Fast CMT
... There are three main types of earthquakes. Normal faulting events that happen due to the Earth’s crust being extended and pulled apart, thrust faulting events that happen due to compression, and lateral events which happen because of two plates sliding past each other. All three of these events are ...
... There are three main types of earthquakes. Normal faulting events that happen due to the Earth’s crust being extended and pulled apart, thrust faulting events that happen due to compression, and lateral events which happen because of two plates sliding past each other. All three of these events are ...
Earthquakes - Cal State LA
... northeastward and the Eurasian plate (Asia) squeezing it from the west. ...
... northeastward and the Eurasian plate (Asia) squeezing it from the west. ...
Earthquakes
... Earthquakes Epicenter - The point directly above the focus or source of the earthquake. (Often described using the largest nearby city) Magnitude - Amount of energy released from the earthquake. (Often described using a number) ...
... Earthquakes Epicenter - The point directly above the focus or source of the earthquake. (Often described using the largest nearby city) Magnitude - Amount of energy released from the earthquake. (Often described using a number) ...
An Earthquake
... The world has seen many disasters over the years. It's very difficult to rank them because there are different ways of defining "worst" some would just count the dead, others would include the injured. These disasters take a lot of lives every year. An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of ...
... The world has seen many disasters over the years. It's very difficult to rank them because there are different ways of defining "worst" some would just count the dead, others would include the injured. These disasters take a lot of lives every year. An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of ...
Earthquakes 1. How is most of the energy of an earthquake
... I. the distance of the region from the epicenter II. the distance of the region from a seismic detection station III. the type of construction in the region ...
... I. the distance of the region from the epicenter II. the distance of the region from a seismic detection station III. the type of construction in the region ...
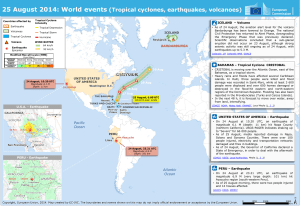
25 August 2014: World events (Tropical cyclones, earthquakes
... • Heavy rains and floods have affected several Caribbean islands. In Haiti, three people were killed and flood damage was recorded in Saint-Marc, while at least 3 600 people were displaced and over 600 homes damaged or destroyed in the flood-hit eastern and north-eastern regions of the Dominican Rep ...
... • Heavy rains and floods have affected several Caribbean islands. In Haiti, three people were killed and flood damage was recorded in Saint-Marc, while at least 3 600 people were displaced and over 600 homes damaged or destroyed in the flood-hit eastern and north-eastern regions of the Dominican Rep ...
What is an Earthquake? - Live it, breathe it, love GEOGRAPHY
... • An earthquake is the shaking and vibration of the Earth's crust due to movement of the Earth's plates (plate tectonics). Earthquakes can happen along any type of plate boundary ...
... • An earthquake is the shaking and vibration of the Earth's crust due to movement of the Earth's plates (plate tectonics). Earthquakes can happen along any type of plate boundary ...
Good Friday Earthquake Katie Puthoff and Gwen Harpring
... • This earthquake was the second largest earthquake ever recorded in world history, leaving Anchorage in ruins. • There were almost 10,000 aftershocks of the quake that lasted for 18 months after the disaster. ...
... • This earthquake was the second largest earthquake ever recorded in world history, leaving Anchorage in ruins. • There were almost 10,000 aftershocks of the quake that lasted for 18 months after the disaster. ...
April 2015 Nepal earthquake

The April 2015 Nepal earthquake (also known as the Gorkha earthquake) killed more than 9,000 people and injured more than 23,000. It occurred at 11:56 NST on 25 April, with a magnitude of 7.8Mw or 8.1Ms and a maximum Mercalli Intensity of IX (Violent). Its epicenter was east of the district of Lamjung, and its hypocenter was at a depth of approximately 8.2 km (5.1 mi). It was the worst natural disaster to strike Nepal since the 1934 Nepal–Bihar earthquake.The earthquake triggered an avalanche on Mount Everest, killing at least 19, making April 25, 2015 the deadliest day on the mountain in history. The earthquake triggered another huge avalanche in the Langtang valley, where 250 people were reported missing.Hundreds of thousands of people were made homeless with entire villages flattened, across many districts of the country. Centuries-old buildings were destroyed at UNESCO World Heritage sites in the Kathmandu Valley, including some at the Kathmandu Durbar Square, the Patan Durbar Square, the Bhaktapur Durbar Square, the Changu Narayan Temple and the Swayambhunath Stupa. Geophysicists and other experts had warned for decades that Nepal was vulnerable to a deadly earthquake, particularly because of its geology, urbanization, and architecture.Continued aftershocks occurred throughout Nepal at the intervals of 15–20 minutes, with one shock reaching a magnitude of 6.7 on 26 April at 12:54:08 NST. The country also had a continued risk of landslides.A major aftershock occurred on 12 May 2015 at 12:51 NST with a moment magnitude (Mw) of 7.3. The epicenter was near the Chinese border between the capital of Kathmandu and Mt. Everest. More than 200 people were killed and more than 2,500 were injured by this aftershock.