Motor Controller Marking
... This paragraph means that the branch circuit overcurrent protection for overload relays in motor controllers must be no greater than the maximum size as shown in the manufacturer’s overload relay table. These maximum branch circuit sizes must be observed even though other portions of 430.52 allow la ...
... This paragraph means that the branch circuit overcurrent protection for overload relays in motor controllers must be no greater than the maximum size as shown in the manufacturer’s overload relay table. These maximum branch circuit sizes must be observed even though other portions of 430.52 allow la ...
File - MIT Section X
... Inductor stores energy in its magnetic field. When a series RL circuit is connected to a d.c voltage source, there is an exponential growth of current through the inductor and the current decays exponentially when the voltage source is removed. Time constant of a series RL circuit is ...
... Inductor stores energy in its magnetic field. When a series RL circuit is connected to a d.c voltage source, there is an exponential growth of current through the inductor and the current decays exponentially when the voltage source is removed. Time constant of a series RL circuit is ...
Answers to SPARKS Magazine – September Issue 2014
... Permit – to – Work: The permit-to-work system must be applied to work on high voltage (HV) systems that have been made ‘dead’ and for certain low voltage (LV) work such as the case when more than one person will be working on the isolated circuit A Permit is a statement that a circuit or item of equ ...
... Permit – to – Work: The permit-to-work system must be applied to work on high voltage (HV) systems that have been made ‘dead’ and for certain low voltage (LV) work such as the case when more than one person will be working on the isolated circuit A Permit is a statement that a circuit or item of equ ...
Int. to Basic Electronics - Kashif Bashir
... •Such electrons that can move freely from one atom to atom to the next are often called free electrons. The movement of free electrons that provides electric current in a metal conductor. •When electrons can move easily from atom to atom in a material, it is a conductor. • In general all the metals ...
... •Such electrons that can move freely from one atom to atom to the next are often called free electrons. The movement of free electrons that provides electric current in a metal conductor. •When electrons can move easily from atom to atom in a material, it is a conductor. • In general all the metals ...
Problem Solving Guidelines
... – has only two terminals – is described mathematically in terms of current and/or voltage – Cannot be subdivided into other elements ...
... – has only two terminals – is described mathematically in terms of current and/or voltage – Cannot be subdivided into other elements ...
This is a preliminary list of courses for the study year 2016/2017
... The subject is devoted to simulation of electrical circuits. Principles of composing of differential equation systems for electrical equipment, of their numerical calculation, and its features in MATLAB are given in the first significant part of the course. The second part is devoted to PSPICE circu ...
... The subject is devoted to simulation of electrical circuits. Principles of composing of differential equation systems for electrical equipment, of their numerical calculation, and its features in MATLAB are given in the first significant part of the course. The second part is devoted to PSPICE circu ...
Slash Rated Devices 1
... its ability to open an overcurrent at a specified voltage utilizing only one pole of the circuit breaker. What are the single-pole interrupting capabilities for overcurrent devices? Per ANSI C37.13 and C37.16, an airframe/power circuit breaker has a single-pole interrupting rating of 87% of its thre ...
... its ability to open an overcurrent at a specified voltage utilizing only one pole of the circuit breaker. What are the single-pole interrupting capabilities for overcurrent devices? Per ANSI C37.13 and C37.16, an airframe/power circuit breaker has a single-pole interrupting rating of 87% of its thre ...
Chapter 16 Study Guide
... Review the following facts: The domains in an unmagnetized material that can be magnetized are aligned in all directions. The strength of an electromagnet cannot be increased by reversing the current. Moving a magnet in and out of a coil of wire produces an electric current. If both coils o ...
... Review the following facts: The domains in an unmagnetized material that can be magnetized are aligned in all directions. The strength of an electromagnet cannot be increased by reversing the current. Moving a magnet in and out of a coil of wire produces an electric current. If both coils o ...
Basic Electrical Quantities - Pojęcia
... central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Hydrogen is the simplest atom.  atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus.  atomic weight – approximately the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.  copper – the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.  sh ...
... central nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons. Hydrogen is the simplest atom.  atomic number – the number of protons in the nucleus.  atomic weight – approximately the numbers of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.  copper – the most commonly used metal in electrical applications.  sh ...
An Introduction to Electrical Power for the Non-Power
... Direct current means that current always flows in one direction and is the simplest type of circuit to grasp for reasons we’ll cover soon. Alternating current means the voltage and current are sine waves that change direction (flow) or oscillate continuously. In North America this typically happens ...
... Direct current means that current always flows in one direction and is the simplest type of circuit to grasp for reasons we’ll cover soon. Alternating current means the voltage and current are sine waves that change direction (flow) or oscillate continuously. In North America this typically happens ...
Electric charge
... How is voltage measured? Voltage is measured using a voltmeter or a digital multimeter. ...
... How is voltage measured? Voltage is measured using a voltmeter or a digital multimeter. ...
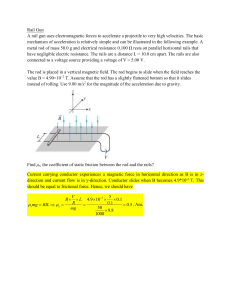
A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to
... Rail Gun A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rail ...
... Rail Gun A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 50.0 g and electrical resistance 0.100 Ω rests on parallel horizontal rail ...
Electric Current and Circuits Powerpoint
... • When a wire connects the terminals of a battery or generators, then the voltage will push and pull electrons through a conductor. – One terminal has extra electrons thus a negative charge. The other terminal has a deficit of electrons and thus a positive charge. – Electrons in the wire are pushed ...
... • When a wire connects the terminals of a battery or generators, then the voltage will push and pull electrons through a conductor. – One terminal has extra electrons thus a negative charge. The other terminal has a deficit of electrons and thus a positive charge. – Electrons in the wire are pushed ...
generators and transformers
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
... outlet in your house, you will find is that the power looks like a sine wave, and that wave oscillates between -170 volts and 170 volts (the peaks are indeed at 170 volts; it is the effective (rms) voltage that is 120 volts). • The rate of oscillation for the sine wave is 60 cycles per second. Oscil ...
Grounding and Bonding
... The following terms are used throughout this section. Note: Where different terms are used for the same object, the AT&T alternative names to which these terms apply are listed in brackets after the term. Alternating Current Equipment Grounding Conductor (ACEG) - The conductor used to connect the no ...
... The following terms are used throughout this section. Note: Where different terms are used for the same object, the AT&T alternative names to which these terms apply are listed in brackets after the term. Alternating Current Equipment Grounding Conductor (ACEG) - The conductor used to connect the no ...
HPSC OBJ: Electrcity
... Define electric potential energy and explain how the amount of electric potential energy can change Define electric potential (voltage) and the SI unit used to measure it Describe how charges move and how their energy changes within a closed conducting path when that path contains a voltage so ...
... Define electric potential energy and explain how the amount of electric potential energy can change Define electric potential (voltage) and the SI unit used to measure it Describe how charges move and how their energy changes within a closed conducting path when that path contains a voltage so ...