File
... more) substrates, the shape of the active site determines the orientation of the reactants. This ensures that they are held together in such a way that the reaction can take place ...
... more) substrates, the shape of the active site determines the orientation of the reactants. This ensures that they are held together in such a way that the reaction can take place ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17
... 8. In an alpha helix, the coiling is stabilized by a. the hydrophobic nature of the R chains, which causes the chain to coil with the R groups inward. b. hydrogen bonding of the N—H groups on one amino acid and the C=O groups on another. c. repulsion of the R chains from each other, causing the coil ...
... 8. In an alpha helix, the coiling is stabilized by a. the hydrophobic nature of the R chains, which causes the chain to coil with the R groups inward. b. hydrogen bonding of the N—H groups on one amino acid and the C=O groups on another. c. repulsion of the R chains from each other, causing the coil ...
Biochemistry PowerPoint
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: substances that speed up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
... Enzymes are Catalysts Catalysts: substances that speed up chemical reactions without being affected by the reactions themselves. Enzyme: a protein that increases the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. ...
Organic Chemistry DEFINE the following Vocabulary: Adhesion
... Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. Part B: Describe how the structures of proteins differ from the structures of ...
... Proteins are a major part of every living cell and have many different functions within each cell. Carbohydrates also perform numerous roles in living things. Part A: Describe the general composition of a protein molecule. Part B: Describe how the structures of proteins differ from the structures of ...
Student PPT Notes
... as substrate/enzyme levels increase, the rxn rate increases until active sites of all enzymes are being continuously occupied by a new substrate Genes that code for enzymes can turn ________________(i.e. marathon runners after high-carb pre-competition meals) Some enzymes only synthesized at _ ...
... as substrate/enzyme levels increase, the rxn rate increases until active sites of all enzymes are being continuously occupied by a new substrate Genes that code for enzymes can turn ________________(i.e. marathon runners after high-carb pre-competition meals) Some enzymes only synthesized at _ ...
Chapter 2 Chemistry Test Review
... 12. What does the pH scale measure? Amount of H+ ions 13. Where are protons and neutrons found in an atom? Nucleus Where are electrons found in an atom? 14. In a glass of salt water, what is the solute? salt What is the solvent? Water 15. If an atom has an atomic number of 35 and a mass number of 75 ...
... 12. What does the pH scale measure? Amount of H+ ions 13. Where are protons and neutrons found in an atom? Nucleus Where are electrons found in an atom? 14. In a glass of salt water, what is the solute? salt What is the solvent? Water 15. If an atom has an atomic number of 35 and a mass number of 75 ...
E - ČVUT
... precise geometry of these spatial structures is given by regular distances between NH and CO groups in the backbone of a particular protein. Hydrogen and oxygen in these polar groups are attracted by the van der Waals force, by the hydrogen ...
... precise geometry of these spatial structures is given by regular distances between NH and CO groups in the backbone of a particular protein. Hydrogen and oxygen in these polar groups are attracted by the van der Waals force, by the hydrogen ...
Endergonic vs. exergonic reactions
... o ____________________________ Inhibitor Inhibitor & substrate “_________________________” for active site ______________________ blocks enzyme bacteria use to build cell walls disulfiram (________________________) treats chronic alcoholism o blocks enzyme that breaks down ______________________ o ...
... o ____________________________ Inhibitor Inhibitor & substrate “_________________________” for active site ______________________ blocks enzyme bacteria use to build cell walls disulfiram (________________________) treats chronic alcoholism o blocks enzyme that breaks down ______________________ o ...
Chapter 6
... chains of amino acids,the structural unitsof proteins.Glycine and alanine are examples of amino acids.Iftwo amino acids are joined by dehydration synthesis, a peptide bond forms between them. The resulting molecule is a dipeptide. A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids formed by a peptide bond. ...
... chains of amino acids,the structural unitsof proteins.Glycine and alanine are examples of amino acids.Iftwo amino acids are joined by dehydration synthesis, a peptide bond forms between them. The resulting molecule is a dipeptide. A polypeptide is a chain of amino acids formed by a peptide bond. ...
