Physical Science
... Chemical reactions take place when chemical bonds are either formed or broken. Strong chemical bonds resist change: glass Weak chemical bonds breakdown easily: wood ...
... Chemical reactions take place when chemical bonds are either formed or broken. Strong chemical bonds resist change: glass Weak chemical bonds breakdown easily: wood ...
An Overview of Organic Reactions
... If the value of Keq is greater than 1, this indicates that at equilibrium most of the material is present as products § If Keq is 10, then the concentration of the product is ten times that of the reactant A value of Keq less than one indicates that at equilibrium most of the material is present as ...
... If the value of Keq is greater than 1, this indicates that at equilibrium most of the material is present as products § If Keq is 10, then the concentration of the product is ten times that of the reactant A value of Keq less than one indicates that at equilibrium most of the material is present as ...
Study Guide for Chapter 5 in Fox
... What does “glycolysis” mean? Where in the cell does this process occur? What happens to glucose immediately as it enters a cell? Glucose could be stored in a cell as a molecule of ____________ In what 2 tissues is this storage most likely to occur? If glucose-6-P is to be broken down (catabolized), ...
... What does “glycolysis” mean? Where in the cell does this process occur? What happens to glucose immediately as it enters a cell? Glucose could be stored in a cell as a molecule of ____________ In what 2 tissues is this storage most likely to occur? If glucose-6-P is to be broken down (catabolized), ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... Pyridine is the most basic as the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is available to bond with H+. Pyrrole is the least basic as the “lone pair” of electrons on nitrogen is part of the aromatic π-electron system and is delocalised around the ring. It is not available for bonding with H+ ions. N-Phen ...
... Pyridine is the most basic as the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is available to bond with H+. Pyrrole is the least basic as the “lone pair” of electrons on nitrogen is part of the aromatic π-electron system and is delocalised around the ring. It is not available for bonding with H+ ions. N-Phen ...
Stoichiometry
... Two compounds are involved with the cation of one compound EXCHANGING with the cation of another compound. AX + BZ AZ + BX These reactions proceed if one of the ff. is satisfied: 1. An insoluble/slightly soluble product is formed (PRECIPITATE formation) 2. A weakly ionized species is produced. The ...
... Two compounds are involved with the cation of one compound EXCHANGING with the cation of another compound. AX + BZ AZ + BX These reactions proceed if one of the ff. is satisfied: 1. An insoluble/slightly soluble product is formed (PRECIPITATE formation) 2. A weakly ionized species is produced. The ...
Chapter 6
... number it would have if it were a monatomic ion. – A. Hydrogen can be either +1 or –1. – B. Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of –2. • In peroxides, oxygen is –1. ...
... number it would have if it were a monatomic ion. – A. Hydrogen can be either +1 or –1. – B. Oxygen usually has an oxidation number of –2. • In peroxides, oxygen is –1. ...
atoms-chemical
... • While all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons (atomic number), they may differ in the number of neutrons and atomic mass. • Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. • For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). 1% of ...
... • While all atoms of a given element have the same number of protons (atomic number), they may differ in the number of neutrons and atomic mass. • Two atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. • For example, 99% of carbon atoms have 6 neutrons (12C). 1% of ...
Updated Recovery Packet for Biochemistry.
... a.) Saturated – only single C bonds, “Sat” with H, “bad” for you, solid at room T (raises cholesterol) b.) Unsaturated – at least 1 C double bond, “unsat.” with H) “good” for you, liquid at room T (ex. Cooking oils) c. Nucleic Acids 1.) contain: C, H, O, N, P 2.) monomers: NUCLEOTIDES - 5 carbon sug ...
... a.) Saturated – only single C bonds, “Sat” with H, “bad” for you, solid at room T (raises cholesterol) b.) Unsaturated – at least 1 C double bond, “unsat.” with H) “good” for you, liquid at room T (ex. Cooking oils) c. Nucleic Acids 1.) contain: C, H, O, N, P 2.) monomers: NUCLEOTIDES - 5 carbon sug ...
BITSAT Chemistry
... Q 45: 0.3708 g of CO2, 0.1427 g of H2O and an undetermined quantity of methane are obtained on the on the combustion of 50 ml. of a gaseous hydrocarbon at S.T.P. The hydrocarbon would be a ...
