get PDF-file
... Gutenberg-University Medical School, Mainz, Germany U Monocytes/macrophages frequently infiltrate malignant gliomas and play a central role in the tumor-associated immune response as they process tumor antigen and present it to T-lymphocytes. Findings have accumulated that peripheral blood monocytes ...
... Gutenberg-University Medical School, Mainz, Germany U Monocytes/macrophages frequently infiltrate malignant gliomas and play a central role in the tumor-associated immune response as they process tumor antigen and present it to T-lymphocytes. Findings have accumulated that peripheral blood monocytes ...
Trogocytic intercellular membrane exchanges among hematological
... expression by tumors as a prominent immune escape mechanism was supported by numerous studies and for both solid and liquid tumors (for review, see [36,37]). HLA-G is not a tumorigenic molecule per se, but it could contribute to tumorigenesis if expressed by cancer stem cells or precancerous cells, ...
... expression by tumors as a prominent immune escape mechanism was supported by numerous studies and for both solid and liquid tumors (for review, see [36,37]). HLA-G is not a tumorigenic molecule per se, but it could contribute to tumorigenesis if expressed by cancer stem cells or precancerous cells, ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... Monoclonal antibodies are used for medical diagnosis, pregnancy testing and cancer ...
... Monoclonal antibodies are used for medical diagnosis, pregnancy testing and cancer ...
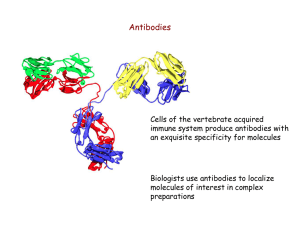
antibodies
... Lymphocytes can generate millions of different antigen binding sites by DNA rearrangement and mutation - processes restricted to immune cells!! Antigens bind hyper-variable regions at the tips of Fab fragments antigen binding has been compared to a lock-andkey fit (complementary surfaces) ...
... Lymphocytes can generate millions of different antigen binding sites by DNA rearrangement and mutation - processes restricted to immune cells!! Antigens bind hyper-variable regions at the tips of Fab fragments antigen binding has been compared to a lock-andkey fit (complementary surfaces) ...
Physiology of Blood I. Components, Characteristics, Functions of
... Hematopoiesis and Erythropoiesis 1. hematopoiesis (hemopoiesis) - the maturation, development and formation of blood cells a. red bone marrow (myeloid tissue) - location of hematopoiesis; in blood sinusoids which connect with capillaries; mainly in axial skeleton and heads of femur & humerus b. hemo ...
... Hematopoiesis and Erythropoiesis 1. hematopoiesis (hemopoiesis) - the maturation, development and formation of blood cells a. red bone marrow (myeloid tissue) - location of hematopoiesis; in blood sinusoids which connect with capillaries; mainly in axial skeleton and heads of femur & humerus b. hemo ...
Transcripts
... immunity that you’re hearing about in a lot of the other lectures. This does, however, apply to the things that you all should be thinking about because essentially the mucosa that we talk about is the entire gastrointestinal tract (starting with the mouth) and includes some of the special functions ...
... immunity that you’re hearing about in a lot of the other lectures. This does, however, apply to the things that you all should be thinking about because essentially the mucosa that we talk about is the entire gastrointestinal tract (starting with the mouth) and includes some of the special functions ...
cell-mediated immunity.
... Monoclonal antibodies are used for medical diagnosis, pregnancy testing and cancer ...
... Monoclonal antibodies are used for medical diagnosis, pregnancy testing and cancer ...
Host parasite communications—Messages from
... organisms like helminths [38,39]. It has recently been discovered that parasitic helminths produce exosomes. This was initially reported in the excretory-secretory components of the trematodes, Echinostoma caproni and Fasciola hepatica, which infect the gastrointestinal tract and liver respectively ...
... organisms like helminths [38,39]. It has recently been discovered that parasitic helminths produce exosomes. This was initially reported in the excretory-secretory components of the trematodes, Echinostoma caproni and Fasciola hepatica, which infect the gastrointestinal tract and liver respectively ...
Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune
... inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), dysregulation of these interactions, mediated by tumour necrosis factor signalling and by myosin light chain kinase activity, leads to IEC cytoskeletal rearrangements that disrupt tight junctions and increase permeability189,190. These findings suggest that IEC tigh ...
... inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), dysregulation of these interactions, mediated by tumour necrosis factor signalling and by myosin light chain kinase activity, leads to IEC cytoskeletal rearrangements that disrupt tight junctions and increase permeability189,190. These findings suggest that IEC tigh ...
I , Apr. 2005, p. 2012–2019 Vol. 73, No. 4 ⫹0 doi:10.1128/IAI.73.4.2012–2019.2005
... The production of melanin pigments is associated with virulence for many microbes. Melanin is believed to contribute to microbial virulence by protecting microbial cells from oxidative attack during infection. However, there is also evidence from various systems that melanins have immunomodulatory p ...
... The production of melanin pigments is associated with virulence for many microbes. Melanin is believed to contribute to microbial virulence by protecting microbial cells from oxidative attack during infection. However, there is also evidence from various systems that melanins have immunomodulatory p ...
Innate and adaptive effects of inflammasomes on T cell
... starting from eight hours after Listeria monocytogenes infection [52]. Inflammatory monocytes were the key cells eliciting, in a caspase 1-dependent manner, lymphocytederived IFN-g release, suggesting that different cell subsets could contribute to IL-18 secretion either sequentially or depending on ...
... starting from eight hours after Listeria monocytogenes infection [52]. Inflammatory monocytes were the key cells eliciting, in a caspase 1-dependent manner, lymphocytederived IFN-g release, suggesting that different cell subsets could contribute to IL-18 secretion either sequentially or depending on ...
Review series on helminths, immune modulation
... which helminth antigens such as those from S. mansoni mediate these effects is under investigation by several groups. IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-b play immunomodulatory roles and are produced by cells of both the innate and the adaptive immune response. IL-10 is induced by several in ...
... which helminth antigens such as those from S. mansoni mediate these effects is under investigation by several groups. IL-10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)-b play immunomodulatory roles and are produced by cells of both the innate and the adaptive immune response. IL-10 is induced by several in ...
An Introduction to Artificial Immune Systems
... Some History Developed from the field of theoretical immunology in the mid 1980’s. Suggested we ‘might look’ at the IS ...
... Some History Developed from the field of theoretical immunology in the mid 1980’s. Suggested we ‘might look’ at the IS ...
Chapter 1 General introduction and outine of the thesis
... Skin resident immune cells include dermal Tcells and macrophages (Mφ) and epidermal Langerhans cells7,8. These cells are important for immune surveillance, but also prevent the immune system from reacting to harmless agents7. ...
... Skin resident immune cells include dermal Tcells and macrophages (Mφ) and epidermal Langerhans cells7,8. These cells are important for immune surveillance, but also prevent the immune system from reacting to harmless agents7. ...
1 Modulation of HLA-G and HLA-E expression in - HAL
... In contrast to classical MHC class I which surface expression was increased by RABV infection, HLA-E molecules could not be detected on the cell surface, suggesting they cannot be exported. Such a pattern has been observed in human tumours which may not express HLA-E on cell surface despite the expr ...
... In contrast to classical MHC class I which surface expression was increased by RABV infection, HLA-E molecules could not be detected on the cell surface, suggesting they cannot be exported. Such a pattern has been observed in human tumours which may not express HLA-E on cell surface despite the expr ...
Basophils
... basophils release their granule contents including histamine, and generate and release LTC4. In addition, activated basophils produce cytokines, most notably IL-4 and IL-13 but also MIP-1α. Thus the physiological role of basophils is thought to be the release of cytokines, leukotrienes and histamine ...
... basophils release their granule contents including histamine, and generate and release LTC4. In addition, activated basophils produce cytokines, most notably IL-4 and IL-13 but also MIP-1α. Thus the physiological role of basophils is thought to be the release of cytokines, leukotrienes and histamine ...
Document
... basophils release their granule contents including histamine, and generate and release LTC4. In addition, activated basophils produce cytokines, most notably IL-4 and IL-13 but also MIP-1α. Thus the physiological role of basophils is thought to be the release of cytokines, leukotrienes and histamine ...
