Acid Base Equilibria
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
... Weak acid: one that only partially dissociates in aqueous solution and therefore exists in the solution as a mixture of acid molecules component ions: For example, HF dissociates in water to give H+ and F-. It is a weak acid with a dissociation equation that is HF (aq) ↔ H+ (aq) + F-(aq) Note the us ...
Characterization of Lamprey Fibrinopeptides
... Alkaline hydrolysis was conducted in 0-2 M-Ba(OH)2 at 115-120° for 20 hr. The Ba(OH)2 solution was made up with hot water and filtered with a stemless funnel just before use. Tubes were sealed immediately. The hydrolysate (usually 50 ,ul.) was applied directly to the paperelectrophoresis strips for ...
... Alkaline hydrolysis was conducted in 0-2 M-Ba(OH)2 at 115-120° for 20 hr. The Ba(OH)2 solution was made up with hot water and filtered with a stemless funnel just before use. Tubes were sealed immediately. The hydrolysate (usually 50 ,ul.) was applied directly to the paperelectrophoresis strips for ...
32_Metabolism of ammonia. Biosynthesis of urea and its disorders
... Hypotheses toxicity of ammonia A. The binding of ammonia in the synthesis of glutamate causes an outflow of α-ketoglutarate from the tricarboxylic acid cycle, with decreased formation of ATP energy and deteriorates the activity of cells. B. Ammonium ions NH4 + caused alkalization of blood plasma. Th ...
... Hypotheses toxicity of ammonia A. The binding of ammonia in the synthesis of glutamate causes an outflow of α-ketoglutarate from the tricarboxylic acid cycle, with decreased formation of ATP energy and deteriorates the activity of cells. B. Ammonium ions NH4 + caused alkalization of blood plasma. Th ...
Enzymes - Land of Mayo
... tryptophan binds to enzyme used in tryptophan production this binding changes the shape of the enzyme and this inactivates the enzyme no more tryptophan is produced if there is too little tryptophan the enzyme is free to make more tryptophan ...
... tryptophan binds to enzyme used in tryptophan production this binding changes the shape of the enzyme and this inactivates the enzyme no more tryptophan is produced if there is too little tryptophan the enzyme is free to make more tryptophan ...
Ch6-4_Enzymes-New
... Located on the p arm of chromosome 1 in humans, this gene codes for an enzyme involved in the methylation of folic acid, a necessary B vitamin. Methylated (folate) and non-methylated (folic acid) forms are found in leafy greens, beans, and whole grains. ...
... Located on the p arm of chromosome 1 in humans, this gene codes for an enzyme involved in the methylation of folic acid, a necessary B vitamin. Methylated (folate) and non-methylated (folic acid) forms are found in leafy greens, beans, and whole grains. ...
Examination 2: Chapters 8 through 11
... Oxidation of cystine to form 2 cysteine molecules Reduction of cystine to form carboxyl groups which would be more soluble Reduction of methionine in the diet, since this is a precursor to the synthesis of cysteine Feeding of reduced glutathione, since this will oxidize cystine Forming a salt bond b ...
... Oxidation of cystine to form 2 cysteine molecules Reduction of cystine to form carboxyl groups which would be more soluble Reduction of methionine in the diet, since this is a precursor to the synthesis of cysteine Feeding of reduced glutathione, since this will oxidize cystine Forming a salt bond b ...
Water Soluble Vitamin
... • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid and Folate inclusive) is essential to numerous bodily functions ranging from nucleotide synthesis to the remethylation of homocysteine. • It is especially important during periods of rapid cell division and growth. • Both children and adults require folic acid to produce hea ...
... • Vitamin B9 (Folic acid and Folate inclusive) is essential to numerous bodily functions ranging from nucleotide synthesis to the remethylation of homocysteine. • It is especially important during periods of rapid cell division and growth. • Both children and adults require folic acid to produce hea ...
Quantitative analysis of complex amino acids and RGD peptides by
... polysaccharides and lipids through the spectral contrast arising from differences in elemental composition and characteristic functional groups [10,11] Indeed, XPS has been used to characterize RGD-modified surfaces.[12-16] We have recently examined Schwann cell response on the surfaces of poly--ca ...
... polysaccharides and lipids through the spectral contrast arising from differences in elemental composition and characteristic functional groups [10,11] Indeed, XPS has been used to characterize RGD-modified surfaces.[12-16] We have recently examined Schwann cell response on the surfaces of poly--ca ...
Adenylate Energy Charge during Batch Culture of
... prokaryotes (Rickenberg, 1974). Cyclic AMP levels are involved in the control of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme synthesis (Takahashi, I 975) and various membrane-associated phenomena (see Patrick & Dobrogosz, I 973) including cytochrome synthesis (Broman, Dobrogosz & White, 197& membrane transport ...
... prokaryotes (Rickenberg, 1974). Cyclic AMP levels are involved in the control of tricarboxylic acid cycle enzyme synthesis (Takahashi, I 975) and various membrane-associated phenomena (see Patrick & Dobrogosz, I 973) including cytochrome synthesis (Broman, Dobrogosz & White, 197& membrane transport ...