... Q 45: 0.3708 g of CO2, 0.1427 g of H2O and an undetermined quantity of methane are obtained on the on the combustion of 50 ml. of a gaseous hydrocarbon at S.T.P. The hydrocarbon would be a ...
Interactive comment on “Reactivity of chlorine radical with submicron
... constant for the H-abstraction reaction (R1) must be likely different for each species due to the nature of the carbon chain (linear for PA or branched for Sq) and also the functional group (ether for DOS and acid for PA). As secondary chemistry was also highlighted for each heterogeneous reaction, ...
... constant for the H-abstraction reaction (R1) must be likely different for each species due to the nature of the carbon chain (linear for PA or branched for Sq) and also the functional group (ether for DOS and acid for PA). As secondary chemistry was also highlighted for each heterogeneous reaction, ...
Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... Draw the line structure of an alkane that contains ten carbon atoms. What is the chemical formula of this compound? What is the condensed structural formula of this compound? Draw the line structures of two isomers of this compound. What are their chemical formulae (explain)? What are their condense ...
... Draw the line structure of an alkane that contains ten carbon atoms. What is the chemical formula of this compound? What is the condensed structural formula of this compound? Draw the line structures of two isomers of this compound. What are their chemical formulae (explain)? What are their condense ...
HL Biology H4 - Liver function 1. A number of chemicals have been
... A number of chemicals have been shown to cause tissue damage due to the production of free radicals. Free radicals are chemicals, such as superoxides and peroxides, which can react to damage DNA and lipids. Antioxidants produced by our body, such as reduced glutathione, combine with free radicals an ...
... A number of chemicals have been shown to cause tissue damage due to the production of free radicals. Free radicals are chemicals, such as superoxides and peroxides, which can react to damage DNA and lipids. Antioxidants produced by our body, such as reduced glutathione, combine with free radicals an ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes
... d. Electrolytes—substances that dissociate into ions in solution, and can conduct electricity. e. The amount of [H+] in a solution is expressed as pH. Fig. 7. i. pH = log[H+] ii. Increasing [H+] increases acidity. (Lower pH) iii. Increasing [OH] increases alkalinity. (Higher pH) iv. Acidic solutio ...
... d. Electrolytes—substances that dissociate into ions in solution, and can conduct electricity. e. The amount of [H+] in a solution is expressed as pH. Fig. 7. i. pH = log[H+] ii. Increasing [H+] increases acidity. (Lower pH) iii. Increasing [OH] increases alkalinity. (Higher pH) iv. Acidic solutio ...
Chapter 7
... In any chemical reaction, atoms are conserved… That is, the same number of atoms used in the reaction is the same number of atoms in the products. This is conservation of mass (or matter)…Matter is not created or destroyed, it just changes form. ...
... In any chemical reaction, atoms are conserved… That is, the same number of atoms used in the reaction is the same number of atoms in the products. This is conservation of mass (or matter)…Matter is not created or destroyed, it just changes form. ...
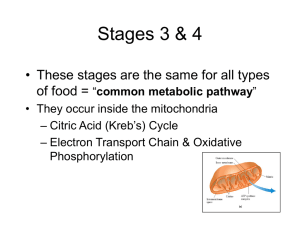
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
... Series of electron carriers Each carrier exists in oxidized or reduced form High energy electrons pass down the electron transport chain in a series of redox reactions These reactions are coupled with ATP synthesis (oxidative phosphorylation). They lose energy as they pass along the chain ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... 59) An excess of hydrogen ions in the body fluids can have disastrous results because A) excess hydrogen ions can change the shape of large complex molecules, rendering them nonfunctional. B) excess hydrogen ions can break chemical bonds. C) excess hydrogen ions can disrupt tissue functions. D) all ...
... 59) An excess of hydrogen ions in the body fluids can have disastrous results because A) excess hydrogen ions can change the shape of large complex molecules, rendering them nonfunctional. B) excess hydrogen ions can break chemical bonds. C) excess hydrogen ions can disrupt tissue functions. D) all ...
Take notes on this document while you are watching the recorded
... 1. The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility (will dissolve) in nonpolar5 organic solvents (e.g. ether, chloroform, acetone & benzene) and general insolubility in water (do not dissolve in water - repel water; hydrophobic). ...