... basophils release their granule contents including histamine, and generate and release LTC4. In addition, activated basophils produce cytokines, most notably IL-4 and IL-13 but also MIP-1α. Thus the physiological role of basophils is thought to be the release of cytokines, leukotrienes and histamine ...
The effect of Sambucol, a black elderberry
... comparison to the untreated control monocytes, which represent physiological levels, are presented in Table 2: IL-1beta (Table 2a), TNF-alpha (Table 2b), IL-6 (Table 2c) and IL-8 (Table 2d). The highest stimulation index was observed with the E.Ex., followed by B.E. and A.D. which contain the same a ...
... comparison to the untreated control monocytes, which represent physiological levels, are presented in Table 2: IL-1beta (Table 2a), TNF-alpha (Table 2b), IL-6 (Table 2c) and IL-8 (Table 2d). The highest stimulation index was observed with the E.Ex., followed by B.E. and A.D. which contain the same a ...
Regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses by
... Bacteria are classified as Gram-positive or Gram-negative, depending on their cell wall structure. The role of the bacterial cell wall in immune regulation is the focus of the current work. Most Gram-positive bacteria stimulate monocytes to produce large amounts of IL12. IL-12 induces production of ...
... Bacteria are classified as Gram-positive or Gram-negative, depending on their cell wall structure. The role of the bacterial cell wall in immune regulation is the focus of the current work. Most Gram-positive bacteria stimulate monocytes to produce large amounts of IL12. IL-12 induces production of ...
Hooper LV, Macpherson AJ.. Immune adaptations that maintain
... Despite these challenges, the intestinal immune system is remarkably effective at minimizing adverse health effects from the microbiota, as shown by the fact that sepsis and inflammation are rare in immunologically healthy hosts. In this Review, we discuss the unique adaptations of the intestinal im ...
... Despite these challenges, the intestinal immune system is remarkably effective at minimizing adverse health effects from the microbiota, as shown by the fact that sepsis and inflammation are rare in immunologically healthy hosts. In this Review, we discuss the unique adaptations of the intestinal im ...
Phagocyte

Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting (phagocytosing) harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek phagein, ""to eat"" or ""devour"", and ""-cyte"", the suffix in biology denoting ""cell"", from the Greek kutos, ""hollow vessel"". They are essential for fighting infections and for subsequent immunity. Phagocytes are important throughout the animal kingdom and are highly developed within vertebrates. One litre of human blood contains about six billion phagocytes. They were first discovered in 1882 by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov while he was studying starfish larvae. Mechnikov was awarded the 1908 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discovery. Phagocytes occur in many species; some amoebae behave like macrophage phagocytes, which suggests that phagocytes appeared early in the evolution of life.Phagocytes of humans and other animals are called ""professional"" or ""non-professional"" depending on how effective they are at phagocytosis. The professional phagocytes include many types of white blood cells (such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, mast cells, and dendritic cells). The main difference between professional and non-professional phagocytes is that the professional phagocytes have molecules called receptors on their surfaces that can detect harmful objects, such as bacteria, that are not normally found in the body. Phagocytes are crucial in fighting infections, as well as in maintaining healthy tissues by removing dead and dying cells that have reached the end of their lifespan.During an infection, chemical signals attract phagocytes to places where the pathogen has invaded the body. These chemicals may come from bacteria or from other phagocytes already present. The phagocytes move by a method called chemotaxis. When phagocytes come into contact with bacteria, the receptors on the phagocyte's surface will bind to them. This binding will lead to the engulfing of the bacteria by the phagocyte. Some phagocytes kill the ingested pathogen with oxidants and nitric oxide. After phagocytosis, macrophages and dendritic cells can also participate in antigen presentation, a process in which a phagocyte moves parts of the ingested material back to its surface. This material is then displayed to other cells of the immune system. Some phagocytes then travel to the body's lymph nodes and display the material to white blood cells called lymphocytes. This process is important in building immunity, and many pathogens have evolved methods to evade attacks by phagocytes.