SC.912.L.18.11 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower
... substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction is called a substrate. Enzymes act only on specific substrates. An enzyme’s shape determines its activity. Typically, an enzyme is a large protein with one or more deep folds on its surface. These folds form pockets called active sites. As ...
... substance on which an enzyme acts during a chemical reaction is called a substrate. Enzymes act only on specific substrates. An enzyme’s shape determines its activity. Typically, an enzyme is a large protein with one or more deep folds on its surface. These folds form pockets called active sites. As ...
Slide 1
... molecules and join them together to form complex molecules. For example, glucose molecules go through a condensation reaction forming many glycosidic bonds between molecules and eventually forming the ...
... molecules and join them together to form complex molecules. For example, glucose molecules go through a condensation reaction forming many glycosidic bonds between molecules and eventually forming the ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Studying Enzyme Kinetics by Means of Progress - Beilstein
... constant over the time period of the measurements. For enzymes exhibiting self-activation or inactivation this condition is obviously not met. Second, the initial-rate method is laborious as it requires a series of parallel assays differing in the initial concentrations of the reactants and effector ...
... constant over the time period of the measurements. For enzymes exhibiting self-activation or inactivation this condition is obviously not met. Second, the initial-rate method is laborious as it requires a series of parallel assays differing in the initial concentrations of the reactants and effector ...
Bio Day 3 - Edublogs
... Biochemistry BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES Exit Slip Imagine you are looking at a sample of human body tissue through a high-powered scanning electron microscope. This microscope enables you to see objects as small as atoms and molecules. Describe what you would observe as you examine the body tissue, and e ...
... Biochemistry BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES Exit Slip Imagine you are looking at a sample of human body tissue through a high-powered scanning electron microscope. This microscope enables you to see objects as small as atoms and molecules. Describe what you would observe as you examine the body tissue, and e ...
Enzymes 1 and 2
... What are enzymes, and what do they do? What characteristic features define enzymes? Can the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction be defined in a mathematical way? What equations define the kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions? What can be learned from the inhibition of enzyme activity? ...
... What are enzymes, and what do they do? What characteristic features define enzymes? Can the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction be defined in a mathematical way? What equations define the kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions? What can be learned from the inhibition of enzyme activity? ...
Part I Power generation in fuel cells
... Recent advances in electrochemistry and technology have led to the introduction of a compact source of power in which fuels are used to produce electricity without the intervention of thermal devices such as boilers, turbines and generators: these fuel cells can be much more efficient than conventio ...
... Recent advances in electrochemistry and technology have led to the introduction of a compact source of power in which fuels are used to produce electricity without the intervention of thermal devices such as boilers, turbines and generators: these fuel cells can be much more efficient than conventio ...
king fahd university of petroleum and minerals chemistry
... 37. A semiconductor made mainly from silicon (Si) is doped with a small amount of boron (B). This means that it is a/an: A) B) C) D) ...
... 37. A semiconductor made mainly from silicon (Si) is doped with a small amount of boron (B). This means that it is a/an: A) B) C) D) ...
Chapter8 - Louisiana Tech University
... The basic abstraction of thermodynamics is the division of the world into systems delimited by real or ideal boundaries. The systems not directly under consideration are lumped into the surrounding. Usually systems can be assigned a well-defined state solid/liquid or a gas which can be summarized by ...
... The basic abstraction of thermodynamics is the division of the world into systems delimited by real or ideal boundaries. The systems not directly under consideration are lumped into the surrounding. Usually systems can be assigned a well-defined state solid/liquid or a gas which can be summarized by ...
Free radicals
... Many of these molecular species are oxygen (and sometimes nitrogen and chloride) centered. The molecular oxygen we breathe is a free radical. ...
... Many of these molecular species are oxygen (and sometimes nitrogen and chloride) centered. The molecular oxygen we breathe is a free radical. ...
Computational Geometry of Molecular Structure
... o Hold-out subset 1; combine subsets 2-10 into one training set for learning a model; use trained model to predict classes of instances in subset 1 o Repeat previous step 9 more times (e.g., hold-out subset 2, combine subsets 1 and 3-10 together to train a model, use model to predict subset 2, etc) ...
