Impact of Amendment 1 of the 17th
... cables concealed in a wall or partition (at a depth of less than 50mm) by a 30mA RCD where the installation is not intended to be under the supervision of a skilled or instructed person if the normal methods of protection including use of cables with an earthed metallic covering, earthed conduit/tru ...
... cables concealed in a wall or partition (at a depth of less than 50mm) by a 30mA RCD where the installation is not intended to be under the supervision of a skilled or instructed person if the normal methods of protection including use of cables with an earthed metallic covering, earthed conduit/tru ...
Series versus Parallel Circuits
... Anything that is plugged into an outlet requires electrical energy! That energy is moved around in CIRCUITS! EX: Hair dryer 1. The dryer has to be plugged into the outlet to operate. 2. A generator at the power plant produces a voltage difference across the outlet that makes charges move when the ci ...
... Anything that is plugged into an outlet requires electrical energy! That energy is moved around in CIRCUITS! EX: Hair dryer 1. The dryer has to be plugged into the outlet to operate. 2. A generator at the power plant produces a voltage difference across the outlet that makes charges move when the ci ...
Commonly used electrical symbols
... The instrument connected could be a different instrument or several different instruments identified by the letter. ...
... The instrument connected could be a different instrument or several different instruments identified by the letter. ...
16.3 Ohm`s Law / Energy and Power / Electric Meters
... Typical sources of potential difference are batteries (which are just two or more cells connected together), and power supplies (electron pumps). In drawing a cell or battery on a circuit schematic, remember that the longer side of the symbol is the positive terminal. ...
... Typical sources of potential difference are batteries (which are just two or more cells connected together), and power supplies (electron pumps). In drawing a cell or battery on a circuit schematic, remember that the longer side of the symbol is the positive terminal. ...
Pengantar Teknik Elektro Sejarah, Pendidikan dan
... • A voltmeter measures the potential difference (voltage) between two points • An ohmmeter measures resistance • A multimeter combines these functions, and possibly some additional ones as well, into a single instrument ...
... • A voltmeter measures the potential difference (voltage) between two points • An ohmmeter measures resistance • A multimeter combines these functions, and possibly some additional ones as well, into a single instrument ...
Glossary
... Meter setup for most residential and small business load requirements limited to 320 amps and/or 240 volts. The meter is connected directly to the customer’s electrical service wires so if the meter is removed, the power to the premise will be de-energized. Customer load requirements pass directly t ...
... Meter setup for most residential and small business load requirements limited to 320 amps and/or 240 volts. The meter is connected directly to the customer’s electrical service wires so if the meter is removed, the power to the premise will be de-energized. Customer load requirements pass directly t ...
Current-Only Directional Overcurrent Relay
... protection of power transmission systems. Distributionside protection, e.g., for radial and ring-main units [2], mostly employs non-directional relays. Here, a fault generally means an overcurrent [3], mainly from a short circuit. The nondirectional relay typically monitors the overcurrent (from the ...
... protection of power transmission systems. Distributionside protection, e.g., for radial and ring-main units [2], mostly employs non-directional relays. Here, a fault generally means an overcurrent [3], mainly from a short circuit. The nondirectional relay typically monitors the overcurrent (from the ...
Mahe Karthikeyan January 16, 2015 Layers of Earth There are four
... There are four layers of Earth. They are the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Scientists have learned about what’s inside Earth by studying seismic waves. The crust is the thinnest layer of all the other layers of Earth. It is also the layer that we are living on. Without the c ...
... There are four layers of Earth. They are the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and the inner core. Scientists have learned about what’s inside Earth by studying seismic waves. The crust is the thinnest layer of all the other layers of Earth. It is also the layer that we are living on. Without the c ...
What Is Rectification? What Is Smoothing?
... What Is Rectification? What Is Smoothing? Rectification is the conversion of alternating current to direct current. Rectification is performed by a diode that allows current to flow in one direction but not in the opposite direction. Direct current that has only been rectified, however, has various ...
... What Is Rectification? What Is Smoothing? Rectification is the conversion of alternating current to direct current. Rectification is performed by a diode that allows current to flow in one direction but not in the opposite direction. Direct current that has only been rectified, however, has various ...
CN-0077 利用AD5422提供16位电压输出和4 mA至20 mA输出简化解决方案
... the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, "Circuits from the Lab" are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of merchantabilit ...
... the "Circuits from the Lab". Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, "Circuits from the Lab" are supplied "as is" and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of merchantabilit ...
Eye on Safety - Berkley Agribusiness
... An electrical hazard exists when the wire is too small a gauge for the current it will carry. For example, if you use an extension cord that can’t safely handle the current used by the tool, the wire will overheat and could cause a fire. Wires and other components in a circuit have a maximum amount ...
... An electrical hazard exists when the wire is too small a gauge for the current it will carry. For example, if you use an extension cord that can’t safely handle the current used by the tool, the wire will overheat and could cause a fire. Wires and other components in a circuit have a maximum amount ...
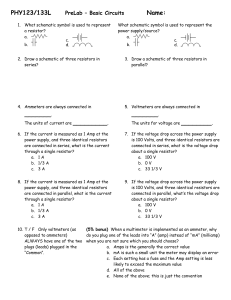
Basic Ciruits
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
... 9. If the voltage drop across the power supply is 100 Volts, and three identical resistors are connected in parallel, what’s the voltage drop about a single resistor? a. 100 V b. 0 V c. 33 1/3 V ...
U-Electric_Shock_Lecture_Notes
... • They sense the development of an imbalance in the current going out of the outlet and the current returning to the outlet. • They will shut off the current flow if an imbalance is sensed. ...
... • They sense the development of an imbalance in the current going out of the outlet and the current returning to the outlet. • They will shut off the current flow if an imbalance is sensed. ...