Interior Angles of a Polygon_solutions.jnt
... Algebra & Analytic Geometry Interior Angles of a Polygon ...
... Algebra & Analytic Geometry Interior Angles of a Polygon ...
Format:
... (Good tessellated figures made by students in other countries can be found in this web page.) http://www18.big.or.jp/~mnaka/home.index.html (Interesting tessellated figures with animation effects can be found.) ...
... (Good tessellated figures made by students in other countries can be found in this web page.) http://www18.big.or.jp/~mnaka/home.index.html (Interesting tessellated figures with animation effects can be found.) ...
polygon
... Learn to classify the different types of lines (7-4) Learn to classify triangles and solve problems involving angle and side measures of triangles (7-5) Learn to identify, classify, and compare quadrilaterals (7-6) Learn to identify regular and not regular polygons and to find the angle measures of ...
... Learn to classify the different types of lines (7-4) Learn to classify triangles and solve problems involving angle and side measures of triangles (7-5) Learn to identify, classify, and compare quadrilaterals (7-6) Learn to identify regular and not regular polygons and to find the angle measures of ...
7.1 - Each angle.notebook
... 3.) Measure of Each Interior Angle b.) Find the measure of each exterior angle. ...
... 3.) Measure of Each Interior Angle b.) Find the measure of each exterior angle. ...
Fibonnaci Numbers, The Golden Ratio, and Platonic Solids
... • There are only 5. These are the regular tetrahedron, octahedron and icosahedron, wherein 3, 4 and 5 triangles respectively meet at each vertex, the cube (or regular hexahedron), wherein 3 squares meet at each vertex, and the regular dodecahedron, wherein 3 pentagons meet at each vertex. These have ...
... • There are only 5. These are the regular tetrahedron, octahedron and icosahedron, wherein 3, 4 and 5 triangles respectively meet at each vertex, the cube (or regular hexahedron), wherein 3 squares meet at each vertex, and the regular dodecahedron, wherein 3 pentagons meet at each vertex. These have ...
Areas of Circles and Regular Polygons
... Polygon – The word "polygon" derives from the Greek words poly (many) and gonu (knee). So a polygon is a thing with many knees! It must have straight edges that connect at vertices. Polygons can be concave or convex and irregular or regular. “Regular” – all sides congruent Today we will just be focu ...
... Polygon – The word "polygon" derives from the Greek words poly (many) and gonu (knee). So a polygon is a thing with many knees! It must have straight edges that connect at vertices. Polygons can be concave or convex and irregular or regular. “Regular” – all sides congruent Today we will just be focu ...
Lesson Plan Format
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
Using Algeblocks to Multiply Binomials, Part I
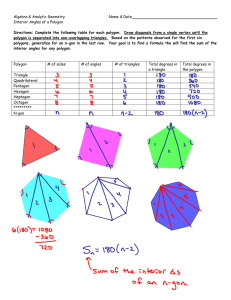
... possible types of polygons that satisfy this condition. c. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of the polygon is 1980. Determine the number of sides in the polygon, showing all appropriate reasoning. ...
... possible types of polygons that satisfy this condition. c. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of the polygon is 1980. Determine the number of sides in the polygon, showing all appropriate reasoning. ...
11–3 Areas of Regular Polygons and Circles
... Write the formula for the area of a regular polygon under the tab for Lesson 11-3. ...
... Write the formula for the area of a regular polygon under the tab for Lesson 11-3. ...
List of regular polytopes and compounds
This page lists the regular polytopes and regular polytope compounds in Euclidean, spherical and hyperbolic spaces.The Schläfli symbol describes every regular tessellation of an n-sphere, Euclidean and hyperbolic spaces. A Schläfli symbol describing an n-polytope equivalently describes a tessellation of a (n-1)-sphere. In addition, the symmetry of a regular polytope or tessellation is expressed as a Coxeter group, which Coxeter expressed identically to the Schläfli symbol, except delimiting by square brackets, a notation that is called Coxeter notation. Another related symbol is the Coxeter-Dynkin diagram which represents a symmetry group with no rings, and the represents regular polytope or tessellation with a ring on the first node. For example the cube has Schläfli symbol {4,3}, and with its octahedral symmetry, [4,3] or File:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png, is represented by Coxeter diagram File:CDel node 1.pngFile:CDel 4.pngFile:CDel node.pngFile:CDel 3.pngFile:CDel node.png.The regular polytopes are grouped by dimension and subgrouped by convex, nonconvex and infinite forms. Nonconvex forms use the same vertices as the convex forms, but have intersecting facets. Infinite forms tessellate a one-lower-dimensional Euclidean space.Infinite forms can be extended to tessellate a hyperbolic space. Hyperbolic space is like normal space at a small scale, but parallel lines diverge at a distance. This allows vertex figures to have negative angle defects, like making a vertex with seven equilateral triangles and allowing it to lie flat. It cannot be done in a regular plane, but can be at the right scale of a hyperbolic plane.A more general definition of regular polytopes which do not have simple Schläfli symbols includes regular skew polytopes and regular skew apeirotopes with nonplanar facets or vertex figures.