... o Hold-out subset 1; combine subsets 2-10 into one training set for learning a model; use trained model to predict classes of instances in subset 1 o Repeat previous step 9 more times (e.g., hold-out subset 2, combine subsets 1 and 3-10 together to train a model, use model to predict subset 2, etc) ...
Document
... Example of Ping-Pong Enzyme: Aspartate aminotransferase: Catalyzes the conversion of aspartate to glutamate with production of oxaloacetate and consumption of alphaketoglutarate. The reaction sequence starts with the binding of aspartate to the enzyme followed by its conversion to oxaloacetate, in t ...
... Example of Ping-Pong Enzyme: Aspartate aminotransferase: Catalyzes the conversion of aspartate to glutamate with production of oxaloacetate and consumption of alphaketoglutarate. The reaction sequence starts with the binding of aspartate to the enzyme followed by its conversion to oxaloacetate, in t ...
enzymes - MrsGorukhomework
... Demo – scissors used to cut paper, stapler used to put together, both not changed Metabolism – (Greek for change) all chemical processes Enzymes are globular protein catalysts. Catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed or used up themselves. Reactions require bonds th ...
... Demo – scissors used to cut paper, stapler used to put together, both not changed Metabolism – (Greek for change) all chemical processes Enzymes are globular protein catalysts. Catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed or used up themselves. Reactions require bonds th ...
Reaction Analysis and PAT Tools
... ReactIR collects data in the mid infrared spectral region, which provides characteristic fingerprint region bands that are associated with fundamental vibrations in the molecules of interest. iC IR takes this spectral data and converts it to reaction information that is then used for understanding t ...
... ReactIR collects data in the mid infrared spectral region, which provides characteristic fingerprint region bands that are associated with fundamental vibrations in the molecules of interest. iC IR takes this spectral data and converts it to reaction information that is then used for understanding t ...
Why a need for Systems Biology
... - Interactomics (studying the interactome, which is the interaction among proteins) -Metabolomics (the study of small-molecule metabolite profiles in cells) - Phenomics (describes the state of an organism as it changes with time) - and so on...... ...
... - Interactomics (studying the interactome, which is the interaction among proteins) -Metabolomics (the study of small-molecule metabolite profiles in cells) - Phenomics (describes the state of an organism as it changes with time) - and so on...... ...
and y-crystallin X - Prof. N. Srinivasan
... connecting peptide. Here the topological equivalent hydrophobic residues that have been appended are Val 43, Val 56, Ile 81 and Val 132, Leu 145, Ile 170. C: Two subunits of OB2 associate about a 2-fold axis, perpendicular to the page, allowing dimer formation using very similar interdomain contacts ...
... connecting peptide. Here the topological equivalent hydrophobic residues that have been appended are Val 43, Val 56, Ile 81 and Val 132, Leu 145, Ile 170. C: Two subunits of OB2 associate about a 2-fold axis, perpendicular to the page, allowing dimer formation using very similar interdomain contacts ...
Problems - Department of Chemistry HKU
... reaction is being driven by light absorption. Thus the steady-state concentration of products and reactants might differ significantly from equilibrium values. For instance, suppose the reaction A → B is driven by light absorption, and that its rate is Ia, but that the reverse reaction B → A is bimo ...
... reaction is being driven by light absorption. Thus the steady-state concentration of products and reactants might differ significantly from equilibrium values. For instance, suppose the reaction A → B is driven by light absorption, and that its rate is Ia, but that the reverse reaction B → A is bimo ...
Presentation
... domains offer an interesting look into the flexing of the protein’s tertiary structure Monitoring exactly how this conformational change takes place would offer some insight into how the amino acid backbone shifts and contracts to allow proper binding to pERK. ...
... domains offer an interesting look into the flexing of the protein’s tertiary structure Monitoring exactly how this conformational change takes place would offer some insight into how the amino acid backbone shifts and contracts to allow proper binding to pERK. ...