Oxidation of fatty acids in eukaryotes
... of different chain lengths [7]. Their chain-length specificities are the basis for classifying these enzymes as short-chain, medium-chain, long-chain and very-long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases. A short-chain-specific acetyl-CoA synthetase that is present in mammalian mitochondria has been purified and ...
... of different chain lengths [7]. Their chain-length specificities are the basis for classifying these enzymes as short-chain, medium-chain, long-chain and very-long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases. A short-chain-specific acetyl-CoA synthetase that is present in mammalian mitochondria has been purified and ...
BioN04 Enzymes 2015 v2
... cellular compartments • For example, lysosomes contain many of the proteolytic enzymes responsible for protein degradation • Another example, synthesis of fatty acids are located in cytosol, whereas enzymes responsible for oxidation (break-sown) of fatty acids are located in the mitochondria ...
... cellular compartments • For example, lysosomes contain many of the proteolytic enzymes responsible for protein degradation • Another example, synthesis of fatty acids are located in cytosol, whereas enzymes responsible for oxidation (break-sown) of fatty acids are located in the mitochondria ...
Chapter 9
... • growth depression can be overcome by supplementation with an amino acids structurally similar to the antagonist • Ex: lysine and Arginine. (structure similar) • Excess of lysine→ growth depress →improve by addition of arginine • Antagonist differ from imbalance of amino acids ...
... • growth depression can be overcome by supplementation with an amino acids structurally similar to the antagonist • Ex: lysine and Arginine. (structure similar) • Excess of lysine→ growth depress →improve by addition of arginine • Antagonist differ from imbalance of amino acids ...
1. Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. In the small intestine, it is
... The diagram shows the events that occur in the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids. These molecules enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine by diffusion. Once inside they are reassembled into triglycerides in organelle Q. The triglyceride molecules are formed into chylomicrons in ...
... The diagram shows the events that occur in the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids. These molecules enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine by diffusion. Once inside they are reassembled into triglycerides in organelle Q. The triglyceride molecules are formed into chylomicrons in ...
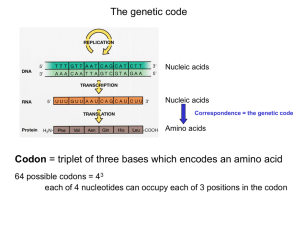
Codon - Cloudfront.net
... DNA and Translation • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
... DNA and Translation • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
Threonine Metabolism via Two-carbon Compounds
... by Pseudomonas oxalaticus via acetyl-CoA glycine rather than aminoacetone. Threoninegrown bacteria adapted to growth on acetate+glycine medium without a lag and rapidly oxidized an equimolar mixture of these compounds. It appeared likely that acetyl-CoA was oxidized via the TCA cycle and that glycin ...
... by Pseudomonas oxalaticus via acetyl-CoA glycine rather than aminoacetone. Threoninegrown bacteria adapted to growth on acetate+glycine medium without a lag and rapidly oxidized an equimolar mixture of these compounds. It appeared likely that acetyl-CoA was oxidized via the TCA cycle and that glycin ...
ATP regulation in bioproduction
... of ATP-generating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck) from Actinobacillus succinogenes in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli effectively enhances cell growth and succinic acid production [27] (Fig. 3). Further, succinic acid production by Enterobacter aerogenes is enhanced using a similar stra ...
... of ATP-generating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck) from Actinobacillus succinogenes in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli effectively enhances cell growth and succinic acid production [27] (Fig. 3). Further, succinic acid production by Enterobacter aerogenes is enhanced using a similar stra ...
ATP regulation in bioproduction
... of ATP-generating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck) from Actinobacillus succinogenes in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli effectively enhances cell growth and succinic acid production [27] (Fig. 3). Further, succinic acid production by Enterobacter aerogenes is enhanced using a similar stra ...
... of ATP-generating phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck) from Actinobacillus succinogenes in a mutant strain of Escherichia coli effectively enhances cell growth and succinic acid production [27] (Fig. 3). Further, succinic acid production by Enterobacter aerogenes is enhanced using a similar stra ...
AUG
... wobble hypothesis: the pairing between codon and anticodon at the first two codon positions always follows the usual rules, but exceptional “wobbles” occur at the third position Base in first position Base recognized in third of anticodon position of codon U A/G C G A U G C/U ...
... wobble hypothesis: the pairing between codon and anticodon at the first two codon positions always follows the usual rules, but exceptional “wobbles” occur at the third position Base in first position Base recognized in third of anticodon position of codon U A/G C G A U G C/U ...
Citric acid cycle
The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle – is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids as well as the reducing agent NADH that is used in numerous other biochemical reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest established components of cellular metabolism and may have originated abiogenically.The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from citric acid (a type of tricarboxylic acid) that is consumed and then regenerated by this sequence of reactions to complete the cycle. In addition, the cycle consumes acetate (in the form of acetyl-CoA) and water, reduces NAD+ to NADH, and produces carbon dioxide as a waste byproduct. The NADH generated by the TCA cycle is fed into the oxidative phosphorylation (electron transport) pathway. The net result of these two closely linked pathways is the oxidation of nutrients to produce usable chemical energy in the form of ATP.In eukaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria which lack mitochondria, the TCA reaction sequence is performed in the cytosol with the proton gradient for ATP production being across the cell's surface (plasma membrane) rather than the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.