File
... and participate in catalysis but are not considered substrates of the reaction • function as intermediate carriers of electrons, specific atoms or functional groups that are transferred in the overall reaction • Examples: NAD, NADP, FAD, CoEnzymeA ...
... and participate in catalysis but are not considered substrates of the reaction • function as intermediate carriers of electrons, specific atoms or functional groups that are transferred in the overall reaction • Examples: NAD, NADP, FAD, CoEnzymeA ...
Harvesting Energy
... Consider the metabolism in your muscle cells. At rest or during light exercise, when oxygen is plentiful, pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle and continues to be metabolized through cellular respiration. During heavy exercise, your lungs and circulatory system can't transport oxygen to your muscles ...
... Consider the metabolism in your muscle cells. At rest or during light exercise, when oxygen is plentiful, pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle and continues to be metabolized through cellular respiration. During heavy exercise, your lungs and circulatory system can't transport oxygen to your muscles ...
Relationship between the structure and function of proteins
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
... Its function is to store and transport oxygen in the skeletal muscles. It is a relatively small protein made up of a single polypeptide chain that contains 153 amino acid residues . It contains a heme group (which is a prosthetic group consisting of a protoporphyrin organic ring and a central iron a ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... protein called ATP Synthase. As H+ move through ATP Synthase like water through a dam, energy is used to convert ADP to ATP. Each pair of electrons can produce between two and three ATPs (Depends on if they came from NADH or FADH) 9NADH= 28 ATP 2FADH= 4 ATP Total of 32 ATPs created during ETC!!!! ...
... protein called ATP Synthase. As H+ move through ATP Synthase like water through a dam, energy is used to convert ADP to ATP. Each pair of electrons can produce between two and three ATPs (Depends on if they came from NADH or FADH) 9NADH= 28 ATP 2FADH= 4 ATP Total of 32 ATPs created during ETC!!!! ...
Cellular Respiration
... NADH) are transferred from one membrane carrier to another membrane carrier (Cytochromes) • The electrons lose energy as they are transferred (like hot potato) • This energy drives membrane pumps involved with Chemiosmosis ...
... NADH) are transferred from one membrane carrier to another membrane carrier (Cytochromes) • The electrons lose energy as they are transferred (like hot potato) • This energy drives membrane pumps involved with Chemiosmosis ...
Net Ionic Equations
... Important because: the binding of atoms results from the transfer or sharing of electrons. ...
... Important because: the binding of atoms results from the transfer or sharing of electrons. ...
Balancing reaction equations, oxidation state, and reduction
... Important because: the binding of atoms results from the transfer or sharing of electrons. ...
... Important because: the binding of atoms results from the transfer or sharing of electrons. ...
PowerPoint Lecture
... • Mastery of anatomical terminology • Ability to focus at many levels (systemic to cellular to molecular) • Study of basic physical principles (e.g., electrical currents, pressure, and movement) • Study of basic chemical principles ...
... • Mastery of anatomical terminology • Ability to focus at many levels (systemic to cellular to molecular) • Study of basic physical principles (e.g., electrical currents, pressure, and movement) • Study of basic chemical principles ...
p Research Article NAGARAJA NAIK*, H. VIJAY KUMAR, ANITHA
... occurring antioxidants are whole grains, fruits and vegetables. Plant sourced food antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenes, phenolic acids, phytate and phytoestrogens have been recognized as having the potential to reduce disease risk4-5. Recently, much attention has been focused on dietar ...
... occurring antioxidants are whole grains, fruits and vegetables. Plant sourced food antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, carotenes, phenolic acids, phytate and phytoestrogens have been recognized as having the potential to reduce disease risk4-5. Recently, much attention has been focused on dietar ...
Cellular Respiration
... In a general sense, fermentation is the conversion of a carbohydrate such as sugar into an acid or an alcohol. More specifically, fermentation can refer to the use of yeast to change sugar into alcohol or the use of bacteria to create lactic acid in certain foods. Fermentation occurs naturally in ma ...
