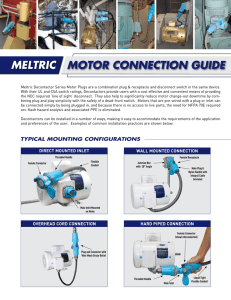
Electric Currents
... down), improves efficiency by the square of the change in voltage (or current). In this case raising V by a factor of 10, cut the line loss by a factor of 100! ...
... down), improves efficiency by the square of the change in voltage (or current). In this case raising V by a factor of 10, cut the line loss by a factor of 100! ...
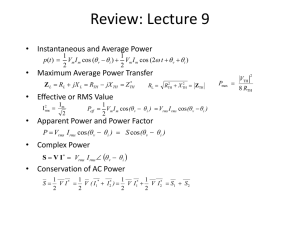
Review: Lecture 9
... Calculate the energy stored in the coupled inductors at time t = 1s if v=60cos(4t +30°) V. ...
... Calculate the energy stored in the coupled inductors at time t = 1s if v=60cos(4t +30°) V. ...
Current limitation 347KB
... • Download the presentation file • Print the Notes pages and read them as you view the presentation in the “Slide Show” view. In this way you see the slides in large format and have animation (when available) ...
... • Download the presentation file • Print the Notes pages and read them as you view the presentation in the “Slide Show” view. In this way you see the slides in large format and have animation (when available) ...
17th Edition (BS 7671:2008) incorporating Amendment No 1
... The natural protection of the human body is considerably reduced when certain clinical procedures are being performed on it. Patients under treatment may have their skin resistance broken or their defensive capacity either reduced by medication or nullified while anaesthetised. These conditions incr ...
... The natural protection of the human body is considerably reduced when certain clinical procedures are being performed on it. Patients under treatment may have their skin resistance broken or their defensive capacity either reduced by medication or nullified while anaesthetised. These conditions incr ...
Principles of Electricity
... There is no voltage drop if two or more loads are connected in parallel. Example – A vanity light that has three lights. If wired in parallel, the voltage at all three loads is 120V, same as the source. If wired in series each light bulb would produce only 40 volts each ...
... There is no voltage drop if two or more loads are connected in parallel. Example – A vanity light that has three lights. If wired in parallel, the voltage at all three loads is 120V, same as the source. If wired in series each light bulb would produce only 40 volts each ...
Lesson C7-1
... circuits are used for common uses such as lighting and appliances 240-volt circuits are used for equipment and appliances with greater demand, such as ...
... circuits are used for common uses such as lighting and appliances 240-volt circuits are used for equipment and appliances with greater demand, such as ...
Ohms Law Practice Answers 1. How much current is in a circuit that
... 12. What could you do to a closed circuit consisting of 2 batteries, 2 light bulbs and a switch to INCREASE the current? Put the light bulbs in parallel. Each bulb would get the full amount of voltage from the batteries drawing more current. 13. What could you do to a closed circuit consisting of 2 ...
... 12. What could you do to a closed circuit consisting of 2 batteries, 2 light bulbs and a switch to INCREASE the current? Put the light bulbs in parallel. Each bulb would get the full amount of voltage from the batteries drawing more current. 13. What could you do to a closed circuit consisting of 2 ...
Importance of Isolated System
... running over power cable or equipment being dropped) In any case result would be the same The level of electrical safety has now been reduced. Such occurrences on an Isolated Power System (IPS) would as described above result in the LIM alarming and warning being issued of potential fault hazard. ...
... running over power cable or equipment being dropped) In any case result would be the same The level of electrical safety has now been reduced. Such occurrences on an Isolated Power System (IPS) would as described above result in the LIM alarming and warning being issued of potential fault hazard. ...
Yr - Bethlehem College .::. Welcome
... _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ___ ...
... _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ___ ...
doc
... Now eq. (9) provides the change in the bus voltages due to the fault. Change from what? It is the change from the voltage without the fault, i.e., it is the pre-fault voltage. Consider any bus, let’s say bus j, with a prefault voltage of Vj. Then we can compute the bus j voltage under the faulted co ...
... Now eq. (9) provides the change in the bus voltages due to the fault. Change from what? It is the change from the voltage without the fault, i.e., it is the pre-fault voltage. Consider any bus, let’s say bus j, with a prefault voltage of Vj. Then we can compute the bus j voltage under the faulted co ...
Electric Groundsb
... occur through exposure to lightning or other voltages higher than that for which the circuit is designed. Another purpose in grounding one of the wires of the system is to limit the maximum voltage to ground under normal operating conditions. Also, a system which operates with one of its conductors ...
... occur through exposure to lightning or other voltages higher than that for which the circuit is designed. Another purpose in grounding one of the wires of the system is to limit the maximum voltage to ground under normal operating conditions. Also, a system which operates with one of its conductors ...
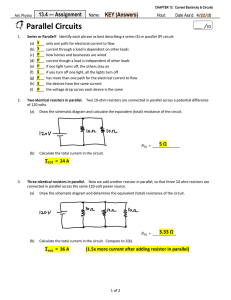
Parallel Circuits - Mr. Britton / FHS Physics
... if one light turns off, the others stay on if you turn off one light, all the lights turn off has more than one path for the electrical current to flow the devices have the same current the voltage drop across each device is the same ...
... if one light turns off, the others stay on if you turn off one light, all the lights turn off has more than one path for the electrical current to flow the devices have the same current the voltage drop across each device is the same ...
Series and parallel circuits
... circuit. Then add voltmeter to measure the potential difference across one of the lamps. ...
... circuit. Then add voltmeter to measure the potential difference across one of the lamps. ...
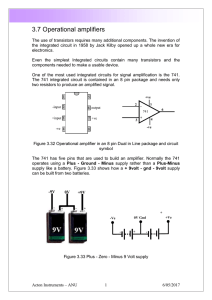
3.7 Operational amplifiers
... When the circuit is operational monitor the waveforms on the oscilloscope and try different values of Rf to change the gain. With only a single 9 Volt battery a different approach has to be taken to make the device operate as an amplifier. The power supply is based around a voltage divider and with ...
... When the circuit is operational monitor the waveforms on the oscilloscope and try different values of Rf to change the gain. With only a single 9 Volt battery a different approach has to be taken to make the device operate as an amplifier. The power supply is based around a voltage divider and with ...