Cognitive Dissonance and Group Interaction
... Social facilitation – the presence of others enhance performance (competitions, recitals, plays, speeches) Social loafing – the presence of others diminishes performance (group project) Deindividuation – the presence of others makes one act in unrestrained ways (fans at sports event) ...
... Social facilitation – the presence of others enhance performance (competitions, recitals, plays, speeches) Social loafing – the presence of others diminishes performance (group project) Deindividuation – the presence of others makes one act in unrestrained ways (fans at sports event) ...
Module 9: Group Dynamics Lecture 36: Social facilitation
... presentation could lead to social facilitation. For example, Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman (1969) noted that among animals, including insects, social facilitation could be observed. Since it may be difficult to assume that animals care for evaluation apprehension or self-presentation, these factor m ...
... presentation could lead to social facilitation. For example, Zajonc, Heingartner, & Herman (1969) noted that among animals, including insects, social facilitation could be observed. Since it may be difficult to assume that animals care for evaluation apprehension or self-presentation, these factor m ...
Social Psychology
... YOU THINK TO YOURSELF, “WOW, THIS FLOOR IS UNEVEN AND DANGEROUS, SOMEONE SHOULD FIX IT!” THIS ILLUSTRATES THE PSYCHOLOGICAL CONCEPT CALLED: A. B. C. D. ...
... YOU THINK TO YOURSELF, “WOW, THIS FLOOR IS UNEVEN AND DANGEROUS, SOMEONE SHOULD FIX IT!” THIS ILLUSTRATES THE PSYCHOLOGICAL CONCEPT CALLED: A. B. C. D. ...
Social Psychology Key Terms 1. Social Norms 2. Asch Effect 3
... This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., ...
... This part of the course focuses on how individuals relate to one another in social situations. Social psychologists study social attitudes, social influence, and other social phenomena. AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., ...
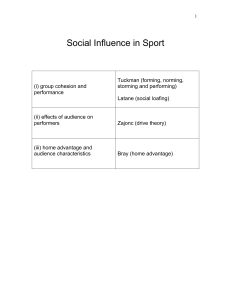
f) Social influence in sport
... • for complex tasks the dominant response will be incorrect due to over-arousal and will thus lead to a decline in performance. However many psychologists nowadays believe that drive theory is too simplistic. According to the inverted U hypothesis of arousal, the presence of others may enhance perfo ...
... • for complex tasks the dominant response will be incorrect due to over-arousal and will thus lead to a decline in performance. However many psychologists nowadays believe that drive theory is too simplistic. According to the inverted U hypothesis of arousal, the presence of others may enhance perfo ...
Understanding ourselves
... Cognitive dissonance • What happens when your actions are inconsistent with your beliefs? – Doomsday cults – Festinger’s boring tasks ...
... Cognitive dissonance • What happens when your actions are inconsistent with your beliefs? – Doomsday cults – Festinger’s boring tasks ...
Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) Apply attribution theory to
... Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) 1. Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). ...
... Unit 14. Social Psychology (8–10%) 1. Apply attribution theory to explain motives (e.g., fundamental attribution error, self-serving bias). ...
Group Influences PowerPoint
... How can being in the presence of others: Motivate people to exert themselves or tempt them to free-ride on the efforts of others. Make easy tasks easier and difficult tasks harder Enhance humor or fuel mob violence ...
... How can being in the presence of others: Motivate people to exert themselves or tempt them to free-ride on the efforts of others. Make easy tasks easier and difficult tasks harder Enhance humor or fuel mob violence ...
Social Influences on Behavior
... that are most dominant (the ones we know best) – Improves performance for easy, familiar tasks – Performance may suffer for hard, unfamiliar tasks ...
... that are most dominant (the ones we know best) – Improves performance for easy, familiar tasks – Performance may suffer for hard, unfamiliar tasks ...
Social Influences on Behavior
... – Exerting less effort when performing a group task than when performing the same task alone – Harder to evaluate the performance of individuals when in group – Rewards may come to group regardless of individual giving more ...
... – Exerting less effort when performing a group task than when performing the same task alone – Harder to evaluate the performance of individuals when in group – Rewards may come to group regardless of individual giving more ...