Urinary tract infection
... obstructed kidney, which leads to suppurative destruction of the renal parenchyma and potential loss of renal function. Because of the extent of the infection and the presence of urinary obstruction, sepsis may rapidly ensue, requiring rapid diagnosis and management ...
... obstructed kidney, which leads to suppurative destruction of the renal parenchyma and potential loss of renal function. Because of the extent of the infection and the presence of urinary obstruction, sepsis may rapidly ensue, requiring rapid diagnosis and management ...
Ocular immunopathology
... T cells and APCs Inflammation leads to an influx of large numbers of cells Patterns of cytokine secretion change during the course of disease The tissue does not return to its basal state ...
... T cells and APCs Inflammation leads to an influx of large numbers of cells Patterns of cytokine secretion change during the course of disease The tissue does not return to its basal state ...
class review 2010 - College of Natural Resources
... The genetic structure of the clonally reproducing Sudden Oak Death (SOD) pathogen in California was investigated using seven variable microsatellites. A total of 35 multilocus genotypes were identified among 292 samples representative of populations from 14 forest sites and of the nursery trade. AMO ...
... The genetic structure of the clonally reproducing Sudden Oak Death (SOD) pathogen in California was investigated using seven variable microsatellites. A total of 35 multilocus genotypes were identified among 292 samples representative of populations from 14 forest sites and of the nursery trade. AMO ...
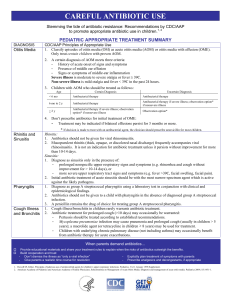
Carefull Antibiotic Use: Pediatric Appropriate
... 2. Mucopurulent rhinitis (thick, opaque, or discolored nasal discharge) frequently accompanies viral rhinosinusitis. It is not an indication for antibiotic treatment unless it persists without improvement for more than 10-14 days. Sinusitis: 1. Diagnose as sinusitis only in the presence of: - prolon ...
... 2. Mucopurulent rhinitis (thick, opaque, or discolored nasal discharge) frequently accompanies viral rhinosinusitis. It is not an indication for antibiotic treatment unless it persists without improvement for more than 10-14 days. Sinusitis: 1. Diagnose as sinusitis only in the presence of: - prolon ...
INFECTIVE / INFLAMMATORY CONDITIONS OF THE HEART
... shop’, the person’s blood stream provides an ideal environment for proliferation. Bacterial endocarditis is often caused when bacteria are introduced to the bloodstream during dental surgery or other medical procedures. Anyone with underlying abnormalities of the heart may, therefore, be predisposed ...
... shop’, the person’s blood stream provides an ideal environment for proliferation. Bacterial endocarditis is often caused when bacteria are introduced to the bloodstream during dental surgery or other medical procedures. Anyone with underlying abnormalities of the heart may, therefore, be predisposed ...
Path pages 357-381 Gram-Positive Bacterial Infections
... Hidradenitis – chronic suppurative inflammation of apocrine glands, most often in axilla Paronychia – infections of nail bed; very painful Felons – infections on palmar side of fingertips; very painful o Lung infections have PMN infiltrate similar to pneumococcus; cause more tissue destruction ...
... Hidradenitis – chronic suppurative inflammation of apocrine glands, most often in axilla Paronychia – infections of nail bed; very painful Felons – infections on palmar side of fingertips; very painful o Lung infections have PMN infiltrate similar to pneumococcus; cause more tissue destruction ...
Slide () - Access Emergency Medicine
... Herpes labialis (A) With primary HSV infection, virus replicates in the oropharyngeal epithelium, ascends peripheral sensory nerves into the trigeminal ganglion. Herpes labialis (B) HSV persists in a latent phase within the trigeminal ganglion for the life of the individual. (C) Various stimuli init ...
... Herpes labialis (A) With primary HSV infection, virus replicates in the oropharyngeal epithelium, ascends peripheral sensory nerves into the trigeminal ganglion. Herpes labialis (B) HSV persists in a latent phase within the trigeminal ganglion for the life of the individual. (C) Various stimuli init ...
