PowerPoint Presentation - Mesopotamia
... the southern part of Mesopotamia. They created bricks to build structures. Trade brought riches to Sumerian cities. The Sumerians were the first to make wheeled vehicles. In each Sumerian city-state, the ruler was responsible for maintaining the city walls and irrigations systems. Each Sumeria ...
... the southern part of Mesopotamia. They created bricks to build structures. Trade brought riches to Sumerian cities. The Sumerians were the first to make wheeled vehicles. In each Sumerian city-state, the ruler was responsible for maintaining the city walls and irrigations systems. Each Sumeria ...
Social Studies: Chapter 4 lesson 1 Class Notes
... The writing system they developed was the earliest know system in the world They created a way of writing called cuneiform Only a few people – mostly wealthy boys – learned how to read and write Some became scribes = official record keepers The world’s oldest known story is from Sumer= Epic of Gilga ...
... The writing system they developed was the earliest know system in the world They created a way of writing called cuneiform Only a few people – mostly wealthy boys – learned how to read and write Some became scribes = official record keepers The world’s oldest known story is from Sumer= Epic of Gilga ...
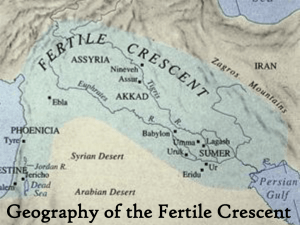
Fertile Crescent
... systems, wheeled vehicles, the potter’s wheel, and sailboats. • The invention of the wheel greatly helped trade as they could now use horse powered carts to move goods, and helped in battle with the use of war chariots. The wheel also helped them travel greater distances than they could only on foot ...
... systems, wheeled vehicles, the potter’s wheel, and sailboats. • The invention of the wheel greatly helped trade as they could now use horse powered carts to move goods, and helped in battle with the use of war chariots. The wheel also helped them travel greater distances than they could only on foot ...
Mesopotamia/Sumer
... Came from Central Asia or Asia Minor (were IndoEuropeans) Settled in the lower part of Fertile Crescent – a.k.a. Sumer Birthplace of cities Created 12 city-states ...
... Came from Central Asia or Asia Minor (were IndoEuropeans) Settled in the lower part of Fertile Crescent – a.k.a. Sumer Birthplace of cities Created 12 city-states ...
Web Quest on Mesopotamia and Gilgamesh
... Go to the following website to answer the following questions: http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/ 1. What does the word Mesopotamia in ancient Greek mean? 2. What two great rivers are found in Mesopotamia? 3. The three distinct regions of Mesopotamia were called what? 4. In addition to providing the king ...
... Go to the following website to answer the following questions: http://www.mesopotamia.co.uk/ 1. What does the word Mesopotamia in ancient Greek mean? 2. What two great rivers are found in Mesopotamia? 3. The three distinct regions of Mesopotamia were called what? 4. In addition to providing the king ...
Chapter 3 Mesopotamia Study guide - 6th Grade History
... of our worksheets on there so you can practice filling them out again to help you study. If you have any questions while you are studying, please feel free to email me at [email protected] and I will get back to you as soon as I can! ...
... of our worksheets on there so you can practice filling them out again to help you study. If you have any questions while you are studying, please feel free to email me at [email protected] and I will get back to you as soon as I can! ...
Source 2
... another. Major cities included Eridu, Uruk, Ur, and Lagash. Uruk was one of the largest cities; at one time it may have had 80,000 people living in and around the city. This time period began a great human migration from the countryside into the city. Mesopotamia invented new technology. They were t ...
... another. Major cities included Eridu, Uruk, Ur, and Lagash. Uruk was one of the largest cities; at one time it may have had 80,000 people living in and around the city. This time period began a great human migration from the countryside into the city. Mesopotamia invented new technology. They were t ...
Mesopotamia Study Guide
... Important Civilizations of Mesopotamia Know the differences amongst these civilizations and the major advances or achievements they were responsible for: ...
... Important Civilizations of Mesopotamia Know the differences amongst these civilizations and the major advances or achievements they were responsible for: ...
City-States in Mesopotamia
... Goal: Appease gods to control nature Art and literature focus on gods and religion Epic of Gilgamesh ...
... Goal: Appease gods to control nature Art and literature focus on gods and religion Epic of Gilgamesh ...
Test Three: Mesopotamia Study Guide
... 1. True or False: The first civilizations in Mesopotamia began on the plain between the Euphrates River and the Mediterranean Sea? 2. What technologies/methods did Mesopotamian farmers use to control the seasonal floods AND keep their crops watered during the summer and fall? 3. How was seasonal flo ...
... 1. True or False: The first civilizations in Mesopotamia began on the plain between the Euphrates River and the Mediterranean Sea? 2. What technologies/methods did Mesopotamian farmers use to control the seasonal floods AND keep their crops watered during the summer and fall? 3. How was seasonal flo ...
World H - Mesopotamia - HFAWorldHistory-Kos
... – Believed to have invented the first battering ram – Also devised an early form of relaying messages through the empire ...
... – Believed to have invented the first battering ram – Also devised an early form of relaying messages through the empire ...
AP World History
... Mesopotamia Civilization Civilization Cultural hearths Mesopotamia Semitic Sumerians city-states Akkadians Empire (Sargon I) Cultural diffusion Fertile Crescent Theocracies Hammurabi Babylonians Hittites Assyrians New Babylonians: Chaldeans Hammurabi’s Code / “marker event” Cuneiform The Epic of Gil ...
... Mesopotamia Civilization Civilization Cultural hearths Mesopotamia Semitic Sumerians city-states Akkadians Empire (Sargon I) Cultural diffusion Fertile Crescent Theocracies Hammurabi Babylonians Hittites Assyrians New Babylonians: Chaldeans Hammurabi’s Code / “marker event” Cuneiform The Epic of Gil ...
HERBERT MASON`S verse translation
... 7th millennium: Tiny settlements start to grow into villages. 4th millennium: Irrigation agriculture of southern Mesopotamia is starting to be developed; some of the villages start to grow into cities: Eridu and Uruk were among the first. Around 3500: City-states in southern Mesopotamia develop, and ...
... 7th millennium: Tiny settlements start to grow into villages. 4th millennium: Irrigation agriculture of southern Mesopotamia is starting to be developed; some of the villages start to grow into cities: Eridu and Uruk were among the first. Around 3500: City-states in southern Mesopotamia develop, and ...
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia (/ˌmɛsəpəˈteɪmiə/, from the Ancient Greek: Μεσοποταμία ""[land] between rivers""; Arabic: بلاد الرافدين bilād ar-rāfidayn; Persian: میانرودان miyān rodān; Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪܝܢ Beth Nahrain ""land of rivers"") is a name for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, corresponding to modern-day Iraq, Kuwait, the northeastern section of Syria, as well as parts of southeastern Turkey and of southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization by the Western world, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires, all native to the territory of modern-day Iraq. In the Iron Age, it was controlled by the Neo-Assyrian and Neo-Babylonian Empires. The indigenous Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BC) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire.Around 150 BC, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In AD 226, it fell to the Sassanid Persians and remained under Persian rule until the 7th century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire. A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BC and 3rd century AD, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra.