... “designability” has been demonstrated[25] and whose biotechnological relevance has been established.[26] Directed evolution allows us to engineer into this enzyme functions not required or permitted in its natural biological context. For example, a P450 BM-3 variant which efficiently hydroxylates al ...
27. GE_7.27 Gluconeo.. - College of Pharmacy at Howard University
... Hexokinase, which catalyzes the entry of free glucose into the glycolytic pathway, is a regulatory enzyme. There are four isozymes (designated I to IV). Hexokinase II has a high affinity for glucose Muscle hexokinases I and II are allosteric ally inhibited by their product, glucose 6phosphat ...
... Hexokinase, which catalyzes the entry of free glucose into the glycolytic pathway, is a regulatory enzyme. There are four isozymes (designated I to IV). Hexokinase II has a high affinity for glucose Muscle hexokinases I and II are allosteric ally inhibited by their product, glucose 6phosphat ...
Mapping Enzyme Active Sites in Complex Proteomes
... In summary, we report the use of a gel-free version of ABPP to map the sites of probe labeling on enzymes isolated from whole proteomes. In comparing this approach to gel-based ABPP, several advantages of the former method are apparent. First and foremost, gel-free ABPP consolidates into a single st ...
... In summary, we report the use of a gel-free version of ABPP to map the sites of probe labeling on enzymes isolated from whole proteomes. In comparing this approach to gel-based ABPP, several advantages of the former method are apparent. First and foremost, gel-free ABPP consolidates into a single st ...
Intermediary Metabolism Intermediary Metabolism
... and PPY. Their structure, synthesis, related peptides, secretion, regulation, receptors and effects. Effect of exercise on insulin and on ...
... and PPY. Their structure, synthesis, related peptides, secretion, regulation, receptors and effects. Effect of exercise on insulin and on ...
Lecture Notes Ch21
... – The active site has a rigid shape – Only substrates with the matching shape can fit – The substrate is a key that fits the lock of the active site ...
... – The active site has a rigid shape – Only substrates with the matching shape can fit – The substrate is a key that fits the lock of the active site ...
October 12 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... E) weak interactions form between inhibitor and enzyme. ...
... E) weak interactions form between inhibitor and enzyme. ...
Chemistry 20 Chapters 15 Enzymes
... Metal ions: many enzymes must contain a metal ion to carry out their catalytic activity. The metal ions are bonded to one or more of the amino acid side chains. The metal ions from the minerals that we obtain from foods in our diet have various functions in catalysis. Ions such as Fe2+ and Cu2+ are ...
... Metal ions: many enzymes must contain a metal ion to carry out their catalytic activity. The metal ions are bonded to one or more of the amino acid side chains. The metal ions from the minerals that we obtain from foods in our diet have various functions in catalysis. Ions such as Fe2+ and Cu2+ are ...
B324notesTheme 2
... The pathway of glycolysis from glucose-6-phosphate to lactate can be considered as an example of a pathway that can be analysed. Although the key control enzyme is phosphofructokinase, the rate of lactate production is not simply controlled by this enzyme because of the influence of all the othe ...
... The pathway of glycolysis from glucose-6-phosphate to lactate can be considered as an example of a pathway that can be analysed. Although the key control enzyme is phosphofructokinase, the rate of lactate production is not simply controlled by this enzyme because of the influence of all the othe ...
Student notes in ppt
... The majority of acetyl CoA used for fatty acid synthesis in the cytosol is derived from reactions that take place in the mitochondrial matrix. However, mitochondria do not contain an acetyl CoA transporter, therefore a shuttle system, called the citrate shuttle, is required to move the C2 units acro ...
... The majority of acetyl CoA used for fatty acid synthesis in the cytosol is derived from reactions that take place in the mitochondrial matrix. However, mitochondria do not contain an acetyl CoA transporter, therefore a shuttle system, called the citrate shuttle, is required to move the C2 units acro ...
Genes and Enzymes in Man
... orders, the so-called inborn errors of metabolism, are due to titative differences in rates of synthesis, attributable to genes at genetically determined deficiencies of specific enzymes (7). so-called regulator or operator loci, or whether qualitative Quite a large number of these conditions are no ...
... orders, the so-called inborn errors of metabolism, are due to titative differences in rates of synthesis, attributable to genes at genetically determined deficiencies of specific enzymes (7). so-called regulator or operator loci, or whether qualitative Quite a large number of these conditions are no ...
Ch t 19 apter 19 The Citric Acid Cycle
... • The catabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fatty acids all feed into the citric acid cycle at one or more points Protein Protein ...
... • The catabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fatty acids all feed into the citric acid cycle at one or more points Protein Protein ...
Coenzymes and Cofactors (PDF Available)
... of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving complex (Hoganson and Babcock, 1997), have been proposed to initiate catalysis in similar ways, via initial H atom abstraction from the substrate. ...
... of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving complex (Hoganson and Babcock, 1997), have been proposed to initiate catalysis in similar ways, via initial H atom abstraction from the substrate. ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
citric acid cycle
... 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate onto ADP, forming ATP (substrate-level phosphorylation) and 3phosphoglycerate. Since two molecules of triose phosphate are formed per molecule of glucose, two molecules of ATP are generated at this stage per molecule of glucose undergoing glycolysis. 8- 3-Phosphoglycerate is ...
... 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate onto ADP, forming ATP (substrate-level phosphorylation) and 3phosphoglycerate. Since two molecules of triose phosphate are formed per molecule of glucose, two molecules of ATP are generated at this stage per molecule of glucose undergoing glycolysis. 8- 3-Phosphoglycerate is ...
COURSE SYLLABUS CHM 521 Biochemistry I 3(3
... Nucleotide structure Amino acid structure Amino acid properties and peptides Protein function and classification Protein purification and sequencing Structure of fibrous proteins; collagen Structure of globular proteins Hemoglobin and immunoglobulins ...
... Nucleotide structure Amino acid structure Amino acid properties and peptides Protein function and classification Protein purification and sequencing Structure of fibrous proteins; collagen Structure of globular proteins Hemoglobin and immunoglobulins ...
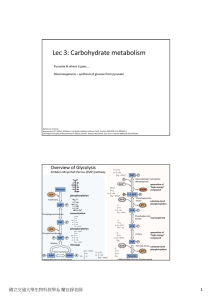
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... When O2 is present, respiration takes place. NADH generated passes its electrons onto O2, forming water. ...
... When O2 is present, respiration takes place. NADH generated passes its electrons onto O2, forming water. ...
Metabolic network modelling

Metabolic network reconstruction and simulation allows for an in-depth insight into the molecular mechanisms of a particular organism. In particular, these models correlate the genome with molecular physiology. A reconstruction breaks down metabolic pathways (such as glycolysis and the Citric acid cycle) into their respective reactions and enzymes, and analyzes them within the perspective of the entire network. In simplified terms, a reconstruction collects all of the relevant metabolic information of an organism and compiles it in a mathematical model. Validation and analysis of reconstructions can allow identification of key features of metabolism such as growth yield, resource distribution, network robustness, and gene essentiality. This knowledge can then be applied to create novel biotechnology.In general, the process to build a reconstruction is as follows: Draft a reconstruction Refine the model Convert model into a mathematical/computational representation Evaluate and debug model through experimentation↑