Aeromonas hydrophila
... Prognosis If immunocompetent, the mild gastroenteritis is usually self-clearing. In immunocompromised people who have the dysenteric diarrhea may need a course of antibiotics, and fluids. In the wound infections, antibiotics may need to be administered and the wound needs to be kept very clean. ...
... Prognosis If immunocompetent, the mild gastroenteritis is usually self-clearing. In immunocompromised people who have the dysenteric diarrhea may need a course of antibiotics, and fluids. In the wound infections, antibiotics may need to be administered and the wound needs to be kept very clean. ...
CM Heme-Onc Exam 2 Lecture 15
... matrix. o Common clinical finding o Multiple etiologies, can be caused by a vast array of diseases and drugs. o Some nodal presentations suggest a specific disease process Diagnostic approach o H&P-etiology is often obvious after complete H&P Age: cervical adenopathy in a child much less worriso ...
... matrix. o Common clinical finding o Multiple etiologies, can be caused by a vast array of diseases and drugs. o Some nodal presentations suggest a specific disease process Diagnostic approach o H&P-etiology is often obvious after complete H&P Age: cervical adenopathy in a child much less worriso ...
Learn more and review the policy
... immunodeficiency (HIV), Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) present a risk to students, faculty, staff and patients. Preventing the transmission of bloodborne pathogens from patients to healthcare workers and from healthcare workers to patients requires a comprehensive approach that ...
... immunodeficiency (HIV), Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV) present a risk to students, faculty, staff and patients. Preventing the transmission of bloodborne pathogens from patients to healthcare workers and from healthcare workers to patients requires a comprehensive approach that ...
Cleaning and Disinfection of Operating Rooms A
... A deep incision that spontaneously dehisces or is deliberately opened by a surgeon and is culture positive or not cultured and the patient has at least one of the following signs or symptoms: Fever (>38ºC) or Localized pain or tenderness An abscess or other evidence of infection involving the de ...
... A deep incision that spontaneously dehisces or is deliberately opened by a surgeon and is culture positive or not cultured and the patient has at least one of the following signs or symptoms: Fever (>38ºC) or Localized pain or tenderness An abscess or other evidence of infection involving the de ...
The role of IL-12/IL-23 in Crohn`s disease
... large intestine (colon), but may involve any part from the mouth to the anus. 1,2 In Europe 250,000 people are living with Crohn’s disease, with around 18,000 new cases diagnosed each year.3 Though anyone can be affected by Crohn’s disease at any age, it most often impacts those between the ages of ...
... large intestine (colon), but may involve any part from the mouth to the anus. 1,2 In Europe 250,000 people are living with Crohn’s disease, with around 18,000 new cases diagnosed each year.3 Though anyone can be affected by Crohn’s disease at any age, it most often impacts those between the ages of ...
Human Health
... significant numbers of Bm cells present in the various lymph nodes. c) Second Infection with the same antigen d) The result is a rapid production of antibodies to higher levels. The rapid response is due to increased probability of antigen encountering the specific Bm lymphocyte. The high levels of ...
... significant numbers of Bm cells present in the various lymph nodes. c) Second Infection with the same antigen d) The result is a rapid production of antibodies to higher levels. The rapid response is due to increased probability of antigen encountering the specific Bm lymphocyte. The high levels of ...
title - JustAnswer
... The metaphysis is the area where bone growth occurs in puppies; the long bones in the body grow in length at specific areas known as “growth plates;” these areas usually continue to produce bone until the bones are fully developed, at which time, no further growth is needed; the growth plates then “ ...
... The metaphysis is the area where bone growth occurs in puppies; the long bones in the body grow in length at specific areas known as “growth plates;” these areas usually continue to produce bone until the bones are fully developed, at which time, no further growth is needed; the growth plates then “ ...
