Selective Binding of Lisinopril in Angiotensin
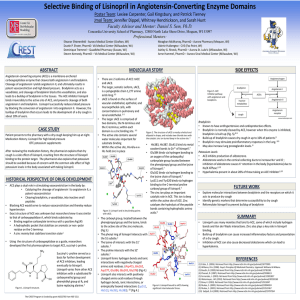
... ACE plays a dual role in stimulating vasoconstriction in the body by: • Catalyzing the cleavage of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor • Cleaving bradykinin, a vasodilator, into inactive small peptides Blocking ACE would serve to reduce vasoconstriction and thereby reduce hyper ...
... ACE plays a dual role in stimulating vasoconstriction in the body by: • Catalyzing the cleavage of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor • Cleaving bradykinin, a vasodilator, into inactive small peptides Blocking ACE would serve to reduce vasoconstriction and thereby reduce hyper ...
Hexose Monophosphate Shunt (HMP Shunt)
... HMP shunt (PPP) is less active in skeletal muscle & non-lactating mammary glands Site:- ...
... HMP shunt (PPP) is less active in skeletal muscle & non-lactating mammary glands Site:- ...
Amino Acid Oxidation, the Production of Urea, and Amino Acid
... Elastase by cleaving one or more small activation peptides from each of the zymogens. Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Collagenase, and Elastase are endoproteases, they cleave proteins at specific sites within the molecule. The Aminopeptidases and Carboxypeptidases cleave one amino acid at a time starting at ...
... Elastase by cleaving one or more small activation peptides from each of the zymogens. Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Collagenase, and Elastase are endoproteases, they cleave proteins at specific sites within the molecule. The Aminopeptidases and Carboxypeptidases cleave one amino acid at a time starting at ...
Enzymes in Milk: Their Function in the Mammary Gland, in Milk, and
... incomplete tight junctions and of the small volumes secreted before the second or third day postpartum. This is true for amylase (4,22), lysozyme, lactoferrin (23,24), and other proteins, such as IgA (23,24). Mammary secretory cells, present in human milk throughout lactation, can also be used to le ...
... incomplete tight junctions and of the small volumes secreted before the second or third day postpartum. This is true for amylase (4,22), lysozyme, lactoferrin (23,24), and other proteins, such as IgA (23,24). Mammary secretory cells, present in human milk throughout lactation, can also be used to le ...
lec 7 Metabolism of purine nucleotides
... Inhibitors of the amidotransferase: The enzyme is inhibited by the final products of the pathway (IMP, AMP and GMP). ...
... Inhibitors of the amidotransferase: The enzyme is inhibited by the final products of the pathway (IMP, AMP and GMP). ...
The electric field induced by light can explain cellular responses to
... could act in the reverse mode (when appropriate conditions were met), synthesizing ATP from ADP and Pi. This ATP synthesis was enhanced by both visible and NIR laser irradiation and also by a pulsed electric field (110 Hz, 0.11 mV/ cm). These effects were non-thermal, since the temperature of the samp ...
... could act in the reverse mode (when appropriate conditions were met), synthesizing ATP from ADP and Pi. This ATP synthesis was enhanced by both visible and NIR laser irradiation and also by a pulsed electric field (110 Hz, 0.11 mV/ cm). These effects were non-thermal, since the temperature of the samp ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Assignment of the
... he preparation of fully protected peptides suitable for successive coupling to a growing COOH-terminal fragment may be of value in the syntheses of longchained polypeptides or proteins. We have described a modified solid phase method in which peptides were synthesized by the solid phase method of Me ...
... he preparation of fully protected peptides suitable for successive coupling to a growing COOH-terminal fragment may be of value in the syntheses of longchained polypeptides or proteins. We have described a modified solid phase method in which peptides were synthesized by the solid phase method of Me ...
Amino Acids - Portal UniMAP
... - carboxyl group of an amino acid is unprotonated. conjugate base form (-COO-) - amino group of an amino acid is protonated. in its conjugate acid form (+NH3) Thus, each amino acid can behave as an acid or base referred as amphoteric (substance that can act as acid or base) ...
... - carboxyl group of an amino acid is unprotonated. conjugate base form (-COO-) - amino group of an amino acid is protonated. in its conjugate acid form (+NH3) Thus, each amino acid can behave as an acid or base referred as amphoteric (substance that can act as acid or base) ...
A structural determinant in the uracil DNA glycosylase superfamily
... double-stranded uracil-containing DNA. Binding analysis shows that the substitution enhances the binding affinity of K68N to all uracil-containing double-stranded DNA. Genetic analysis suggests that the K68N mutant can act as a UDG to remove uracil from A/U base pairs, which are formed by misincorpo ...
... double-stranded uracil-containing DNA. Binding analysis shows that the substitution enhances the binding affinity of K68N to all uracil-containing double-stranded DNA. Genetic analysis suggests that the K68N mutant can act as a UDG to remove uracil from A/U base pairs, which are formed by misincorpo ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... albumin, and in the cell they are attached to a fatty acid-binding protein ...
... albumin, and in the cell they are attached to a fatty acid-binding protein ...
