ATP Molecules
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) • carries amino acids to mRNA • carries anticodon to mRNA • translates a codon of mRNA into an amino acid Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – • provides structure and enzyme activity for ribosomes ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) • carries amino acids to mRNA • carries anticodon to mRNA • translates a codon of mRNA into an amino acid Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – • provides structure and enzyme activity for ribosomes ...
Biofuel alternatives to ethanol: pumping the microbial well
... and pesticide requirements than currently used crops such as oil palms, corn or soybeans [67]. These characteristics should serve to make biofuels more competitive with petroleum, while making them less competitive with food production for arable land. To date, pathway manipulations have largely bee ...
... and pesticide requirements than currently used crops such as oil palms, corn or soybeans [67]. These characteristics should serve to make biofuels more competitive with petroleum, while making them less competitive with food production for arable land. To date, pathway manipulations have largely bee ...
Enzymes - كنانة أونلاين
... extracts that lacked any living yeast cells to ferment sugar. In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". In 190 ...
... extracts that lacked any living yeast cells to ferment sugar. In a series of experiments at the University of Berlin, he found that the sugar was fermented even when there were no living yeast cells in the mixture. • He named the enzyme that brought about the fermentation of sucrose "zymase". In 190 ...
Slide 1
... inflammatory responses and associate them with OSA. Obesity is the common factor that connects OSA TO Metabolic syndrome. Monocytes and Macrophages abound and increase through what is known as the “Cascade”. Monocytes>>Macrophages eat/destroy Adipokines-Fat derived Cytokines-One is Leptin. Leptin pl ...
... inflammatory responses and associate them with OSA. Obesity is the common factor that connects OSA TO Metabolic syndrome. Monocytes and Macrophages abound and increase through what is known as the “Cascade”. Monocytes>>Macrophages eat/destroy Adipokines-Fat derived Cytokines-One is Leptin. Leptin pl ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... represents a protein and each edge represents the interaction between two proteins. Predict function of each protein in the map (black circle in Figure C), based on the functions of ‘n-neighbouring proteins’, which are defined as a set of proteins reached via n physical interactions at most (n is an ...
... represents a protein and each edge represents the interaction between two proteins. Predict function of each protein in the map (black circle in Figure C), based on the functions of ‘n-neighbouring proteins’, which are defined as a set of proteins reached via n physical interactions at most (n is an ...
Metabolomics in Nutrition Research, and Implications in Blood Type
... Martin Kohlmeier, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ...
... Martin Kohlmeier, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... Kreb’s Cycle Summary • Remember, we get 3NADH from TCA along with the one we got from the Pyruvate DH reaction and then an FADH2 (a lot like NADH, but less reducing power) and an ATP and this is just from ...
... Kreb’s Cycle Summary • Remember, we get 3NADH from TCA along with the one we got from the Pyruvate DH reaction and then an FADH2 (a lot like NADH, but less reducing power) and an ATP and this is just from ...
Topic guide 5.2: Studying the feasibility of reactions
... reactants which gives a minimum value of Gibbs energy. The formation of this equilibrium mixture from either reactants or products will be feasible, since in both cases the Gibbs energy decreases during the reaction. The sign of ΔGƟ allows us to make predictions about the proportion of products whic ...
... reactants which gives a minimum value of Gibbs energy. The formation of this equilibrium mixture from either reactants or products will be feasible, since in both cases the Gibbs energy decreases during the reaction. The sign of ΔGƟ allows us to make predictions about the proportion of products whic ...
Amino Acid Metabolism (day-2)
... How Do Organisms Synthesize Amino Acids? • Plants and microorganisms can make all 20 amino acids and all other needed N metabolites • In these organisms, glutamate is the source of N, via transamination (aminotransferase) reactions of α-keto acid analogue of the amino acid • Mammals can make only 1 ...
... How Do Organisms Synthesize Amino Acids? • Plants and microorganisms can make all 20 amino acids and all other needed N metabolites • In these organisms, glutamate is the source of N, via transamination (aminotransferase) reactions of α-keto acid analogue of the amino acid • Mammals can make only 1 ...
Phase-I metabolism
... cytochrome P-450 enzymes: • Aliphatic hydroxylation: – Mainly occur on the ultimate (ω) or penultimate (ω-1) carbon atom in the structure. – Also it occurs at an activated carbon atom, that is next to sp , sp2 carbons: ...
... cytochrome P-450 enzymes: • Aliphatic hydroxylation: – Mainly occur on the ultimate (ω) or penultimate (ω-1) carbon atom in the structure. – Also it occurs at an activated carbon atom, that is next to sp , sp2 carbons: ...
Enzymes - دانشکده پزشکی
... According to Holum, the non-protein portion may be: • A coenzyme - a non-protein organic substance which is loosely attached to the protein part. • A prosthetic group - an organic substance which is firmly attached to the protein or apoenzyme portion. • A cofactor - these include K+, Fe++, Fe+++, Cu ...
