Unit 2: Geography
... are flat drawings of all or part of the Earth’s surface Maps are more convenient to carry around than globes Maps can show small areas in great detail Maps can show political borders, population densities, area resources, etc. Maps cannot show true size, shape, distance and direction at ...
... are flat drawings of all or part of the Earth’s surface Maps are more convenient to carry around than globes Maps can show small areas in great detail Maps can show political borders, population densities, area resources, etc. Maps cannot show true size, shape, distance and direction at ...
#1: Define site and provide two examples. #2: Define situation and
... Choropleth Map NATURAL BREAKS (JENKS’ FORMULA) ...
... Choropleth Map NATURAL BREAKS (JENKS’ FORMULA) ...
Answers
... (10) If an earthquake occurs, the first waves to arrive at a seismograph are the: (a) P waves ...
... (10) If an earthquake occurs, the first waves to arrive at a seismograph are the: (a) P waves ...
Geologic Time Scale
... Geologic events Eras are divided by major mass extinctions Periods further divide time in tens of millions of years ...
... Geologic events Eras are divided by major mass extinctions Periods further divide time in tens of millions of years ...
Printable Geologic Time Scale
... Index fossils are fossils used to define and identify geologic periods. If geologists find specific fossils in sedimentary rock deposits they are able to estimate how long ago the rocks formed. In this lab you will identify and date fossils using the geologic time scale on the back of this lab. Reco ...
... Index fossils are fossils used to define and identify geologic periods. If geologists find specific fossils in sedimentary rock deposits they are able to estimate how long ago the rocks formed. In this lab you will identify and date fossils using the geologic time scale on the back of this lab. Reco ...
Terrestrial Coordinate System/Chart Projections and Numbering
... • Great Circle: the intersection of a plane passing through two points on the surface of the earth and the center of the earth. • Some key points: – A great circle is the largest circle that can be drawn on the face of the earth. – A great circle represents the shortest distance between two points o ...
... • Great Circle: the intersection of a plane passing through two points on the surface of the earth and the center of the earth. • Some key points: – A great circle is the largest circle that can be drawn on the face of the earth. – A great circle represents the shortest distance between two points o ...
Quiz 1 - Word Document
... coordinates or a grid system designed for locational purposes, e.g., latitude and longitude. Built landscape - the part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the buildings, roads, bridges, and similar structures large and small of the cultural landscape. Cartogram - a map that ...
... coordinates or a grid system designed for locational purposes, e.g., latitude and longitude. Built landscape - the part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the buildings, roads, bridges, and similar structures large and small of the cultural landscape. Cartogram - a map that ...
Geography - Foxfire Schools
... imaginary lines that break the Earth into distance measurements from the Prime Meridian. i.e. – lines parallel to the Prime Meridian running North and South 180 degrees ...
... imaginary lines that break the Earth into distance measurements from the Prime Meridian. i.e. – lines parallel to the Prime Meridian running North and South 180 degrees ...
2A-Map_Projections_and_Scales.pps
... Attempt to eliminate distortion in one or several aspects of the map. The map maker must choose which distortions are less important than the others. They may choose to allow a little distortion in all four of the following aspects to produce the right type of map. •Conformality - the shapes of plac ...
... Attempt to eliminate distortion in one or several aspects of the map. The map maker must choose which distortions are less important than the others. They may choose to allow a little distortion in all four of the following aspects to produce the right type of map. •Conformality - the shapes of plac ...
Section 1- Geography - Warren County Schools
... Because Earth is a 3D sphere and maps are flat (2D), the size and shape of features get distorted, or stretched. Globes are most accurate, but not as handy as maps. There are different MAP PROJECTIONS that work best for what geographers want to study. The photos on page 4 of your Interactive Noteboo ...
... Because Earth is a 3D sphere and maps are flat (2D), the size and shape of features get distorted, or stretched. Globes are most accurate, but not as handy as maps. There are different MAP PROJECTIONS that work best for what geographers want to study. The photos on page 4 of your Interactive Noteboo ...
Mapping Earth`s Surface
... Scales and Ratios A ratio compares two numbers by division. For example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
... Scales and Ratios A ratio compares two numbers by division. For example, the scale of a map given as a ratio is 1:250,000. At this scale, the distance between two points on the map measures 23.5 cm. How would you find the actual distance? 1. Write the scale as a fraction. ...
Ch_ 1
... Map projection of a world map which shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image. The meridians curve gently, avoiding extremes, but thereby stretch the poles into long lines inst ...
... Map projection of a world map which shows the entire world at once. It was specifically created in an attempt to find a good compromise to the problem of readily showing the whole globe as a flat image. The meridians curve gently, avoiding extremes, but thereby stretch the poles into long lines inst ...
Review Guide Key
... Map developed in your mind – it is used to carry out daily activities, give directions, and understand world events – it is refined by using reference points or relative locations and comparing mental maps to real world maps and atlases 6. List three primary sources of information used by cartograph ...
... Map developed in your mind – it is used to carry out daily activities, give directions, and understand world events – it is refined by using reference points or relative locations and comparing mental maps to real world maps and atlases 6. List three primary sources of information used by cartograph ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... What are some advantages and disadvantages of using a globe to show the Earth’s surface? Why do all maps have distortion? Why are there so many different types of map projections? How can knowing the parts of a map help you? How do cartographers use the different parts of the map? ...
... What are some advantages and disadvantages of using a globe to show the Earth’s surface? Why do all maps have distortion? Why are there so many different types of map projections? How can knowing the parts of a map help you? How do cartographers use the different parts of the map? ...