... In a general sense, fermentation is the conversion of a carbohydrate such as sugar into an acid or an alcohol. More specifically, fermentation can refer to the use of yeast to change sugar into alcohol or the use of bacteria to create lactic acid in certain foods. Fermentation occurs naturally in ma ...
Chemistry B11 Chapter 4 Chemical reactions
... using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical equation (immediately following each reactant and product). We use the symbol (g) for gas, ...
... using chemical formulas for the reactants and products, and an arrow to indicate the direction in which the reaction proceeds. Note: It is important to show the state of each reactant and product in a chemical equation (immediately following each reactant and product). We use the symbol (g) for gas, ...
File
... • photosynthesis & cellular respiration are cyclic processes • the products of one are the reactants of the other ...
... • photosynthesis & cellular respiration are cyclic processes • the products of one are the reactants of the other ...
Chemical Reactions (Part One)
... Food scientists can tell producers and supermarkets the best conditions for slowing down or speeding up the ripening process so that fruit and vegetables arrive in the shops perfectly ripe. ...
... Food scientists can tell producers and supermarkets the best conditions for slowing down or speeding up the ripening process so that fruit and vegetables arrive in the shops perfectly ripe. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... respiration has produced from one glucose molecule a net total of 4 ATP (two from glycolysis, and two from the Krebs Cycle). c. Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis. The remaining energy (not yet stored in ATP) from the glucose molecule is stored in the hydrogen atoms attached to NADH and FADH2 ...
... respiration has produced from one glucose molecule a net total of 4 ATP (two from glycolysis, and two from the Krebs Cycle). c. Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis. The remaining energy (not yet stored in ATP) from the glucose molecule is stored in the hydrogen atoms attached to NADH and FADH2 ...
Cyclooxygenase mechanisms Lawrence J Marnett
... at Arg120, Tyr355, and Glu524 before bending up toward Leu531. This conformation is inconsistent with catalysis but may correspond to an inhibitory conformation of substrate bound to enzyme. The cyclooxygenase active sites of COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar but there are subtle structural differenc ...
... at Arg120, Tyr355, and Glu524 before bending up toward Leu531. This conformation is inconsistent with catalysis but may correspond to an inhibitory conformation of substrate bound to enzyme. The cyclooxygenase active sites of COX-1 and COX-2 are very similar but there are subtle structural differenc ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... used as a flavor enhancer in food. They are the same thing chemically, except that MSG has a sodium where glutamic acid has a hydrogen. ...
... used as a flavor enhancer in food. They are the same thing chemically, except that MSG has a sodium where glutamic acid has a hydrogen. ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... • PhosphorylaDon is the process of adding a phosphate group to an organic molecule (oNen a protein) to acDvate or inacDvate the molecule. • ATP is oNen a source of phosphate groups for these rea ...
... • PhosphorylaDon is the process of adding a phosphate group to an organic molecule (oNen a protein) to acDvate or inacDvate the molecule. • ATP is oNen a source of phosphate groups for these rea ...
Enzyme cofactors
... active form of the vitamin B1 (the first discovered vitamin) contains substituted heterocycles pyrimidine and thiazol reactions – reversible cleavage on the C—C bond connecting C=O group with the vicinal reactive group (usually —COOH or —OH) – transfer of 2C-residues in transketolase reactions in th ...
... active form of the vitamin B1 (the first discovered vitamin) contains substituted heterocycles pyrimidine and thiazol reactions – reversible cleavage on the C—C bond connecting C=O group with the vicinal reactive group (usually —COOH or —OH) – transfer of 2C-residues in transketolase reactions in th ...
8 Aerobic Respiration
... The NADH and FADH2 give off their electron, which powers each protein channel in sequence.* The NAD+ and FAD+ then return to pick up another electron *REMEMBER: If we can’t do this step, then the cell has to do fermentation instead. ...
... The NADH and FADH2 give off their electron, which powers each protein channel in sequence.* The NAD+ and FAD+ then return to pick up another electron *REMEMBER: If we can’t do this step, then the cell has to do fermentation instead. ...
