Chapter 8 PowerPoint Notes
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were ____________________________. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
... Pavlov and Watson believed that laws of learning were ____________________________. Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
PSYC 210 Spring 1998, Quiz 1 Use A for True, B for False
... A problem with experiments on sensory deprivation is that a. there isn’t much for the organism to do b. the organism spends much of its time sleeping c. it is diflicult to eliminate all stimuli d. all of the above ...
... A problem with experiments on sensory deprivation is that a. there isn’t much for the organism to do b. the organism spends much of its time sleeping c. it is diflicult to eliminate all stimuli d. all of the above ...
Final Exam Practice Questions
... D) type of sleep. 32. Ernest Hilgard's experiments in which subjects hypnotized to be deaf raised a finger in response to the question “Is there some part of you that can hear?” is good evidence for which of the following theories? A) divided consciousness theory B) hypnotic suggestibility theory C) ...
... D) type of sleep. 32. Ernest Hilgard's experiments in which subjects hypnotized to be deaf raised a finger in response to the question “Is there some part of you that can hear?” is good evidence for which of the following theories? A) divided consciousness theory B) hypnotic suggestibility theory C) ...
Agenda * Wednesday, January 8th
... Social-Cultural • Behavior comes from cultural norms & social setting • Relationship between people and culture • Example: Sports teams; pursuing a life of crime; mannerisms ...
... Social-Cultural • Behavior comes from cultural norms & social setting • Relationship between people and culture • Example: Sports teams; pursuing a life of crime; mannerisms ...
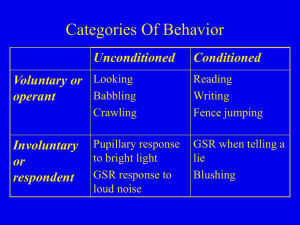
Learning is behavior based on experience
... Classical conditioning is learning where a meaningless stimulus, such as a hand signal to a dog, is associated with reward or punishment. ...
... Classical conditioning is learning where a meaningless stimulus, such as a hand signal to a dog, is associated with reward or punishment. ...
Behavioral Biology: Ethology
... provide the only feature in which there is no continuum between humans and other animals. • No other species comes close to matching the social learning and cultural transmission that occurs ...
... provide the only feature in which there is no continuum between humans and other animals. • No other species comes close to matching the social learning and cultural transmission that occurs ...
Chapter 10
... •From a learning point of view, anxieties after traumas, like other learned fears, may be acquired through simple association or conditioning principles •Neutral stimuli associated with aversive events or outcomes may come to elicit anxiety in their own right… such aversively conditioned emotional r ...
... •From a learning point of view, anxieties after traumas, like other learned fears, may be acquired through simple association or conditioning principles •Neutral stimuli associated with aversive events or outcomes may come to elicit anxiety in their own right… such aversively conditioned emotional r ...
Reflective Practice – Week 3 Behavior Management Observable
... must examine how certain reinforcements and punishments in the classroom environment shape behavior (Skinner and Gange). A teacher must adopt strategies that ‘shape desired terminal behavior’ and ignore undesired behavior. Through shaping teachers will promote the learning of complex behaviors’ by r ...
... must examine how certain reinforcements and punishments in the classroom environment shape behavior (Skinner and Gange). A teacher must adopt strategies that ‘shape desired terminal behavior’ and ignore undesired behavior. Through shaping teachers will promote the learning of complex behaviors’ by r ...
Chapter 1 Section 2 Notes Handout
... ring of the tuning fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the sound with the food. • This is known as conditioning or the conditional reflex ...
... ring of the tuning fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the sound with the food. • This is known as conditioning or the conditional reflex ...
Section 2 Approaches to Psychology - Copy
... fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the sound with the food. This is known as conditioning or the conditional reflex ...
... fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the sound with the food. This is known as conditioning or the conditional reflex ...
Skinner B F. Science and human behavior. New York: Macmillan
... During World War II, when my colleagues and I were conditioning pigeons to guide missiles, we discovered even more powerful ways of shaping and maintaining behavior. I was fascinated by the implications for human behavior in the world at large and discussed2them with my colleagues on Project Pigeon ...
... During World War II, when my colleagues and I were conditioning pigeons to guide missiles, we discovered even more powerful ways of shaping and maintaining behavior. I was fascinated by the implications for human behavior in the world at large and discussed2them with my colleagues on Project Pigeon ...
Empirical Law of Effect
... game effectively, we must work out a program of educational reinforcement in which appropriate responses "pay off" frequently. If the patient is to return for further counsel, the psychotherapist must make sure that the behavior of coming to him is in some measure reinforced. We evaluate the strengt ...
... game effectively, we must work out a program of educational reinforcement in which appropriate responses "pay off" frequently. If the patient is to return for further counsel, the psychotherapist must make sure that the behavior of coming to him is in some measure reinforced. We evaluate the strengt ...
H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT
... H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF BEHAVIOR 1. Explain how hormones can affect the environment during development and result in differences in behavior between males and females. 2. What is the adaptive significance of restricted developmental programs (a ...
... H09-STUDY QUESTIONS- ENVIRONMENT and DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT AND DEVELOPMENT OF BEHAVIOR 1. Explain how hormones can affect the environment during development and result in differences in behavior between males and females. 2. What is the adaptive significance of restricted developmental programs (a ...
