
Universal Precautions and Sanitary Practices Policy
... sample for use in their program. At a minimum, you must fill in the blanks on this form. You may modify the format and content to meet standards used by your program. This sample meets compliance with current licensing requirements as of January 1, 2014. Providers remain responsible for reading, und ...
... sample for use in their program. At a minimum, you must fill in the blanks on this form. You may modify the format and content to meet standards used by your program. This sample meets compliance with current licensing requirements as of January 1, 2014. Providers remain responsible for reading, und ...
WHO clinical staging of HIV disease in adults and adolescents (2/4)
... • Reduction in the CD4 cell number and the effects on their function reduces the capacity of the body to fight infectious diseases. • Individuals with HIV infection are therefore increasingly susceptible to many infections especially at later stages of HIV infection ...
... • Reduction in the CD4 cell number and the effects on their function reduces the capacity of the body to fight infectious diseases. • Individuals with HIV infection are therefore increasingly susceptible to many infections especially at later stages of HIV infection ...
PORTFOLIO CONTENT - Curry International Tuberculosis Center
... Not place a PPD as it will probably react positive; do a chest x-ray instead Disregard the BCG history if it was given more than one year ago Do nothing, as BCG prevents TB infection and disease Ask patient for proof by showing his/her BCG scar ...
... Not place a PPD as it will probably react positive; do a chest x-ray instead Disregard the BCG history if it was given more than one year ago Do nothing, as BCG prevents TB infection and disease Ask patient for proof by showing his/her BCG scar ...
Tool 45: Post-test - Curry International Tuberculosis Center
... Not place a PPD as it will probably react positive; do a chest x-ray instead Disregard the BCG history if it was given more than one year ago Do nothing, as BCG prevents TB infection and disease Ask patient for proof by showing his/her BCG scar ...
... Not place a PPD as it will probably react positive; do a chest x-ray instead Disregard the BCG history if it was given more than one year ago Do nothing, as BCG prevents TB infection and disease Ask patient for proof by showing his/her BCG scar ...
Paediatric Infectious Diseases Programme
... Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases (ESPID). The international panel of tutors is led by Andrew Pollard, Professor of Paediatric Infection and Immunity at the University of Oxford, and Honorary Consultant Paediatrician at the Children’s Hospital, Oxford. Professor Pollard also leads Oxford-ba ...
... Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases (ESPID). The international panel of tutors is led by Andrew Pollard, Professor of Paediatric Infection and Immunity at the University of Oxford, and Honorary Consultant Paediatrician at the Children’s Hospital, Oxford. Professor Pollard also leads Oxford-ba ...
T Healthy Smiles, Healthy Hearts
... grow into plaque, causing inflammation and bleeding in the gums.1 When left untreated, the plaque can spread below the gum line, allowing bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Due to the inflammation and the spread of bacteria into the bloodstream, it’s believed that there is an increased risk for othe ...
... grow into plaque, causing inflammation and bleeding in the gums.1 When left untreated, the plaque can spread below the gum line, allowing bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Due to the inflammation and the spread of bacteria into the bloodstream, it’s believed that there is an increased risk for othe ...
Nail Fungus Presentation
... Short nails can cause breaks in the skin, which can lead to fungal infection. ...
... Short nails can cause breaks in the skin, which can lead to fungal infection. ...
Paediatric Infectious Diseases consults
... start to see what the differential diagnosis might be and how to figure it out.” ...
... start to see what the differential diagnosis might be and how to figure it out.” ...
Microbiology 2 – Hospital Acquired Infections
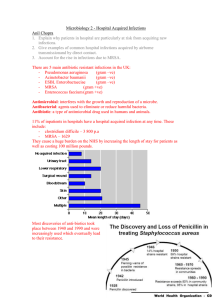
... Antibacterial: agents used to eliminate or reduce harmful bacteria. Antibiotic: a type of antimicrobial drug used in humans and animals. 11% of inpatients in hospitals have a hospital acquired infection at any time. These include: - clostridium difficile – 3 800 p.a - MRSA – 1629 They cause a huge b ...
... Antibacterial: agents used to eliminate or reduce harmful bacteria. Antibiotic: a type of antimicrobial drug used in humans and animals. 11% of inpatients in hospitals have a hospital acquired infection at any time. These include: - clostridium difficile – 3 800 p.a - MRSA – 1629 They cause a huge b ...
A1988M404200001
... of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. The NIH was not entirely uninterested in my proposed overseas gambit but reasoned that I needed seasoning before heading into the field. I disagreed, and, with the encouragement of Harold Stewart at the National Cancer Institute, I applied for and received an Elea ...
... of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. The NIH was not entirely uninterested in my proposed overseas gambit but reasoned that I needed seasoning before heading into the field. I disagreed, and, with the encouragement of Harold Stewart at the National Cancer Institute, I applied for and received an Elea ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... Human Anatomy & Physiology Part 2 Immunologic, Endocrine, and Excretory Systems ...
... Human Anatomy & Physiology Part 2 Immunologic, Endocrine, and Excretory Systems ...
MICROBIOLOGY and PUBLIC HEALTH
... B. host temperature remains 37 degrees Celsius C. anaerobic conditions prevail D. host resistance is lowered E. room temperature exceeds 73 degrees Fahrenheit 39. The elapse of time from initial infection through evaluation of pathogenesis to first appearance of symptoms and signs of disease is call ...