BIO 101
... 26. What is the most common lipid consumed by humans? 27. Before energy can be obtained from a fat molecule, what must first happen to it? 28. What metabolic pathways are involved in the complete oxidation of a free fatty acid? ...
... 26. What is the most common lipid consumed by humans? 27. Before energy can be obtained from a fat molecule, what must first happen to it? 28. What metabolic pathways are involved in the complete oxidation of a free fatty acid? ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the answer sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C, and D. Choose the one you consider correct and r ...
... Write your name, Centre number and candidate number on the answer sheet in the spaces provided unless this has been done for you. There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C, and D. Choose the one you consider correct and r ...
Potential Role of Sulfur-Containing Antioxidant Systems in Highly
... synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) during the oxidation of organic molecules such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Oxidation is a crucial part of both aerobic life and metabolism [1] because it provides energy for the cell to perform its functions. Molecular oxygen, which is ne ...
... synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) during the oxidation of organic molecules such as carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Oxidation is a crucial part of both aerobic life and metabolism [1] because it provides energy for the cell to perform its functions. Molecular oxygen, which is ne ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed - Chemistry
... o There are 92 naturally occurring elements. o Each element has a unique symbol, usually the first one or two letters of its name. Some symbols are derived from Latin or German names. A compound is a substance that consists of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. o Table salt (sodium chloride or ...
... o There are 92 naturally occurring elements. o Each element has a unique symbol, usually the first one or two letters of its name. Some symbols are derived from Latin or German names. A compound is a substance that consists of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. o Table salt (sodium chloride or ...
9.3 student Fill in notes
... • In the first stage of cellular respiration, ________________ is broken down to ________________ during ________________, an ________________ process. ...
... • In the first stage of cellular respiration, ________________ is broken down to ________________ during ________________, an ________________ process. ...
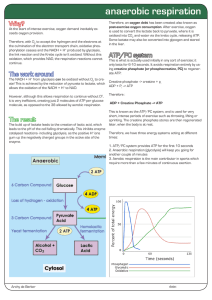
anaerobic respiration
... catalysed reactions- including glycolysis, as the positive H+ ions gum up the negatively charged groups in the active site of the enzyme. ...
... catalysed reactions- including glycolysis, as the positive H+ ions gum up the negatively charged groups in the active site of the enzyme. ...
Radical (chemistry)

In chemistry, a radical (more precisely, a free radical) is an atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valency electrons.With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make free radicals highly chemically reactive towards other substances, or even towards themselves: their molecules will often spontaneously dimerize or polymerize if they come in contact with each other. Most radicals are reasonably stable only at very low concentrations in inert media or in a vacuum.A notable example of a free radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO•), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (:CH2) which have two unpaired electrons. In contrast, the hydroxyl anion (HO−) is not a radical, since the unpaired electron is resolved by the addition of an electron; singlet oxygen and singlet carbene are not radicals as the two electrons are paired.Free radicals may be created in a number of ways, including synthesis with very dilute or rarefied reagents, reactions at very low temperatures, or breakup of larger molecules. The latter can be affected by any process that puts enough energy into the parent molecule, such as ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, electrolysis, and chemical reactions. Indeed, radicals are intermediate stages in many chemical reactions.Free radicals play an important role in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. In living organisms, the free radicals superoxide and nitric oxide and their reaction products regulate many processes, such as control of vascular tone and thus blood pressure. They also play a key role in the intermediary metabolism of various biological compounds. Such radicals can even be messengers in a process dubbed redox signaling. A radical may be trapped within a solvent cage or be otherwise bound.Until late in the 20th century the word ""radical"" was used in chemistry to indicate any connected group of atoms, such as a methyl group or a carboxyl, whether it was part of a larger molecule or a molecule on its own. The qualifier ""free"" was then needed to specify the unbound case. Following recent nomenclature revisions, a part of a larger molecule is now called a functional group or substituent, and ""radical"" now implies ""free"". However, the old nomenclature may still occur in the literature.