Ch. 24 Presentation
... – collect fluid from body tissues and – return it as lymph to the blood. ...
... – collect fluid from body tissues and – return it as lymph to the blood. ...
35 - Southgate Schools
... _______________________________can relax smooth muscles around the airways and relieve asthma symptoms. Autoimmune Diseases Sometimes a disease occurs in which the immune system fails to properly recognize “___________,” and it attacks cells in the body like they were pathogens. When the immune sys ...
... _______________________________can relax smooth muscles around the airways and relieve asthma symptoms. Autoimmune Diseases Sometimes a disease occurs in which the immune system fails to properly recognize “___________,” and it attacks cells in the body like they were pathogens. When the immune sys ...
Innate Immune Defects - Immune Deficiency Foundation
... Primary immunodeficiency diseases are disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly. These disorders can be divided into two groups: 1) Those less common conditions with defects in the innate immune system, a system of cells and mechanisms that defend t ...
... Primary immunodeficiency diseases are disorders in which part of the body's immune system is missing or does not function properly. These disorders can be divided into two groups: 1) Those less common conditions with defects in the innate immune system, a system of cells and mechanisms that defend t ...
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is the most prevalent arbovirus
... inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). At the same time pDCs exhibited only a transient upregulation of surface molecule markers (adhesion markers CD54, CD58, maturation marker CD83, co-stimulatory and activation markers CD40, CD80, CD86, apoptosis ma ...
... inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8 and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). At the same time pDCs exhibited only a transient upregulation of surface molecule markers (adhesion markers CD54, CD58, maturation marker CD83, co-stimulatory and activation markers CD40, CD80, CD86, apoptosis ma ...
Immune Worksheet Key Session 26
... 1) Name and describe the four steps for phagocyte mobilization (how does the phagocyte reach the pathogen in the first place?): Step 1: Leukocytosis: Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow Step 2: Margination: Neutrophils cling to the capillary wall Step 3: Diapedesis: Neutrophils flatten and sque ...
... 1) Name and describe the four steps for phagocyte mobilization (how does the phagocyte reach the pathogen in the first place?): Step 1: Leukocytosis: Neutrophils enter blood from bone marrow Step 2: Margination: Neutrophils cling to the capillary wall Step 3: Diapedesis: Neutrophils flatten and sque ...
Emotions and Body Chemicals
... organs, and entire body systems. At the same time peptides not only coordinate almost all body functions on a physical level, but also on an emotional level. These powerful biochemicals are concentrated in the limbic system (see above), the seat of the emotions, and play an important role in governi ...
... organs, and entire body systems. At the same time peptides not only coordinate almost all body functions on a physical level, but also on an emotional level. These powerful biochemicals are concentrated in the limbic system (see above), the seat of the emotions, and play an important role in governi ...
Bio 347 Ch 12 Cytokines
... 6. T helper cells are divided into T helper 1 and T helper 2 on basis of cytokine production 7. T helper 1 cells can down-regulte T helper 2 cells and vice versa 8. cytokines act in a network (immune response is dependent on pattern of cytokines a cell is exposed to and receptors the cell expresses) ...
... 6. T helper cells are divided into T helper 1 and T helper 2 on basis of cytokine production 7. T helper 1 cells can down-regulte T helper 2 cells and vice versa 8. cytokines act in a network (immune response is dependent on pattern of cytokines a cell is exposed to and receptors the cell expresses) ...
Bio 347 Ch 12 Cytokines
... (acting on cells close by) rather than endocrine (acting on cells at a distance) 3. cytokines regulate expression of own receptor or other cytokine receptors 4. many cytokines act by causing aggregation of receptors at the cell surface 5. Cytoknes act synergistically or antagonistically (bind recept ...
... (acting on cells close by) rather than endocrine (acting on cells at a distance) 3. cytokines regulate expression of own receptor or other cytokine receptors 4. many cytokines act by causing aggregation of receptors at the cell surface 5. Cytoknes act synergistically or antagonistically (bind recept ...
Nobel Prize of physiology or medicine (1984) (4) Part I The
... development of medical immunology. In the present review, we will present an outline of his work concerning skin diseases. The first theory: (Specificity is predetermined) ...
... development of medical immunology. In the present review, we will present an outline of his work concerning skin diseases. The first theory: (Specificity is predetermined) ...
Editorial: Bacterial Exotoxins: How Bacteria Fight the Immune System
... responses with the ultimate goal to eliminate the invader and to return to homeostasis. Occasionally, however, the body may react inadequately, resulting in collateral damage to tissues if the response it too strong or in a failure to eradicate the pathogen if the response is too weak or ephemeral. ...
... responses with the ultimate goal to eliminate the invader and to return to homeostasis. Occasionally, however, the body may react inadequately, resulting in collateral damage to tissues if the response it too strong or in a failure to eradicate the pathogen if the response is too weak or ephemeral. ...
Chronic Stress and The Body
... Stress is perceived by the body, as a threat and therefore the body reacts by amping up the protective capabilities o The hypothalamus signals the adrenal glands to release the hormones of adrenaline and cortisol o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Co ...
