tuberculosis Mycobacterium Early Infection with Dynamic Roles of
... immune responses to intracellular bacteria, including M. tuberculosis. The absolute requirement for IFN-g in the immune control of TB is well established in animal models (3) and humans (4). IFNg–dependent protection is commonly believed to act through increasing the mycobactericidal activity of mac ...
... immune responses to intracellular bacteria, including M. tuberculosis. The absolute requirement for IFN-g in the immune control of TB is well established in animal models (3) and humans (4). IFNg–dependent protection is commonly believed to act through increasing the mycobactericidal activity of mac ...
Dissertation LeWi Fakultät Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
... myopathies and in muscular dystrophies. Thus, the aim of the study was to precisely examine interactions between immune cells, and also analyze characteristic pathological phenomena, such as hypoxia, inflammation and fibrosis. ...
... myopathies and in muscular dystrophies. Thus, the aim of the study was to precisely examine interactions between immune cells, and also analyze characteristic pathological phenomena, such as hypoxia, inflammation and fibrosis. ...
T cells - University of East Anglia
... can sculpt the GIT microbial architecture, diet and metabolic requirements have a major role in the microbiome differences throughout the GIT[70-72]. Interestingly, ileal microbiota display a relative instability over time in humans[73], whereas most bacterial strains of the large intestine reside f ...
... can sculpt the GIT microbial architecture, diet and metabolic requirements have a major role in the microbiome differences throughout the GIT[70-72]. Interestingly, ileal microbiota display a relative instability over time in humans[73], whereas most bacterial strains of the large intestine reside f ...
Cystic Fibrosis Impact on Cellular Function - Carroll Collected
... deficiency of digestive enzymes occurs, leading to badly absorbed undigested foods and malnutrition (1). Islet cells in the pancreas could become damaged with time, leading to a decrease in insulin and glucagon secretion; proper secretion of these essential hormones is important for the regulation o ...
... deficiency of digestive enzymes occurs, leading to badly absorbed undigested foods and malnutrition (1). Islet cells in the pancreas could become damaged with time, leading to a decrease in insulin and glucagon secretion; proper secretion of these essential hormones is important for the regulation o ...
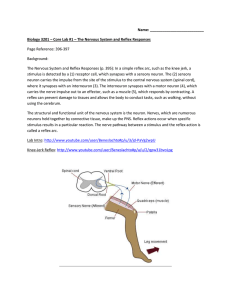
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
Giuliana Magri Characterization of natural killer cell response to human cytomegalovirus
... differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th1 helper cells20,21. Following activation, NK cells have been shown to secrete chemokines, like MIP 1α, MIP 1β, IL-8 and RANTES, with the capacity to recruit T cells, B cells, neutrophils, and other activated NK cells at sites of inflammation22. The traff ...
... differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th1 helper cells20,21. Following activation, NK cells have been shown to secrete chemokines, like MIP 1α, MIP 1β, IL-8 and RANTES, with the capacity to recruit T cells, B cells, neutrophils, and other activated NK cells at sites of inflammation22. The traff ...
Temporal and spatial receptive field characteristics of tectal neurons
... could receive inputs from many different parts of the retina. It can be speculated that this large dendritic integration area might be responsible for the lack of retinotopy within these cells (see results). At this age, the larvae have not yet developed a solid skull and so the only tissue covering ...
... could receive inputs from many different parts of the retina. It can be speculated that this large dendritic integration area might be responsible for the lack of retinotopy within these cells (see results). At this age, the larvae have not yet developed a solid skull and so the only tissue covering ...
Impact of AS03 Adjuvant System on T cell
... group assuming five subjects/per group would be non-evaluable. Seventy subjects in each of the ≥65 year age groups would give 90% power to demonstrate superiority of TIV/AS03 over TIV in vaccine strain-specific CD4+ T-cell responses, assuming a 1.5-fold greater response in the TIV/AS03 recipients co ...
... group assuming five subjects/per group would be non-evaluable. Seventy subjects in each of the ≥65 year age groups would give 90% power to demonstrate superiority of TIV/AS03 over TIV in vaccine strain-specific CD4+ T-cell responses, assuming a 1.5-fold greater response in the TIV/AS03 recipients co ...
PHS 398 (Rev. 9/04), Biographical Sketch Format Page
... Disruption of differentiated functions during viral infection in vivo. V. Mapping of a locus involved in susceptibility of mice to growth hormone deficiency due to persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Virology 281:61-66 (2001) Pertl, U., A.D. Luster, N.M. Varki, D. Homann, G. Gae ...
... Disruption of differentiated functions during viral infection in vivo. V. Mapping of a locus involved in susceptibility of mice to growth hormone deficiency due to persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Virology 281:61-66 (2001) Pertl, U., A.D. Luster, N.M. Varki, D. Homann, G. Gae ...
Study Guide for chapter 14 Innate Immune System
... Study Guide for chapter 14 Innate Immune System 1) Lysozyme type enzymes have bacteroidal properties. These enzymes are most effective against gram (+) or gram (-) type bacterial and why? (3 pts) ...
... Study Guide for chapter 14 Innate Immune System 1) Lysozyme type enzymes have bacteroidal properties. These enzymes are most effective against gram (+) or gram (-) type bacterial and why? (3 pts) ...