Biochemistry of saliva and tooth tissues
... Buffer systems maintain the acid-base balance by neutralizing organic acids (from food and produced by cariogenic bacteria). The most important salivary buffers are: bicarbonate buffer (higher concentration in stimulated saliva): HCO3- + H3O+ H2CO3 + H2O phosphate buffer (higher concentration of uns ...
... Buffer systems maintain the acid-base balance by neutralizing organic acids (from food and produced by cariogenic bacteria). The most important salivary buffers are: bicarbonate buffer (higher concentration in stimulated saliva): HCO3- + H3O+ H2CO3 + H2O phosphate buffer (higher concentration of uns ...
Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids
... Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle. These intermediates are substrates for gluconeogenesis and, therefore, can give rise to the net formation of glucose or glycogen in the liver and glycogen in the muscle. B. Ketogenic amino acids Amino ...
... Amino acids whose catabolism yields pyruvate or one of the intermediates of the citric acid cycle. These intermediates are substrates for gluconeogenesis and, therefore, can give rise to the net formation of glucose or glycogen in the liver and glycogen in the muscle. B. Ketogenic amino acids Amino ...
Carbohydrates Metabolism OVERVIEW Carbohydrates (saccharides
... The conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG) by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is the first oxidationreduction reaction of glycolysis.Because there is only a limited amount of NAD+ in the cell, the NADH formed by this reaction must be reoxidized to NAD+ ...
... The conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG) by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase is the first oxidationreduction reaction of glycolysis.Because there is only a limited amount of NAD+ in the cell, the NADH formed by this reaction must be reoxidized to NAD+ ...
Pharmaceutical Faculty 3- d course Module 1 General principles of
... is used for providing of energy for cells. Choose what metabolic process is activated in this case? A. Deamination of glutamate B. Decarboxylation of histidine C. Transamination of aspartate D. ...
... is used for providing of energy for cells. Choose what metabolic process is activated in this case? A. Deamination of glutamate B. Decarboxylation of histidine C. Transamination of aspartate D. ...
mechanism of photosynthesis
... in the second reaction. Robert Hill have been first time stated that just like that of mitochondria, chloroplast also utilize cytochrome. When a quantum of light of wavelength above 680nm is received by a molecule of PS-I the energy is transferred to a chain of other chlorophyll molecules by inducti ...
... in the second reaction. Robert Hill have been first time stated that just like that of mitochondria, chloroplast also utilize cytochrome. When a quantum of light of wavelength above 680nm is received by a molecule of PS-I the energy is transferred to a chain of other chlorophyll molecules by inducti ...
Chapter 5
... generate that kind of energy at once, the cell has no mechanism to use all the energy released at one instant in time. Most of it would be wasted as excess heat. Instead, the cell uses enzymes to destabilize and break down the sugar through a series of conversions into intermediate compounds. The b ...
... generate that kind of energy at once, the cell has no mechanism to use all the energy released at one instant in time. Most of it would be wasted as excess heat. Instead, the cell uses enzymes to destabilize and break down the sugar through a series of conversions into intermediate compounds. The b ...
File - Mr. Doyle SUIS Science
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
... substrate-level phosphorylation. Two molecules of pyruvate form at this last reaction step. 6 Summing up, glycolysis yields two NADH, two ATP (net), ...
Origins of Life PDF
... different hypotheses. Each team will have 10 minutes to present and instruct the other team. At the end of this section, the entire working group should fully understand the differences between the Replication-First and Metabolism-First hypotheses. Listen carefully, ask questions, and take good note ...
... different hypotheses. Each team will have 10 minutes to present and instruct the other team. At the end of this section, the entire working group should fully understand the differences between the Replication-First and Metabolism-First hypotheses. Listen carefully, ask questions, and take good note ...
Biosynthesis of glucose – gluconeogenesis
... Accumulation of acetyl CoA from fatty acid oxidation signals abundant energy, and directs pyruvate to oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis. Pyruvate carboxylase reaction biotin ...
... Accumulation of acetyl CoA from fatty acid oxidation signals abundant energy, and directs pyruvate to oxaloacetate for gluconeogenesis. Pyruvate carboxylase reaction biotin ...
The energy-less red blood cell is lost
... common cause of CNSHA is pyruvate kinase (PK) deficieny. Second, disorders concerning the Hexose Monophosphate Shunt, which maintains adequate levels of reduced glutathione (GSH). This group of disorders is associated with hemolytic episodes, induced by oxidative stress, drugs, or infections. Defici ...
... common cause of CNSHA is pyruvate kinase (PK) deficieny. Second, disorders concerning the Hexose Monophosphate Shunt, which maintains adequate levels of reduced glutathione (GSH). This group of disorders is associated with hemolytic episodes, induced by oxidative stress, drugs, or infections. Defici ...
Compartmentation of the Metabolism of Lactose
... thus preventing the latter from achieving true equilibrium with the compound at all its locations within the cell. Experimentally, the study of compartmentation in living cells presents certain problems arising from the difficulty of distinguishing between several reservoirs of a substance without f ...
... thus preventing the latter from achieving true equilibrium with the compound at all its locations within the cell. Experimentally, the study of compartmentation in living cells presents certain problems arising from the difficulty of distinguishing between several reservoirs of a substance without f ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.