... According to Holum, the non-protein portion may be: • A coenzyme - a non-protein organic substance which is loosely attached to the protein part. • A prosthetic group - an organic substance which is firmly attached to the protein or apoenzyme portion. • A cofactor - these include K+, Fe++, Fe+++, Cu ...
Groups Basics - Bioinformatics Research Group at SRI International
... reactions catalyzed by the gene product, depending on whether the product of a given gene is an enzyme, and on how many reactions that enzyme catalyzes. Let’s now delete that reaction column before our next example. Now we’ll look at the first way to find related pathways using transformations. Firs ...
... reactions catalyzed by the gene product, depending on whether the product of a given gene is an enzyme, and on how many reactions that enzyme catalyzes. Let’s now delete that reaction column before our next example. Now we’ll look at the first way to find related pathways using transformations. Firs ...
Enzymes: Regulation 1
... Briefly explain the allosteric regulation of ATCase, including its quaternary structure, its role in metabolism, and how its activity is regulated by allosteric inhibition and activation. Include the physiological rationale for the inhibition and activation. Sketch plots of Vo vs. [S] for an alloste ...
... Briefly explain the allosteric regulation of ATCase, including its quaternary structure, its role in metabolism, and how its activity is regulated by allosteric inhibition and activation. Include the physiological rationale for the inhibition and activation. Sketch plots of Vo vs. [S] for an alloste ...
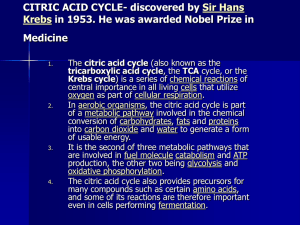
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... Krebs cycle) is a series of chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon ...
... Krebs cycle) is a series of chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon ...
Lecture 26 - Glycolysis 2
... glycerol enter the glycolytic pathway through a variety of routes, many of which require additional enzymatic reactions. For example, fructose is first converted to fructose-1-P which is then cleaved by fructose -1-P aldolase to generate DHAP and glyceraldehyde which is then phosphorylated to produc ...
... glycerol enter the glycolytic pathway through a variety of routes, many of which require additional enzymatic reactions. For example, fructose is first converted to fructose-1-P which is then cleaved by fructose -1-P aldolase to generate DHAP and glyceraldehyde which is then phosphorylated to produc ...
Document
... All the chemical reactions in cytoplasm take place in solution, i.e. in water Water itself takes part in many of these chemical reactions Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
... All the chemical reactions in cytoplasm take place in solution, i.e. in water Water itself takes part in many of these chemical reactions Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
The Chemicals of Living Things
... All the chemical reactions in cytoplasm take place in solution, i.e. in water Water itself takes part in many of these chemical reactions Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
... All the chemical reactions in cytoplasm take place in solution, i.e. in water Water itself takes part in many of these chemical reactions Salts of sodium, potassium and calcium and many others play an important part in these reactions ...
Student notes in ppt
... glycerol enter the glycolytic pathway through a variety of routes, many of which require additional enzymatic reactions. For example, fructose is first converted to fructose-1-P which is then cleaved by fructose -1-P aldolase to generate DHAP and glyceraldehyde which is then phosphorylated to produc ...
... glycerol enter the glycolytic pathway through a variety of routes, many of which require additional enzymatic reactions. For example, fructose is first converted to fructose-1-P which is then cleaved by fructose -1-P aldolase to generate DHAP and glyceraldehyde which is then phosphorylated to produc ...
Detection of the reaction intermediates catalyzed by a copper amine
... microspectroscopy and X-ray crystal structure analysis. From the measurements of UV/vis absorption spectra of the crystals it was found that the two peaks for TPQsq arose during the time course of the experiment, but the spectra for the reaction intermediates could not be observed. However, using X- ...
... microspectroscopy and X-ray crystal structure analysis. From the measurements of UV/vis absorption spectra of the crystals it was found that the two peaks for TPQsq arose during the time course of the experiment, but the spectra for the reaction intermediates could not be observed. However, using X- ...
Check Your Knowledge QuestionSet 2(Download)
... Q.4-A given substrate may be acted upon by a number of different enzymes, each of which uses the same substrate(s) and produces the same product(s). The individual members of a set of enzymes sharing such characteristics are known asa)Group specific enzymes b)Isoenzymes c)Substrate specific enzymes ...
... Q.4-A given substrate may be acted upon by a number of different enzymes, each of which uses the same substrate(s) and produces the same product(s). The individual members of a set of enzymes sharing such characteristics are known asa)Group specific enzymes b)Isoenzymes c)Substrate specific enzymes ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... enzyme specificity (19.5) the ability of an enzyme to bind to only one, or a very few, substrates and thus catalyze only a single reaction. enzyme-substrate complex (19.4) a molecular aggregate formed when the substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme. feedback inhibition (19.9) when produced ...
... enzyme specificity (19.5) the ability of an enzyme to bind to only one, or a very few, substrates and thus catalyze only a single reaction. enzyme-substrate complex (19.4) a molecular aggregate formed when the substrate binds to the active site of the enzyme. feedback inhibition (19.9) when produced ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