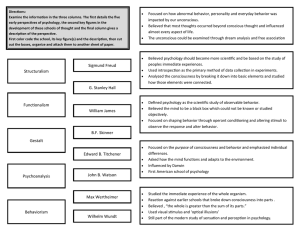
Structuralism Functionalism Gestalt Psychoanalysis Behaviorism
... Reaction against earlier schools that broke down consciousness into parts . Believed , “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.” Used visual stimulus and ‘optical illusions’ Still part of the modern study of sensation and perception in psychology. ...
... Reaction against earlier schools that broke down consciousness into parts . Believed , “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.” Used visual stimulus and ‘optical illusions’ Still part of the modern study of sensation and perception in psychology. ...
(Personality and Learning)
... Chaining – Teaching a dog to roll over, then bark and play dead – reward is given after all three are complete Primary reinforcers- biological - food, water, escaping electric shock Secondary reinforcers- need to be learned – money, grades. Token economy- any system (such as the experiment with scho ...
... Chaining – Teaching a dog to roll over, then bark and play dead – reward is given after all three are complete Primary reinforcers- biological - food, water, escaping electric shock Secondary reinforcers- need to be learned – money, grades. Token economy- any system (such as the experiment with scho ...
Chapter 5 - Behavior Therapy
... Primary motivation for humans is survival Behavior enables humans to get things that facilitate survival ...
... Primary motivation for humans is survival Behavior enables humans to get things that facilitate survival ...
Learning and Memory PP
... Russian Physiologist who discovered that dogs could learn to associate one thing with another (stimulus-response) Ex. “Pavlov’s dog” experiment involving bell and food ...
... Russian Physiologist who discovered that dogs could learn to associate one thing with another (stimulus-response) Ex. “Pavlov’s dog” experiment involving bell and food ...
Name: Date: CH. 6 Learning Active Review Behaviorists define
... 4. A response to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) is called an __________ response (UCR). 5. A response to a conditioned stimulus (CS) is termed a __________ response (CR). 6. Extinguished responses often show __________ recovery as a function of passage of time. 7. In stimulus __________, organisms ...
... 4. A response to an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) is called an __________ response (UCR). 5. A response to a conditioned stimulus (CS) is termed a __________ response (CR). 6. Extinguished responses often show __________ recovery as a function of passage of time. 7. In stimulus __________, organisms ...
Chapter 7 - Operant Conditioning Theor ies of Reinf orcement
... pinball machine to determine which behaviors were prefe rre d – Some children preferr ed playing pinball to eating candy, whereas the reverse was true for other children – Premack found that he could increa se the likelihood of children’s less preferr ed behavior by following it with the opportunity ...
... pinball machine to determine which behaviors were prefe rre d – Some children preferr ed playing pinball to eating candy, whereas the reverse was true for other children – Premack found that he could increa se the likelihood of children’s less preferr ed behavior by following it with the opportunity ...
BEHAVIORISM LEARNING THEORY
... Pavlov was studying the digestive system of dogs and became intrigued with his observation that dogs deprived of food began to salivate when one of his assistants walked into the room. ...
... Pavlov was studying the digestive system of dogs and became intrigued with his observation that dogs deprived of food began to salivate when one of his assistants walked into the room. ...
operant conditioning of feeding behavior in aplysia
... Considerable progress has been made towards a cellular analysis of classical conditioning. In contrast, the cellular mechanisms underlying operant conditioning are poorly understood. This deficit results, in part, from the lack of a suitably tractable preparation that exhibits operant conditioning a ...
... Considerable progress has been made towards a cellular analysis of classical conditioning. In contrast, the cellular mechanisms underlying operant conditioning are poorly understood. This deficit results, in part, from the lack of a suitably tractable preparation that exhibits operant conditioning a ...
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
... • Consciousness is a proper subject matter for psychology but it is not an explanation of behavior. It is what has to be explained (e.g., Tom hit Bill because Tom felt angry). – Why did Tom feel angry? – How did Tom know he was angry? • Consciousness vs. Awareness: – Animals are aware of objects (bu ...
... • Consciousness is a proper subject matter for psychology but it is not an explanation of behavior. It is what has to be explained (e.g., Tom hit Bill because Tom felt angry). – Why did Tom feel angry? – How did Tom know he was angry? • Consciousness vs. Awareness: – Animals are aware of objects (bu ...
Reinforcement Learning in Real
... Compare to human strategies “10 requirements of a challenging and realistic opponent” [Scott] ...
... Compare to human strategies “10 requirements of a challenging and realistic opponent” [Scott] ...
Reinforcement

In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus).Although in many cases a reinforcing stimulus is a rewarding stimulus which is ""valued"" or ""liked"" by the individual (e.g., money received from a slot machine, the taste of the treat, the euphoria produced by an addictive drug), this is not a requirement. Indeed, reinforcement does not even require an individual to consciously perceive an effect elicited by the stimulus. Furthermore, stimuli that are ""rewarding"" or ""liked"" are not always reinforcing: if an individual eats at a fast food restaurant (response) and likes the taste of the food (stimulus), but believes it is bad for their health, they may not eat it again and thus it was not reinforcing in that condition. Thus, reinforcement occurs only if there is an observable strengthening in behavior.In most cases reinforcement refers to an enhancement of behavior but this term may also refer to an enhancement of memory. One example of this effect is called post-training reinforcement where a stimulus (e.g. food) given shortly after a training session enhances the learning. This stimulus can also be an emotional one. A good example is that many people can explain in detail where they were when they found out the World Trade Center was attacked.Reinforcement is an important part of operant or instrumental conditioning.