Test 3
... Bonds between molecules Forces must be overcome to change phase Dipole-Dipole Between polar covalent molecules Hydrogen bonding Between polar molecules where hydrogen is bonded to a very E.N. atom (F, O, N) Strongest intermolecular force Creates higher MP/BP temps Van der Waals Forces (the weak forc ...
... Bonds between molecules Forces must be overcome to change phase Dipole-Dipole Between polar covalent molecules Hydrogen bonding Between polar molecules where hydrogen is bonded to a very E.N. atom (F, O, N) Strongest intermolecular force Creates higher MP/BP temps Van der Waals Forces (the weak forc ...
PROBLEMS FOR CHAPTER 10: Distributed Energy Resources 1
... a. Find the annual cost of electricity for the computer and its associated air conditioning. b. Find the electricity cost per kWh used by the computer. Compare that with the 10¢/kWh cost of electric energy. 6. A solar pond consists of a thin layer of fresh water floating on top of a denser layer of ...
... a. Find the annual cost of electricity for the computer and its associated air conditioning. b. Find the electricity cost per kWh used by the computer. Compare that with the 10¢/kWh cost of electric energy. 6. A solar pond consists of a thin layer of fresh water floating on top of a denser layer of ...
Too Hot to Handle, Too Cold to Hold
... 1) For “high” temperature applications, gas saves 67% on energy and cost. (Hotter than you want to touch). 2) For space/water heating, we have an excess of waste heat from power plants and an abundance of geothermal heat. 3) To fill in gaps and further reduce costs, integrated renewables (wind/solar ...
... 1) For “high” temperature applications, gas saves 67% on energy and cost. (Hotter than you want to touch). 2) For space/water heating, we have an excess of waste heat from power plants and an abundance of geothermal heat. 3) To fill in gaps and further reduce costs, integrated renewables (wind/solar ...
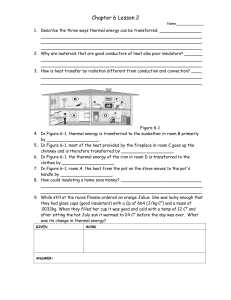
Chapter 6 Lesson 2 Name_____________ Describe the three ways
... In Figure 6-1, thermal energy is transferred to the sunbather in room B primarily by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, most of the heat provided by the fireplace in room C goes up the chimney and is therefore transferred by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, the thermal energy of the iron in ro ...
... In Figure 6-1, thermal energy is transferred to the sunbather in room B primarily by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, most of the heat provided by the fireplace in room C goes up the chimney and is therefore transferred by ____________________. In Figure 6-1, the thermal energy of the iron in ro ...
Chapter 2
... Energy must be put into the system to surpass the boiling point of a liquid. Energy may be released when going down the phase diagram, that is from vapor to liquid, etc. ...
... Energy must be put into the system to surpass the boiling point of a liquid. Energy may be released when going down the phase diagram, that is from vapor to liquid, etc. ...
Answers to Weather Questions pages 427 - 434
... rivers, and streams. Some sinks into the ground, as ground water. Plants absorb the water through their roots and send it back to the air by means of their leaves in the process called transpiration. The water in the lakes, rivers, and streams evaporates to form clouds again. This is called the wate ...
... rivers, and streams. Some sinks into the ground, as ground water. Plants absorb the water through their roots and send it back to the air by means of their leaves in the process called transpiration. The water in the lakes, rivers, and streams evaporates to form clouds again. This is called the wate ...
Document
... Heat ducts inside heated area Install dehumidifier Heat pump Continuous soffit vents ...
... Heat ducts inside heated area Install dehumidifier Heat pump Continuous soffit vents ...
Science 10 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... which highly energetic particles collide with less energetic particles, giving them some energy. ...
... which highly energetic particles collide with less energetic particles, giving them some energy. ...
Specific Heat Capacity - Tasker Milward
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
... Specific Heat Capacity • The specific heat capacity is the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1˚C • We will calculate the specific heat capacity of water by heating it with an electrical heater and measuring the energy required for a fixed temperature ris ...
Thermodynamic Efficiency Energy Conversion Efficiency Ideal Gas
... – For a heat engine, useful work out is always less than the available energy input ...
... – For a heat engine, useful work out is always less than the available energy input ...