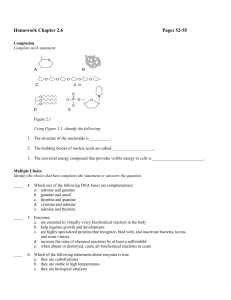
Homework Chapter 2.6 Pages 52-55 Completion Complete each
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
... c. are highly specialized proteins that recognize, bind with, and inactivate bacteria, toxins, and some viruses d. increase the rates of chemical reactions by at least a millionfold e. when absent or destroyed, cause all biochemical reactions to cease ...
Recitation 3 - Department of Chemistry ::: CALTECH
... Consequently, pyruvate is translocated to the mitochondria, decarboxylated and converted into acetyl-CoA Acetyl-CoA then enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also called Krebs cycle, by condensing with oxaloacetate to form citrate. As the acetyl-CoA goes through this cycle, things are bounced ...
... Consequently, pyruvate is translocated to the mitochondria, decarboxylated and converted into acetyl-CoA Acetyl-CoA then enters the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also called Krebs cycle, by condensing with oxaloacetate to form citrate. As the acetyl-CoA goes through this cycle, things are bounced ...
Exam 1
... 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate binding causes an induced fit. ...
... 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate binding causes an induced fit. ...
Chapter 2b Packet
... 9. _____________ are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water. They include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. 10. Phospholipids make up the lipid bilayer of _____ membranes. ___________ include cholesterol, which is found in animal cell membranes 11. ________ are lipids that store e ...
... 9. _____________ are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water. They include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. 10. Phospholipids make up the lipid bilayer of _____ membranes. ___________ include cholesterol, which is found in animal cell membranes 11. ________ are lipids that store e ...
1.4+ billion cows X 200 liters of methane per day = > 7 million tons of
... Why are proteins not completely flexible? Why are proteins not completely stiff? ...
... Why are proteins not completely flexible? Why are proteins not completely stiff? ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... ◦ Catalysts: Special proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the energy needed to start the reaction ◦ Enzyme names end in “–ase” Ex: catalase, sucrase, lactase ...
... ◦ Catalysts: Special proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the energy needed to start the reaction ◦ Enzyme names end in “–ase” Ex: catalase, sucrase, lactase ...
2.2.3 Enzymes Worksheet
... If enzymes are used freely _________________ in a vessel it can be very wasteful as they are ________ at the end of the process To prevent this problem enzymes are often _____________________ or fixed. This means they are ________________ to ______________ or an _________ _______________ and can be ...
... If enzymes are used freely _________________ in a vessel it can be very wasteful as they are ________ at the end of the process To prevent this problem enzymes are often _____________________ or fixed. This means they are ________________ to ______________ or an _________ _______________ and can be ...
Chapter 6
... II. Activation Energy and Reaction Coordinates • Catalysts reduce G‡ • Provide reaction pathway with transition state whose free energy is lower than that in uncatalyzed reaction ...
... II. Activation Energy and Reaction Coordinates • Catalysts reduce G‡ • Provide reaction pathway with transition state whose free energy is lower than that in uncatalyzed reaction ...
Lesson
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
... * Stages involved with formation of proteins * Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
... enzymes; relate structure to function of proteins; and explain enzyme catalysis and regulation; and apply thermodynamic and kinetic theories to enzyme reactions 3. Describe the physical and chemical properties of lipids, their synthesis and function in membranes and metabolism 4. Describe the centra ...
Enzyme

Enzymes /ˈɛnzaɪmz/ are macromolecular biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme converts these into different molecules, called products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. The set of enzymes made in a cell determines which metabolic pathways occur in that cell. The study of enzymes is called enzymology.Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the rate of a reaction by lowering its activation energy. Some enzymes can make their conversion of substrate to product occur many millions of times faster. An extreme example is orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase, which allows a reaction that would otherwise take millions of years to occur in milliseconds. Chemically, enzymes are like any catalyst and are not consumed in chemical reactions, nor do they alter the equilibrium of a reaction. Enzymes differ from most other catalysts by being much more specific. Enzyme activity can be affected by other molecules: inhibitors are molecules that decrease enzyme activity, and activators are molecules that increase activity. Many drugs and poisons are enzyme inhibitors. An enzyme's activity decreases markedly outside its optimal temperature and pH.Some enzymes are used commercially, for example, in the synthesis of antibiotics. Some household products use enzymes to speed up chemical reactions: enzymes in biological washing powders break down protein, starch or fat stains on clothes, and enzymes in meat tenderizer break down proteins into smaller molecules, making the meat easier to chew.