... Stress is perceived by the body, as a threat and therefore the body reacts by amping up the protective capabilities o The hypothalamus signals the adrenal glands to release the hormones of adrenaline and cortisol o Adrenaline increases the heart rate, elevates BP and boosts the supply of energy o Co ...
AP Chapters 42 Study Guide: Circulation and Gas Exchange
... common are ____________________________ (60-70%) of white blood cells. Unfortunately, while these cells are abundant, they tend to self destruct after engulfing a germ. Less abundant, but more effective are the _________________________________ or “big eaters” which develop from monocytes. These cel ...
... common are ____________________________ (60-70%) of white blood cells. Unfortunately, while these cells are abundant, they tend to self destruct after engulfing a germ. Less abundant, but more effective are the _________________________________ or “big eaters” which develop from monocytes. These cel ...
Lymph capillaries, Lymphatic collecting vessels, Valves, Lymph Duct
... A student nurse receives an injection of gamma globin after she has been exposed to viral hepatitis “Borrowed” immunity ...
... A student nurse receives an injection of gamma globin after she has been exposed to viral hepatitis “Borrowed” immunity ...
Immunology Notes
... the targets of HIV infection and the decrease of CD4+ T cells results in AIDS. Some helper T cells secrete cytokines that turn off the immune response once an antigen has been eliminated from the body 3. Regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells) suppress activation of the immune system and maintain im ...
... the targets of HIV infection and the decrease of CD4+ T cells results in AIDS. Some helper T cells secrete cytokines that turn off the immune response once an antigen has been eliminated from the body 3. Regulatory T cells (suppressor T cells) suppress activation of the immune system and maintain im ...
Emerging Concepts and
... Infection of H. Pylori into the gastric mucosa induces infiltration of T-cells, B-cells, macrophages, and neutrophils ...
... Infection of H. Pylori into the gastric mucosa induces infiltration of T-cells, B-cells, macrophages, and neutrophils ...
The Lymphatic System
... by another organism are injected; recipient is immune as long as antibodies remain in circulation 3. maternal immunity: antibodies are passed from mother to fetus or infant; similar to passive immunity ...
... by another organism are injected; recipient is immune as long as antibodies remain in circulation 3. maternal immunity: antibodies are passed from mother to fetus or infant; similar to passive immunity ...
Chapter 20- Lymphatic system
... • II. The Immune system- This is a very complex system with multiple layers and forms of defense. In this section we focus on the organs closely associated with cellular response of the immune system. The immune system identifies and attacks specific pathogens. • A. Lymphocytes and other cells of t ...
... • II. The Immune system- This is a very complex system with multiple layers and forms of defense. In this section we focus on the organs closely associated with cellular response of the immune system. The immune system identifies and attacks specific pathogens. • A. Lymphocytes and other cells of t ...
Unit 4 - Immunology and Public Health
... Epithelial cells (in cavity linings) produce (protective chemical) secretions ...
... Epithelial cells (in cavity linings) produce (protective chemical) secretions ...
PPoint - Dr. Stuart White
... create immediate and delayed responses from the immune/inflammatory systems The following diseases have been associated with food intolerances/allergies: cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, immune, mental/emotional, musculoskeletal, respiratory, skin, migraines First select friend fro ...
... create immediate and delayed responses from the immune/inflammatory systems The following diseases have been associated with food intolerances/allergies: cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, immune, mental/emotional, musculoskeletal, respiratory, skin, migraines First select friend fro ...
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System Student outline
... b. An activated B-cell proliferates when stimulated by a T-cell, enlarging its clone c. Some activated B-cells specialize into antibody producing plasma cells d. Antibodies react against the antigen-bearing agent 6. Types of antibodies-these are soluble proteins called ______________. a. The five ma ...
... b. An activated B-cell proliferates when stimulated by a T-cell, enlarging its clone c. Some activated B-cells specialize into antibody producing plasma cells d. Antibodies react against the antigen-bearing agent 6. Types of antibodies-these are soluble proteins called ______________. a. The five ma ...
Name - Fairfield Public Schools
... Mammals use specific immune responses triggered by natural or artificial agents that disrupt dynamic homeostasis. o The mammalian immune system includes two types of specific responses: cell mediated and humoral. o In the cell-mediated response, cytotoxic T cells, a type of lymphocytic white blood c ...
... Mammals use specific immune responses triggered by natural or artificial agents that disrupt dynamic homeostasis. o The mammalian immune system includes two types of specific responses: cell mediated and humoral. o In the cell-mediated response, cytotoxic T cells, a type of lymphocytic white blood c ...
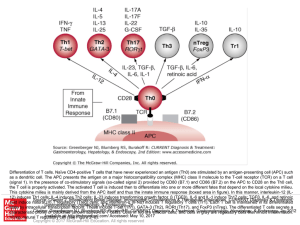
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Differentiation of T cells. Naïve CD4-positive T cells that have never experienced an antigen (Th0) are stimulated by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) such as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on ...
... Differentiation of T cells. Naïve CD4-positive T cells that have never experienced an antigen (Th0) are stimulated by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) such as a dendritic cell. The APC presents the antigen on a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecule to the T-cell receptor (TCR) on ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.