Principles and Applications of Pavlovian Conditioning
... When animals or people are exposed to food, they exhibit a set of unconditioned responses which prepare them to digest, metabolize, and store ingested food. These unconditioned feeding responses include the secretion of saliva, gastric juices, pancreatic enzymes, and insulin. One important action of ...
... When animals or people are exposed to food, they exhibit a set of unconditioned responses which prepare them to digest, metabolize, and store ingested food. These unconditioned feeding responses include the secretion of saliva, gastric juices, pancreatic enzymes, and insulin. One important action of ...
Reproductive Immunology: Biomarkers of
... transplantation can react with autologous T-lymphoblasts primed against the immunizing donor (14). These observations coupled with the finding that primed T-cells display idiotypelike receptors for alloantigens has prompted an idea that T-cell receptors induce the formation of anti-idiotypic antibod ...
... transplantation can react with autologous T-lymphoblasts primed against the immunizing donor (14). These observations coupled with the finding that primed T-cells display idiotypelike receptors for alloantigens has prompted an idea that T-cell receptors induce the formation of anti-idiotypic antibod ...
Dynamic and integrative aspects of the regulation of reproduction by
... pulses, is the code used by the nervous system to control gonadal function. The network of neurons that controls GnRH secretion is thought to be the most direct pathway via which many factors influence gonadal activity, including metabolic status (review: [2]). It has to be noted that the pituitary ...
... pulses, is the code used by the nervous system to control gonadal function. The network of neurons that controls GnRH secretion is thought to be the most direct pathway via which many factors influence gonadal activity, including metabolic status (review: [2]). It has to be noted that the pituitary ...
Document
... Although the control of transplantation, autoimmunity, and the other immune responses are the phenotypic consequences of the function of molecules encoded in the Mhc, understanding the Mhc becomes clear if we think of it in molecular and cellular terms. MHC molecules are cell surface receptors that ...
... Although the control of transplantation, autoimmunity, and the other immune responses are the phenotypic consequences of the function of molecules encoded in the Mhc, understanding the Mhc becomes clear if we think of it in molecular and cellular terms. MHC molecules are cell surface receptors that ...
Role of the PD‐1 Pathway in the Immune Response
... effector function (37). However, a strong positive signaling through CD28 and/or IL-2 receptor can overcome PD-1 inhibitory effects on T cell proliferation, differentiation and survival (5,18,37,38). PD-1 signaling has also been implicated in reversal of the “stop signal” that is mediated by TCR sig ...
... effector function (37). However, a strong positive signaling through CD28 and/or IL-2 receptor can overcome PD-1 inhibitory effects on T cell proliferation, differentiation and survival (5,18,37,38). PD-1 signaling has also been implicated in reversal of the “stop signal” that is mediated by TCR sig ...
Immunology and Serology
... implies that such microbial inhabitants are harmless For the most part, normal flora microorganisms do not cause disease. ...
... implies that such microbial inhabitants are harmless For the most part, normal flora microorganisms do not cause disease. ...
Chronic stress prior to hippocampal stroke
... group. Our results indicate that a history of chronic stress sensitizes hippocampal cells to the damaging consequences of focal ischemia. The opposing effects of CORT-related experiences in this study not only reflect the diversity of glucocorticoid actions in the stress response, but also provide ev ...
... group. Our results indicate that a history of chronic stress sensitizes hippocampal cells to the damaging consequences of focal ischemia. The opposing effects of CORT-related experiences in this study not only reflect the diversity of glucocorticoid actions in the stress response, but also provide ev ...
Raulet, D.H. 2003. Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat Rev Immunol 3:781-790.
... is, perhaps, the best characterized receptor that is associated with responses to cellular distress, defined as transformation, infection or cell stress. This review summarizes recent findings that concern NKG2D, its ligands, its signalling properties and its role in disease, and provides a framewor ...
... is, perhaps, the best characterized receptor that is associated with responses to cellular distress, defined as transformation, infection or cell stress. This review summarizes recent findings that concern NKG2D, its ligands, its signalling properties and its role in disease, and provides a framewor ...
T Cell Receptor (TCR)
... MHC expression on cells-II Expression of MHC molecules is increased by cytokines produced during innate & adaptive immune cells, e.g. IFN ...
... MHC expression on cells-II Expression of MHC molecules is increased by cytokines produced during innate & adaptive immune cells, e.g. IFN ...
Psychoneuroimmunology

Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI), also referred to as psychoendoneuroimmunology (PENI), is the study of the interaction between psychological processes and the nervous and immune systems of the human body. PNI takes an interdisciplinary approach, incorporating psychology, neuroscience, immunology, physiology, genetics, pharmacology, molecular biology, psychiatry, behavioral medicine, infectious diseases, endocrinology, and rheumatology.The main interests of PNI are the interactions between the nervous and immune systems and the relationships between mental processes and health. PNI studies, among other things, the physiological functioning of the neuroimmune system in health and disease; disorders of the neuroimmune system (autoimmune diseases; hypersensitivities; immune deficiency); and the physical, chemical and physiological characteristics of the components of the neuroimmune system in vitro, in situ, and in vivo.