CAD Tools for Circuit Design
... 2. Use ExpressSCH to draw a complete schematic diagram of the circuit. Be sure that every component has an ID label and a value. It may be necessary to create a custom symbol if a part is selected that is not in the library of standard components. 3. Use ExpressPCB to link to the schematic diagram a ...
... 2. Use ExpressSCH to draw a complete schematic diagram of the circuit. Be sure that every component has an ID label and a value. It may be necessary to create a custom symbol if a part is selected that is not in the library of standard components. 3. Use ExpressPCB to link to the schematic diagram a ...
Standard Type Back-fire chip LEDs(Reverse
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
... The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devic ...
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis
... current sources with the corresponding phasors. (All of the sources must have the same frequency.) 2. Replace inductances by their complex impedances ZL ...
... current sources with the corresponding phasors. (All of the sources must have the same frequency.) 2. Replace inductances by their complex impedances ZL ...
Selection Guide
... overcurrent conditions for which traditional fuse protection would prove impractical or undesirable such as ...
... overcurrent conditions for which traditional fuse protection would prove impractical or undesirable such as ...
Installation and Maintenance Sheet - IF 1405 Revision 1
... 1. Frequent inspection should be made. A schedule for maintenance check should be determined by the environment and frequency of use. It is recommended that it should be at least once a year. We recommend an Electrical Preventive Maintenance program as described in the National Fire Protection Assoc ...
... 1. Frequent inspection should be made. A schedule for maintenance check should be determined by the environment and frequency of use. It is recommended that it should be at least once a year. We recommend an Electrical Preventive Maintenance program as described in the National Fire Protection Assoc ...
Reverse Breakdown Voltage Studies
... leakage data available gives no hints. • Statistical analysis of full data set from Minglee – excludes files with strange leakage behaviour, one or more channels with leakage current> 1 nA for V<10V). – This leakage is not an artefact of the test system but is not correlated with ESD. – These device ...
... leakage data available gives no hints. • Statistical analysis of full data set from Minglee – excludes files with strange leakage behaviour, one or more channels with leakage current> 1 nA for V<10V). – This leakage is not an artefact of the test system but is not correlated with ESD. – These device ...
3. Term 3 Test Questions
... There are four possible options for each answer in the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the correct answer and write only A, B, C or D next to the question number. ...
... There are four possible options for each answer in the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the correct answer and write only A, B, C or D next to the question number. ...
Electric Current Notes Electric_Current_Chap_23ppt
... The charge that flows through a circuit originates in the wires of the circuit. The charge carriers in wires are simply the electrons possessed by the atoms which make up the wires. Charge moves abnormally slowly - on average, about 1 meter in an hour - through a circuit. Yet as soon as a switch is ...
... The charge that flows through a circuit originates in the wires of the circuit. The charge carriers in wires are simply the electrons possessed by the atoms which make up the wires. Charge moves abnormally slowly - on average, about 1 meter in an hour - through a circuit. Yet as soon as a switch is ...
The fundamental purpose of overcurrent protection and
... on the supply side and one on the load side of a MCCB, they could theoretically place a fault across a single pole of the circuit breaker at near line voltage. However, the probability of having that fault is very low and the probability that it will be above the fault level for which the MCCB is te ...
... on the supply side and one on the load side of a MCCB, they could theoretically place a fault across a single pole of the circuit breaker at near line voltage. However, the probability of having that fault is very low and the probability that it will be above the fault level for which the MCCB is te ...
Node Voltage with Thevenin Equivalent
... the column under N should be divided by 125 and then multipled by 1ms to determine the time at which each voltage data point ...
... the column under N should be divided by 125 and then multipled by 1ms to determine the time at which each voltage data point ...
Investigating Components having Non-Linear Characteristics 6EM
... Try to calculate the current, I which flows in the circuit and the voltage, V across the diode. It will soon become clear that you can not calculate these answers without knowing the detailed characteristics of the diode (make sure you understand why this is the case). Let us assume that the diode i ...
... Try to calculate the current, I which flows in the circuit and the voltage, V across the diode. It will soon become clear that you can not calculate these answers without knowing the detailed characteristics of the diode (make sure you understand why this is the case). Let us assume that the diode i ...
Lighting Load Protection
... Service disconnecting means can consist of one to six switches for each service (230.71) or for each set of service entrance conductors permitted in 230.2. When more than one switch is used, the switches must be grouped together (230.71). Service equipment must have adequate short circuit ratings fo ...
... Service disconnecting means can consist of one to six switches for each service (230.71) or for each set of service entrance conductors permitted in 230.2. When more than one switch is used, the switches must be grouped together (230.71). Service equipment must have adequate short circuit ratings fo ...
Fault Analysis
... • The AC current flowing in the generator during the sub-transient period is called the sub-transient current and is denoted by I”. The time constant of the sub-transient current is denoted by T” and it can be determined from the slope. This current can be as much as 10 times the steady-state fault ...
... • The AC current flowing in the generator during the sub-transient period is called the sub-transient current and is denoted by I”. The time constant of the sub-transient current is denoted by T” and it can be determined from the slope. This current can be as much as 10 times the steady-state fault ...
ground fault neutralizer
... Figure 2 A modern fast tuning solid core arc suppression coil (right hand of picture) forming the high voltage part of the GFN system The arc suppression coil forms a parallel resonant circuit with the phase-to-ground capacitive leakage (Co) of the network. By this resonant circuit the source impeda ...
... Figure 2 A modern fast tuning solid core arc suppression coil (right hand of picture) forming the high voltage part of the GFN system The arc suppression coil forms a parallel resonant circuit with the phase-to-ground capacitive leakage (Co) of the network. By this resonant circuit the source impeda ...
electroporator
... voltage gradient of 2.5 KV per 0.2 cm = 12.5 V/cm. If the smaller 1-mm cuvettes are used, the input voltage should be reduced to 1.25 KV in order to maintain the same initial voltage gradient of 12.5 V/cm. ...
... voltage gradient of 2.5 KV per 0.2 cm = 12.5 V/cm. If the smaller 1-mm cuvettes are used, the input voltage should be reduced to 1.25 KV in order to maintain the same initial voltage gradient of 12.5 V/cm. ...
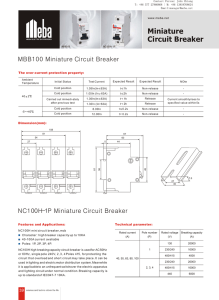
Meba Main switch NC100H 1P 127.26 kB
... NC100H-2P Miniature Circuit Breaker Features and Applications: NC100H mini circuit breaker, mcb Character: high breaker capacity up to 10KA 40-100A current avaliable Poles: 1P, 2P, 3P, 4P. NC100H high breaking capaci ty circuit breaker is used for AC 50Hz or 60Hz, single pole 240V, 2, 3, 4 Poles 415 ...
... NC100H-2P Miniature Circuit Breaker Features and Applications: NC100H mini circuit breaker, mcb Character: high breaker capacity up to 10KA 40-100A current avaliable Poles: 1P, 2P, 3P, 4P. NC100H high breaking capaci ty circuit breaker is used for AC 50Hz or 60Hz, single pole 240V, 2, 3, 4 Poles 415 ...