Mesopotamian Civilizations
... – The first known civilization arose in Mesopotamia, and its culture and innovations influenced later civilizations in the region for thousands of years. ...
... – The first known civilization arose in Mesopotamia, and its culture and innovations influenced later civilizations in the region for thousands of years. ...
From Out of the Mesopotamian Mud
... unknowable, and their actions roots back to the ancient Sumerians and Babylonians. They construct floating islands of reeds on which to put their houses, which are also made of reeds. Reeds have many other uses as were arbitrary and scary well: mats and baskets (a source of cash income), fodder for ...
... unknowable, and their actions roots back to the ancient Sumerians and Babylonians. They construct floating islands of reeds on which to put their houses, which are also made of reeds. Reeds have many other uses as were arbitrary and scary well: mats and baskets (a source of cash income), fodder for ...
the fertile crescent 2012
... human development? • What cultural and scientific achievements make the Fertile Crescent important? • Who were the People who conquered this region, how did they change the culture? ...
... human development? • What cultural and scientific achievements make the Fertile Crescent important? • Who were the People who conquered this region, how did they change the culture? ...
The Rise of the River Valley Civilizations
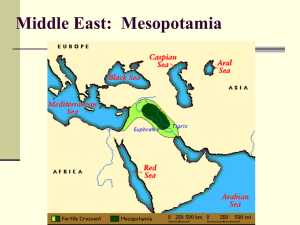
... civilization developed between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Most historians call the land Mesopotamia. This is the first known civilization. ...
... civilization developed between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Most historians call the land Mesopotamia. This is the first known civilization. ...
Mesopotamia and Hammurabi*s Code
... • The two rivers The Tigris and the Euphrates flow southeastward towards the Persian Gulf • When they flooded it would fertilize the ground making optimal ground for farming ...
... • The two rivers The Tigris and the Euphrates flow southeastward towards the Persian Gulf • When they flooded it would fertilize the ground making optimal ground for farming ...
7000 BC Agriculture first develops in Mesopotamia 3000 BC Several
... Peace was broke between Sumer and Sargon when Sargon sought to extend Akkadian territory. Sargon’s soldiers defeated all of the city-states of Sumer. Sargon established the world’s first empire 1770 BC Hammurabi of Babylon issues a written code of laws 1800 BC-1792 BC Babylon (a Sumerian town) has a ...
... Peace was broke between Sumer and Sargon when Sargon sought to extend Akkadian territory. Sargon’s soldiers defeated all of the city-states of Sumer. Sargon established the world’s first empire 1770 BC Hammurabi of Babylon issues a written code of laws 1800 BC-1792 BC Babylon (a Sumerian town) has a ...
Mesopotamia - Badantweb.com
... •The Akkadians came from the Arabic peninsula •The Akkadians migrated north into the Sumerian city-states •In 2340 BC, the military leader, Sargon, conquered Sumer and built an empire •It was the largest empire humans great Akkadian had ever seen up until that point. •It later became the city of Bab ...
... •The Akkadians came from the Arabic peninsula •The Akkadians migrated north into the Sumerian city-states •In 2340 BC, the military leader, Sargon, conquered Sumer and built an empire •It was the largest empire humans great Akkadian had ever seen up until that point. •It later became the city of Bab ...
Mesopotamia
... •The Akkadians came from the Arabic peninsula •The Akkadians migrated north into the Sumerian city-states •In 2340 BC, the military leader, Sargon, conquered Sumer and built an empire •It was the largest empire humans great Akkadian had ever seen up until that point. •It later became the city of Bab ...
... •The Akkadians came from the Arabic peninsula •The Akkadians migrated north into the Sumerian city-states •In 2340 BC, the military leader, Sargon, conquered Sumer and built an empire •It was the largest empire humans great Akkadian had ever seen up until that point. •It later became the city of Bab ...
Early Civilizations
... – Au was the god of sky. – Enil was the god of wind. – Enki was the god of earth and ...
... – Au was the god of sky. – Enil was the god of wind. – Enki was the god of earth and ...
Mesopotamia PowerPoint Notes
... Dates were also very valuable to the Sumerians. They were eaten once ripe or else they were dried for future consumption. Dates also made an excellent wine. ...
... Dates were also very valuable to the Sumerians. They were eaten once ripe or else they were dried for future consumption. Dates also made an excellent wine. ...
Mesopotamia Study Guide
... 5. Identify and explain the powers of the following gods/goddesses/demons: Pazuzu, Anu, Enlil, Utu/Shamash, and Inanna/Ishtar and Marduk. ...
... 5. Identify and explain the powers of the following gods/goddesses/demons: Pazuzu, Anu, Enlil, Utu/Shamash, and Inanna/Ishtar and Marduk. ...
1 st
... • bellowed like a wild bull, and the great god was aroused by the clamour. Enlil heard the clamour and he said to the gods in • council, "The uproar of mankind is intolerable and sleep is no longer possible by reason of the babel." So the gods agreed • to exterminate mankind. Enlil did this, but Ea ...
... • bellowed like a wild bull, and the great god was aroused by the clamour. Enlil heard the clamour and he said to the gods in • council, "The uproar of mankind is intolerable and sleep is no longer possible by reason of the babel." So the gods agreed • to exterminate mankind. Enlil did this, but Ea ...
lesson - mesopotamia
... – These areas could support the farming and survival needs for many people. ...
... – These areas could support the farming and survival needs for many people. ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.