Department of Microbiology and Immunology
... (MLT) students as well as nursing, medical, and graduate students. It offers a graduate program leading to the MS degree in microbiology and immunology. The requirements for admission to the graduate program are stated on pages 32-45 of this catalogue. MBIM 223 Second semester. ...
... (MLT) students as well as nursing, medical, and graduate students. It offers a graduate program leading to the MS degree in microbiology and immunology. The requirements for admission to the graduate program are stated on pages 32-45 of this catalogue. MBIM 223 Second semester. ...
a version - SEA
... Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs expressed in all living organisms. They are essential components of the translation machinery and are responsible for the synthesis of proteins from messenger RNAs. Viruses are obligate parasites that evolved to minimize the size of their genome. As a ...
... Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs expressed in all living organisms. They are essential components of the translation machinery and are responsible for the synthesis of proteins from messenger RNAs. Viruses are obligate parasites that evolved to minimize the size of their genome. As a ...
Unit 3 Autoimmune Diseases That Affect the Oral Cavity 1. Sjogren`s
... enzymes necessary for assembly. The infecting virus also directs intracellular assembly of new particles. Eventually, newly replicated (and enveloped) virus is released, with subsequent infection of other cells. This usually occurs at the expense of the originally infected cell. In certain types of ...
... enzymes necessary for assembly. The infecting virus also directs intracellular assembly of new particles. Eventually, newly replicated (and enveloped) virus is released, with subsequent infection of other cells. This usually occurs at the expense of the originally infected cell. In certain types of ...
JMM Case Reports
... piece of information on the structure of observed trophozoites: length of cilia. Although lack of scale bar makes the precise measurement impossible, elongated and profound cilia with uneven distribution captured in Figure one (Soleimanpour et al. 2015) is in sharp contrast with the classic ‘short’ ...
... piece of information on the structure of observed trophozoites: length of cilia. Although lack of scale bar makes the precise measurement impossible, elongated and profound cilia with uneven distribution captured in Figure one (Soleimanpour et al. 2015) is in sharp contrast with the classic ‘short’ ...
Reviews and Resources
... 530,000 persons a year die from such diseases, a small number when compared to those who die from natural disasters, AIDS, or malaria. Nevertheless, although they typically have a low mortality, NTDs tend to be chronic and often stigmatize the patient. NTDs include diseases spread by helminths, prot ...
... 530,000 persons a year die from such diseases, a small number when compared to those who die from natural disasters, AIDS, or malaria. Nevertheless, although they typically have a low mortality, NTDs tend to be chronic and often stigmatize the patient. NTDs include diseases spread by helminths, prot ...
Research and Regulatory Update
... met. There must be present a susceptible plant (the host) that is subject to infection. There must be a virulent or infectious agent (the pathogen) that is able to infect a host. Finally, there must be suitable conditions (favorable environment) that allow the host-pathogen interaction to take place ...
... met. There must be present a susceptible plant (the host) that is subject to infection. There must be a virulent or infectious agent (the pathogen) that is able to infect a host. Finally, there must be suitable conditions (favorable environment) that allow the host-pathogen interaction to take place ...
SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY SYNDROME (SARS)
... tissue, possibly other bodily fluids, and fomites contaminated with any of these fluids. 6. Transmission: The main route of transmission is direct contact, via the eyes, nose, and mouth, with infectious respiratory droplets. Contamination of inanimate materials or objects by infectious respiratory s ...
... tissue, possibly other bodily fluids, and fomites contaminated with any of these fluids. 6. Transmission: The main route of transmission is direct contact, via the eyes, nose, and mouth, with infectious respiratory droplets. Contamination of inanimate materials or objects by infectious respiratory s ...
Infection

Infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to these organisms and the toxins they produce. Infectious disease, also known as transmissible disease or communicable disease, is illness resulting from an infection.Infections are caused by infectious agents including viruses, viroids, prions, bacteria, nematodes such as parasitic roundworms and pinworms, arthropods such as ticks, mites, fleas, and lice, fungi such as ringworm, and other macroparasites such as tapeworms and other helminths.Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response.Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as Infectious Disease.