... 1. The lipids are a large and diverse group of naturally occurring organic compounds that are related by their solubility (will dissolve) in nonpolar5 organic solvents (e.g. ether, chloroform, acetone & benzene) and general insolubility in water (do not dissolve in water - repel water; hydrophobic). ...
Bio 6B Lecture Slides - B
... • Glycogen, starch, and cellulose are all poly-glucose. • But very different bioactivity (and digestibility) varies because of different chain branching. ...
... • Glycogen, starch, and cellulose are all poly-glucose. • But very different bioactivity (and digestibility) varies because of different chain branching. ...
Chapter 2 Biochemistry Goux Guided Notes
... Section 2.3 Carbon Compounds The Chemistry of Carbon: - Carbon atoms have _____4_______valence electrons - Each electron can join with an electron from another atom to form a strong _covalent__ bond - Carbon can bond with many elements, including _____hydrogen_______ , phosphorus, sulfur, and nitro ...
... Section 2.3 Carbon Compounds The Chemistry of Carbon: - Carbon atoms have _____4_______valence electrons - Each electron can join with an electron from another atom to form a strong _covalent__ bond - Carbon can bond with many elements, including _____hydrogen_______ , phosphorus, sulfur, and nitro ...
Chemical Reactions
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
Science – Chemistry, Biology (5154 /01) version 1.1
... Carbon dioxide is an acidic oxide, which dissolves in water to give carbonic acid. ...
... Carbon dioxide is an acidic oxide, which dissolves in water to give carbonic acid. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Anaerobic respiration- without O2. Aerobic respiration- with O2. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) ...
... Anaerobic respiration- without O2. Aerobic respiration- with O2. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP) ...
Chemical Reactions
... • Spontaneous reactions—occur naturally, the process is unaided. • Example: –Decomposition of dead matter = spontaneous endothermic reactions. (absorbs heat energy) –Forest fire = spontaneous exothermic reactions. (releases heat energy) ...
... • Spontaneous reactions—occur naturally, the process is unaided. • Example: –Decomposition of dead matter = spontaneous endothermic reactions. (absorbs heat energy) –Forest fire = spontaneous exothermic reactions. (releases heat energy) ...
Radical species in the catalytic pathways of enzymes from anaerobes
... Radicals are reactive intermediates of growing importance in enzymatic catalysis. There are reactions in which neutral radicals participate and those where radical anions are involved. The former class is illustrated by lysine 2,3-aminomutase and also by enzymes dependent on coenzyme B12 , that cata ...
... Radicals are reactive intermediates of growing importance in enzymatic catalysis. There are reactions in which neutral radicals participate and those where radical anions are involved. The former class is illustrated by lysine 2,3-aminomutase and also by enzymes dependent on coenzyme B12 , that cata ...
Radical (chemistry)

In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valency electrons.With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances, or even towards themselves: their molecules will often spontaneously dimerize or polymerize if they come in contact with each other. Most radicals are reasonably stable only at very low concentrations in inert media or in a vacuum.A notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO•), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (:CH2) which have two unpaired electrons. In contrast, the hydroxyl anion (HO−) is not a radical, since the unpaired electron is resolved by the addition of an electron; singlet oxygen and singlet carbene are not radicals as the two electrons are paired.Free radicals may be created in a number of ways, including synthesis with very dilute or rarefied reagents, reactions at very low temperatures, or breakup of larger molecules. The latter can be affected by any process that puts enough energy into the parent molecule, such as ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, electrolysis, and chemical reactions. Indeed, radicals are intermediate stages in many chemical reactions.Free radicals play an important role in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. In living organisms, the free radicals superoxide and nitric oxide and their reaction products regulate many processes, such as control of vascular tone and thus blood pressure. They also play a key role in the intermediary metabolism of various biological compounds. Such radicals can even be messengers in a process dubbed redox signaling. A radical may be trapped within a solvent cage or be otherwise bound.Until late in the 20th century the word ""radical"" was used in chemistry to indicate any connected group of atoms, such as a methyl group or a carboxyl, whether it was part of a larger molecule or a molecule on its own. The qualifier ""free"" was then needed to specify the unbound case. Following recent nomenclature revisions, a part of a larger molecule is now called a functional group or substituent, and ""radical"" now implies ""free"". However, the old nomenclature may still occur in the literature.