Synthesis Reaction
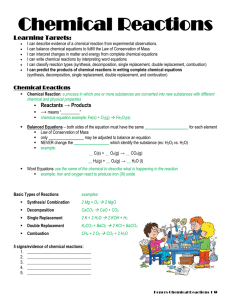
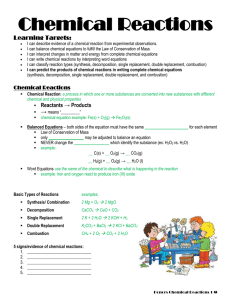
... 2. How does the law of conservation of matter relate to balanced equations? 3. What are 5 signs (evidence) that a chemical reaction has occurred? 4. Recognize the following terms and symbols as they relate to chemical reactions: reactant, product, subscript, coefficient, s, l, g, aq, , diatomic ele ...
... 2. How does the law of conservation of matter relate to balanced equations? 3. What are 5 signs (evidence) that a chemical reaction has occurred? 4. Recognize the following terms and symbols as they relate to chemical reactions: reactant, product, subscript, coefficient, s, l, g, aq, , diatomic ele ...
Document
... 2. How does the law of conservation of matter relate to balanced equations? 3. What are 5 signs (evidence) that a chemical reaction has occurred? 4. Recognize the following terms and symbols as they relate to chemical reactions: reactant, product, subscript, coefficient, s, l, g, aq, , diatomic ele ...
... 2. How does the law of conservation of matter relate to balanced equations? 3. What are 5 signs (evidence) that a chemical reaction has occurred? 4. Recognize the following terms and symbols as they relate to chemical reactions: reactant, product, subscript, coefficient, s, l, g, aq, , diatomic ele ...
Document
... Like all proteins, each enzyme molecule has a particular shape This shape determines which chemical reaction the enzyme can speed up In speeding up the reaction, the enzyme combines temporarily with the substances it is acting on ...
... Like all proteins, each enzyme molecule has a particular shape This shape determines which chemical reaction the enzyme can speed up In speeding up the reaction, the enzyme combines temporarily with the substances it is acting on ...
The Chemicals of Living Things
... Like all proteins, each enzyme molecule has a particular shape This shape determines which chemical reaction the enzyme can speed up In speeding up the reaction, the enzyme combines temporarily with the substances it is acting on ...
... Like all proteins, each enzyme molecule has a particular shape This shape determines which chemical reaction the enzyme can speed up In speeding up the reaction, the enzyme combines temporarily with the substances it is acting on ...
Text S1.
... Figure II-1: the phosphoketolase cycle that results in complete “combustion” of glycerol (or glucose, see Figure II-2) into co2 and h2o. Abbreviations: PKL phosphoketolase; TAL transaldolase; TKT transketolase; PYROX pyruvate oxidase; GLYK glycerol kinase; G3PD1 glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; T ...
... Figure II-1: the phosphoketolase cycle that results in complete “combustion” of glycerol (or glucose, see Figure II-2) into co2 and h2o. Abbreviations: PKL phosphoketolase; TAL transaldolase; TKT transketolase; PYROX pyruvate oxidase; GLYK glycerol kinase; G3PD1 glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; T ...
Structural Insights into Catalysis and Inhibition of O
... enzymes to the same extent and is therefore designated as was verified, and the fragment was cloned into the expression vector pET28a (Novagen), resulting in a cleavable six-histidine either CysK2 or CysM2. The crystal structure analysis of OASS from Salmonella tag at the N terminus of the polypepti ...
... enzymes to the same extent and is therefore designated as was verified, and the fragment was cloned into the expression vector pET28a (Novagen), resulting in a cleavable six-histidine either CysK2 or CysM2. The crystal structure analysis of OASS from Salmonella tag at the N terminus of the polypepti ...
Chapters 10 and 11 Enzymes Enzymes are specialized proteins that
... If Vmax ↓ then inhibitor If Vmax ↑ then activator An enzyme can have separate catalytic and regulatory subunits. Enzyme Regulation 1) Regulate amount of enzyme by a change in the de novo synthesis of the enzyme 2) Modulate enzyme activity with activators, inhibitors, and through covalent modificatio ...
... If Vmax ↓ then inhibitor If Vmax ↑ then activator An enzyme can have separate catalytic and regulatory subunits. Enzyme Regulation 1) Regulate amount of enzyme by a change in the de novo synthesis of the enzyme 2) Modulate enzyme activity with activators, inhibitors, and through covalent modificatio ...