Heat and the Conservation of Energy
... Thermal conduction is when heat is passed along as the motion of one atom does work on an adjacent Conductors are materials that atom making it move conduct heat quickly Metals are good thermal conductors Ceramics, fiberglass etc do not, they are thermal insulators Liquids and Gases are good insulat ...
... Thermal conduction is when heat is passed along as the motion of one atom does work on an adjacent Conductors are materials that atom making it move conduct heat quickly Metals are good thermal conductors Ceramics, fiberglass etc do not, they are thermal insulators Liquids and Gases are good insulat ...
ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
... The reverse process will not occur. 2. Two gases, initially in separated adjoining chambers, will mix uniformly. ...
... The reverse process will not occur. 2. Two gases, initially in separated adjoining chambers, will mix uniformly. ...
Thermocolour paper
... Thermocolour paper changes colour depending on the temperature, providing a striking visual means of displaying temperature changes. The film responds quite rapidly. It can be used to illustrate many concepts linked with heat and temperature, including friction, conduction, insulation, feeling hot a ...
... Thermocolour paper changes colour depending on the temperature, providing a striking visual means of displaying temperature changes. The film responds quite rapidly. It can be used to illustrate many concepts linked with heat and temperature, including friction, conduction, insulation, feeling hot a ...
Conductionconvectionandradiation
... This is the movement of heat energy from hotter parts to cooler parts without any movement of the substance itself. 1- What happens to a metal rod when it is place in hot water? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ __________________________ ...
... This is the movement of heat energy from hotter parts to cooler parts without any movement of the substance itself. 1- What happens to a metal rod when it is place in hot water? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ __________________________ ...
document The Latent Heat Quiz
... Melting and _______________ are processes that require heat to be added. __________ and condensing are processes that release heat. ...
... Melting and _______________ are processes that require heat to be added. __________ and condensing are processes that release heat. ...
Teacher:
... transfer during chemical reactions and changes of state is called thermochemistry. One of the units used to measure heat flow is the calories defined as the amount of heat needed to raise 1 g of water 1oC. The SI unit of heat and energy is joule, which is equal to 0.2390 cal. The specific heat capac ...
... transfer during chemical reactions and changes of state is called thermochemistry. One of the units used to measure heat flow is the calories defined as the amount of heat needed to raise 1 g of water 1oC. The SI unit of heat and energy is joule, which is equal to 0.2390 cal. The specific heat capac ...
PHYSICS 1A
... All energy eventually is transferred to the surroundings, which becomes warmer Sankey diagrams are scale diagrams showing the energy transfers Forms of energy-Electricity, Chemical, Kinetic, Potential (Gravitational & elastic), Sound, Thermal (heat), Nuclear, Light. (Every Child Knows Pork sausages ...
... All energy eventually is transferred to the surroundings, which becomes warmer Sankey diagrams are scale diagrams showing the energy transfers Forms of energy-Electricity, Chemical, Kinetic, Potential (Gravitational & elastic), Sound, Thermal (heat), Nuclear, Light. (Every Child Knows Pork sausages ...
Cogeneration

Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Trigeneration or combined cooling, heat and power (CCHP) refers to the simultaneous generation of electricity and useful heating and cooling from the combustion of a fuel or a solar heat collector. Cogeneration is a thermodynamically efficient use of fuel. In separate production of electricity, some energy must be discarded as waste heat, but in cogeneration this thermal energy is put to use. All thermal power plants emit heat during electricity generation, which can be released into the natural environment through cooling towers, flue gas, or by other means. In contrast, CHP captures some or all of the by-product for heating, either very close to the plant, or—especially in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe—as hot water for district heating with temperatures ranging from approximately 80 to 130 °C. This is also called combined heat and power district heating (CHPDH). Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures (100–180 °C, 212–356 °F) can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling.The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator and the resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating as described in cogeneration. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW) a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Trigeneration differs from cogeneration in that the waste heat is used for both heating and cooling, typically in an absorption refrigerator. CCHP systems can attain higher overall efficiencies than cogeneration or traditional power plants. In the United States, the application of trigeneration in buildings is called building cooling, heating and power (BCHP). Heating and cooling output may operate concurrently or alternately depending on need and system construction.Cogeneration was practiced in some of the earliest installations of electrical generation. Before central stations distributed power, industries generating their own power used exhaust steam for process heating. Large office and apartment buildings, hotels and stores commonly generated their own power and used waste steam for building heat. Due to the high cost of early purchased power, these CHP operations continued for many years after utility electricity became available.