... B. host temperature remains 37 degrees Celsius C. anaerobic conditions prevail D. host resistance is lowered E. room temperature exceeds 73 degrees Fahrenheit 39. The elapse of time from initial infection through evaluation of pathogenesis to first appearance of symptoms and signs of disease is call ...
Newcastle Disease and Avian Influenza
... from the respiratory systems of infected birds. Infection occurs following inhalation of virus. Mechanical spread is also known where virus is carried on objects (fomites). Infection can occur as a result of ingestion of virus but this is less common. ND can infect conjunctivitis. ...
... from the respiratory systems of infected birds. Infection occurs following inhalation of virus. Mechanical spread is also known where virus is carried on objects (fomites). Infection can occur as a result of ingestion of virus but this is less common. ND can infect conjunctivitis. ...
Evolutionary Aspects of Animal Model Use in Infectious Disease
... Zoonotic diseases • 20% of zoonotic diseases are from other primates which are 0.5% of all species • Transmission from animal to human, susceptibility or resistance specific for the pathogen and host • Co-evolution between host and pathogen ...
... Zoonotic diseases • 20% of zoonotic diseases are from other primates which are 0.5% of all species • Transmission from animal to human, susceptibility or resistance specific for the pathogen and host • Co-evolution between host and pathogen ...
Managing Urinary Tract Infections in the Care Home Setting
... • Asymptomatic bacteruria- no clinical symptoms -in care homes this may be as high as 50% in women and 40% for men • Asymptomatic infection frequent in ...
... • Asymptomatic bacteruria- no clinical symptoms -in care homes this may be as high as 50% in women and 40% for men • Asymptomatic infection frequent in ...
Quantitative Microbiology.pdf
... anthrax, pointing explicitly to a bacterium as the cause of this disease. - This validates the germ theory of disease. - In 1881 he developed the use of gelatin on glass plates as a means for culturing bacterial colonies for experiments. - Discovered the causative agents of tuberculosis (Mycobacteri ...
... anthrax, pointing explicitly to a bacterium as the cause of this disease. - This validates the germ theory of disease. - In 1881 he developed the use of gelatin on glass plates as a means for culturing bacterial colonies for experiments. - Discovered the causative agents of tuberculosis (Mycobacteri ...
Surgical site infections - Cincinnati Children`s Hospital Medical Center
... infections, this means that the infection becomes evident 48 hours or more after admission, but each infection must be assessed individually. III. Data Source(s) Dr. Beverly Connelly, CCHMC Division of Infectious Diseases IV. Sampling and Data Collection Plan Numerators: The following methods are us ...
... infections, this means that the infection becomes evident 48 hours or more after admission, but each infection must be assessed individually. III. Data Source(s) Dr. Beverly Connelly, CCHMC Division of Infectious Diseases IV. Sampling and Data Collection Plan Numerators: The following methods are us ...
1 HAEMOPHILUS influenzae type b (Hib)
... Hib is spread through close contact with an infected person by their nose and throat secretions from coughs and sneezes. Hib can also be spread by oral contact such as kissing or sharing drinks or by touching objects contaminated by the infected person and then touching your nose or mouth. What are ...
... Hib is spread through close contact with an infected person by their nose and throat secretions from coughs and sneezes. Hib can also be spread by oral contact such as kissing or sharing drinks or by touching objects contaminated by the infected person and then touching your nose or mouth. What are ...
Robert_Koch[1]final[1].
... • Once he checked the spleen of infected farm animals, he found out that the disease had killed them, and healthy mice in which he inoculated with the blood of other healthy farm animals had no infection ...
... • Once he checked the spleen of infected farm animals, he found out that the disease had killed them, and healthy mice in which he inoculated with the blood of other healthy farm animals had no infection ...
File
... • Helper T cells activate B cells and Cyto-toxic T cells, as the number of helper T cells drops, the body’s immune response decreases • Individuals are left more susceptible to opportunistic infections such as pneumonia, or influenza. • This immune-compromised state arises many years after the initi ...
... • Helper T cells activate B cells and Cyto-toxic T cells, as the number of helper T cells drops, the body’s immune response decreases • Individuals are left more susceptible to opportunistic infections such as pneumonia, or influenza. • This immune-compromised state arises many years after the initi ...
Pathogens - hiscience
... Eventually, the virus copies fill the whole host cell and it bursts open. The viruses then pass out through the bloodstream, the airways, or by other routes. ...
... Eventually, the virus copies fill the whole host cell and it bursts open. The viruses then pass out through the bloodstream, the airways, or by other routes. ...
Prevention of Healthcare and Associated Infection in Surgery
... The Royal Australasian College of Surgeons is committed to ensuring the highest standard of safe and comprehensive surgical care for the community. Healthcare associated infections (HAI) acquired in the hospital setting are a major cause of preventable and sometimes serious harm to patients. The Col ...
... The Royal Australasian College of Surgeons is committed to ensuring the highest standard of safe and comprehensive surgical care for the community. Healthcare associated infections (HAI) acquired in the hospital setting are a major cause of preventable and sometimes serious harm to patients. The Col ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.



















![Robert_Koch[1]final[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008492191_1-416dee83d25526f37eb1a1a3066c4381-300x300.png)


