CHAPTER 3 CAUSES AND EFFECTS OF ELECTRICAL FAULTS
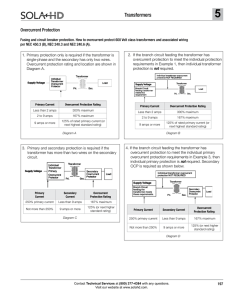
... drive. Aging and thermal cycling cause a decrease in dielectric strength of the insulation in the stator winding. This can produce a low impedance path from the supply to ground resulting in ground fault currents which can be quite high in solidly grounded systems. In resistance grounded systems, th ...
... drive. Aging and thermal cycling cause a decrease in dielectric strength of the insulation in the stator winding. This can produce a low impedance path from the supply to ground resulting in ground fault currents which can be quite high in solidly grounded systems. In resistance grounded systems, th ...
T3200 Insulation Monitoring Relay
... The instrument output has been adapted for connection of a megaohmmeter which indicates the actual insulation level, either by means of two instruments simultaneously indicating for both insulation systems (I and II), or by means of one instrument which can be connected to the two instrument outputs ...
... The instrument output has been adapted for connection of a megaohmmeter which indicates the actual insulation level, either by means of two instruments simultaneously indicating for both insulation systems (I and II), or by means of one instrument which can be connected to the two instrument outputs ...
CFE Generator Protection Guidelines for Setting 40 and 64G
... A solid connection to ground limits the voltage rise on the unfaulted phases for phase-to-ground faults. The ground fault current is limited only by the generator impedance. Because generator zero-sequence impedance is normally low, high ground fault currents are common. Additionally, even if protec ...
... A solid connection to ground limits the voltage rise on the unfaulted phases for phase-to-ground faults. The ground fault current is limited only by the generator impedance. Because generator zero-sequence impedance is normally low, high ground fault currents are common. Additionally, even if protec ...
AESO System Operating Limits Methodology for the Planning Horizon (R1 FAC-010-AB-2.1)
... following either of these multiple contingencies: (i) a common mode outage of two (2) generating units connected to the same switchyard not otherwise addressed by reliability standard FAC-010-AB; or (ii) the loss of multiple bus sections as a result of failure or delayed clearing of a bus tie or bus ...
... following either of these multiple contingencies: (i) a common mode outage of two (2) generating units connected to the same switchyard not otherwise addressed by reliability standard FAC-010-AB; or (ii) the loss of multiple bus sections as a result of failure or delayed clearing of a bus tie or bus ...
Numerical Arc Model Parameter Extraction for SF6 Circuit
... of computer methods is the most affordable approach to study circuit breakers, reducing the cost and space needed when realizing synthetic test circuits. Nowadays the fundamental problem when trying to implement the existing mathematical arc models is to obtain reliable values of the unknown paramet ...
... of computer methods is the most affordable approach to study circuit breakers, reducing the cost and space needed when realizing synthetic test circuits. Nowadays the fundamental problem when trying to implement the existing mathematical arc models is to obtain reliable values of the unknown paramet ...
Protection and Control Requirements for Generators
... An important objective in the interconnection of facilities to the PG&E Power System is minimizing the potential hazard to life and property. A primary safety requirement is the ability to disconnect immediately when a fault is detected. The protection equipment for a generation facility must protec ...
... An important objective in the interconnection of facilities to the PG&E Power System is minimizing the potential hazard to life and property. A primary safety requirement is the ability to disconnect immediately when a fault is detected. The protection equipment for a generation facility must protec ...
Power and automation products and services Global product
... Dry-type medium voltage transformers, available with ratings up to 63 MVA and 72 kV are an excellent solution for data center substations. Virtually maintenance free, with extremely low fire risk, they can also be placed very close to the supplied load, if a dedicated installation should be required ...
... Dry-type medium voltage transformers, available with ratings up to 63 MVA and 72 kV are an excellent solution for data center substations. Virtually maintenance free, with extremely low fire risk, they can also be placed very close to the supplied load, if a dedicated installation should be required ...
conductor maintenance manual
... The Conductor module is fitted with a number of devices designed to detect incorrect operation and prevent damage to the controller. One such device is the MOV fitted to the rear terminals of the Conductor module. The purpose of the MOV is to absorb the energy from spikes on the mains voltage. Howev ...
... The Conductor module is fitted with a number of devices designed to detect incorrect operation and prevent damage to the controller. One such device is the MOV fitted to the rear terminals of the Conductor module. The purpose of the MOV is to absorb the energy from spikes on the mains voltage. Howev ...
Charges forces and fields
... (e) between a thunder cloud and the ground if the p.d between the cloud and the ground is 1000 MV and the cloud is 1 km above it. r for air = 1.000 0536) (f) 4.5 m from the dome of a Van de Graaff generator if the charge on the dome is 2.5x10-5 C 3. Calculate the potentials at the following points: ...
... (e) between a thunder cloud and the ground if the p.d between the cloud and the ground is 1000 MV and the cloud is 1 km above it. r for air = 1.000 0536) (f) 4.5 m from the dome of a Van de Graaff generator if the charge on the dome is 2.5x10-5 C 3. Calculate the potentials at the following points: ...
Lecture 2 rev2
... [5] J. Tschanz et al, “Design optimizations of a high performance microprocessor using combinations of dual-Vt allocation and transistor sizing”, Symposium on VLSI Circuits 2002, pp. 218-219. [6] A. Keshavarzi et al, “Forward body bias for microprocessors in 130nm technology generation and beyond”, ...
... [5] J. Tschanz et al, “Design optimizations of a high performance microprocessor using combinations of dual-Vt allocation and transistor sizing”, Symposium on VLSI Circuits 2002, pp. 218-219. [6] A. Keshavarzi et al, “Forward body bias for microprocessors in 130nm technology generation and beyond”, ...
“When in Doubt, Lock it out!”
... approached nearer than a safe distance by a person. • “Limited Approach Boundary” - distance (based on voltage) from an exposed energized electrical conductor or circuit part within which a shock hazard exists ...
... approached nearer than a safe distance by a person. • “Limited Approach Boundary” - distance (based on voltage) from an exposed energized electrical conductor or circuit part within which a shock hazard exists ...