, but parallel lines diverge at a distance. This allows vertex figures to have negative angle defects, like making a vertex with seven equilateral triangles and allowing it to lie flat. It cannot be done in a regular plane, but can be at the right scale of a hyperbolic plane.A more general definition of regular polytopes which do not have simple Schläfli symbols includes regular skew polytopes and regular skew apeirotopes with nonplanar facets or vertex figures.