Unit One Geography: It`s Nature and Perspectives
... • The representation of real world phenomena at a certain level of reduction or generalization. • The ratio between the size of an area on a map and the actual size of that same area on the earth’s surface. ...
... • The representation of real world phenomena at a certain level of reduction or generalization. • The ratio between the size of an area on a map and the actual size of that same area on the earth’s surface. ...
Name: Date: Chapter 1 Notes The Geographer`s Toolbox 1.1
... Geographic information Systems: geographers use computer based systems to create maps and analyze patterns. They are used for city planning, businesses for marketing, selecting store locations, and for analyzing and displaying weather maps 1.2 Themes and Elements Geographers use the five themes of g ...
... Geographic information Systems: geographers use computer based systems to create maps and analyze patterns. They are used for city planning, businesses for marketing, selecting store locations, and for analyzing and displaying weather maps 1.2 Themes and Elements Geographers use the five themes of g ...
Document
... 7) Revolve -When the Earth orbits the sun in a circular path. It takes 365 ¼ days for the Earth to revolve around the sun. 8) Longitude -Lines that run North and South and measure East and West. 9) Meridians -Lines of Longitude 10) Prime Meridian -An imaginary line of longitude that separates the Ea ...
... 7) Revolve -When the Earth orbits the sun in a circular path. It takes 365 ¼ days for the Earth to revolve around the sun. 8) Longitude -Lines that run North and South and measure East and West. 9) Meridians -Lines of Longitude 10) Prime Meridian -An imaginary line of longitude that separates the Ea ...
Geographic Fundamentals
... The four cardinal or main directions are north, east, south and west. There are also four intermediate directions which are points halfway between each pair of cardinal directions. The intermediate directions are NE, SE, SW and NW. ...
... The four cardinal or main directions are north, east, south and west. There are also four intermediate directions which are points halfway between each pair of cardinal directions. The intermediate directions are NE, SE, SW and NW. ...
Intro to Geography Study Guide
... 8. Give an example of a Primary Source: records made by people who took part or saw an event: diaries, photographs, artifacts 9. Give an example of a Secondary Source: a record of an event by someone who was not at an event at the time it happened *****Map Skills***** ...
... 8. Give an example of a Primary Source: records made by people who took part or saw an event: diaries, photographs, artifacts 9. Give an example of a Secondary Source: a record of an event by someone who was not at an event at the time it happened *****Map Skills***** ...
Geography Handbook Power Point
... A graph is a way of summarizing and presenting information visually. Each part of a graph gives useful info. 1st read a graph’s title to find out the subject. 2nd read the labels along the axes. One axis will tell what is being measured; the other axis will tell units of measurement. Bar graphs use ...
... A graph is a way of summarizing and presenting information visually. Each part of a graph gives useful info. 1st read a graph’s title to find out the subject. 2nd read the labels along the axes. One axis will tell what is being measured; the other axis will tell units of measurement. Bar graphs use ...
Absolute location: Position of an object on the global
... Sense of place: Person’s perspective of the human and physical attributes of a location that give it a unique identity in that person’s mind Simplification: Cartographer’s process of eliminating unnecessary details and focusing on the information that needs to be displayed in the map Site: Internal ...
... Sense of place: Person’s perspective of the human and physical attributes of a location that give it a unique identity in that person’s mind Simplification: Cartographer’s process of eliminating unnecessary details and focusing on the information that needs to be displayed in the map Site: Internal ...
mapprojections - Auburn University
... across the map is called conformal. • A projection that preserves the area of a feature across the map is called equal area or equivalent. • No flat map can be both equivalent and conformal. Most fall between the two as compromises. • To compare or edge-match maps in a GIS, both maps MUST be in the ...
... across the map is called conformal. • A projection that preserves the area of a feature across the map is called equal area or equivalent. • No flat map can be both equivalent and conformal. Most fall between the two as compromises. • To compare or edge-match maps in a GIS, both maps MUST be in the ...
Maps - Jefferson Township Public Schools
... geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. Prime Meridian—The meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for the measurement of l ...
... geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. Prime Meridian—The meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for the measurement of l ...
Chapter 1 Notes - West Essex High School
... Geographic information Systems: geographers use computer based systems to create maps and analyze patterns. They are used for city planning, businesses for marketing, selecting store locations, and for analyzing and displaying weather maps 1.2 Themes and Elements Geographers use the five themes of g ...
... Geographic information Systems: geographers use computer based systems to create maps and analyze patterns. They are used for city planning, businesses for marketing, selecting store locations, and for analyzing and displaying weather maps 1.2 Themes and Elements Geographers use the five themes of g ...
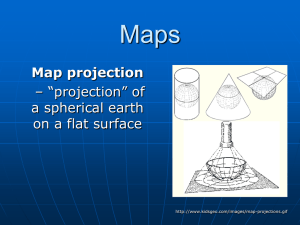
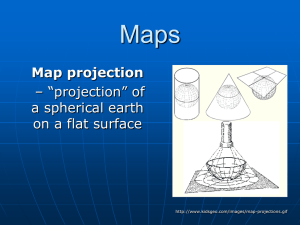
Maps
... geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. Prime Meridian—The meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for the measurement of l ...
... geographical poles and some third point on the Earth's surface. Parallel—A circle or approximation of a circle on the surface of the Earth, parallel to the Equator and connecting points of equal latitude. Prime Meridian—The meridian of longitude 0 degrees, used as the origin for the measurement of l ...