ap human geography - Henry County Schools
... The relative size of different areas may be altered. The distance between two points may be incorrect. The direction from one place to another can be distorted. The shape of an area can be distorted. All of the above can occur. ...
... The relative size of different areas may be altered. The distance between two points may be incorrect. The direction from one place to another can be distorted. The shape of an area can be distorted. All of the above can occur. ...
Unit I - Maps
... All maps are created by projecting the earth’s 3D shape, which in reality is a bumpy oblate spheroid or geoid, onto a 2D surface. 3D shapes can never truly be 2D All flat maps have some distortion in their representation of distance, shape, area, or direction. ...
... All maps are created by projecting the earth’s 3D shape, which in reality is a bumpy oblate spheroid or geoid, onto a 2D surface. 3D shapes can never truly be 2D All flat maps have some distortion in their representation of distance, shape, area, or direction. ...
Document
... ____27. What features do political maps show? A. population density and culture regions B. capitals, cities, and boundaries of nations C. land forms, bodies of water, elevations ...
... ____27. What features do political maps show? A. population density and culture regions B. capitals, cities, and boundaries of nations C. land forms, bodies of water, elevations ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... for maps of the poles. Cylindrical Projection – projecting the globe onto a cylinder. Most accurate near the Equator. Shapes and distances are distorted near the poles. Conic Projection – comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Best sutied for showing limited east-west areas that are not ...
... for maps of the poles. Cylindrical Projection – projecting the globe onto a cylinder. Most accurate near the Equator. Shapes and distances are distorted near the poles. Conic Projection – comes from placing a cone over part of a globe. Best sutied for showing limited east-west areas that are not ...
Map Skills Notes
... There are two basic types of maps: political and physical. Physical maps show elevation and landforms. Political maps show countries, states, etc. There are other types of maps as well such as temperature, products, endangered animals, topographical, etc. A Map key or legend helps provide informatio ...
... There are two basic types of maps: political and physical. Physical maps show elevation and landforms. Political maps show countries, states, etc. There are other types of maps as well such as temperature, products, endangered animals, topographical, etc. A Map key or legend helps provide informatio ...
GEOG 1303 Unit 1 Review
... Orientation — show direction through a compass rose, geographic grid or north arrow Date — the time span in which the map’s data were collected Legend — explain any symbols used in the map to represent features / quantities Scale — a graphic, verbal or fractional scale to indicate the relationship b ...
... Orientation — show direction through a compass rose, geographic grid or north arrow Date — the time span in which the map’s data were collected Legend — explain any symbols used in the map to represent features / quantities Scale — a graphic, verbal or fractional scale to indicate the relationship b ...
Geography Study Guide ANSWER KEY!
... Scale: Tells the distance between two places in real life Map: A visual representation, or model, of part of the Earth Hemisphere: Half of a globe; can be North and South or East and West Projection: A way of showing a curved object on a flat surface Latitude: Imaginary lines that run east to west a ...
... Scale: Tells the distance between two places in real life Map: A visual representation, or model, of part of the Earth Hemisphere: Half of a globe; can be North and South or East and West Projection: A way of showing a curved object on a flat surface Latitude: Imaginary lines that run east to west a ...
Map and Graph Skills
... Lines of Longitude • Imaginary lines that measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian ...
... Lines of Longitude • Imaginary lines that measure distance east and west of the Prime Meridian ...
Multiple Choice
... 5. Geographers are most likely to study landforms and their locations. 6. Geographers study regions so that they can make comparison. 7. A globe is more accurate than a map because a globe can show the true shape of the continents and oceans. 8. Imaginary lines that measure distances east or west of ...
... 5. Geographers are most likely to study landforms and their locations. 6. Geographers study regions so that they can make comparison. 7. A globe is more accurate than a map because a globe can show the true shape of the continents and oceans. 8. Imaginary lines that measure distances east or west of ...
THE HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF GEOGRAPHY
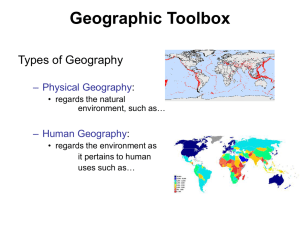
... study of the logical arrangement of human activities in space O Human Geography: study where & why human activities are located where they are; i.e. religions, cities, businesses, schools, malls, military bases etc. O 2 themes constantly present that are in opposition with each other - globalization ...
... study of the logical arrangement of human activities in space O Human Geography: study where & why human activities are located where they are; i.e. religions, cities, businesses, schools, malls, military bases etc. O 2 themes constantly present that are in opposition with each other - globalization ...
answers-to-worksheet-41-43
... • The map helps me to determine where I am. • The legend explains the symbols used in the map and helps me to read the map. • The legend helps me to identify familiar features and important landmarks, which can help me find my way out of the forest. • The legend provides information about the relief ...
... • The map helps me to determine where I am. • The legend explains the symbols used in the map and helps me to read the map. • The legend helps me to identify familiar features and important landmarks, which can help me find my way out of the forest. • The legend provides information about the relief ...
What`s in a map?
... 1. In figure 1-6 what is the distance between the New York Stock Exchange and City Hall? 2. In Fig 1.7 what is the distance between the town of Johar Bahuru and Singapore's airport? 3. In Fig 1.19 what is the distance between the home of the Atlanta Braves and the Kansas City Royals? 4. In Fig 1.15 ...
... 1. In figure 1-6 what is the distance between the New York Stock Exchange and City Hall? 2. In Fig 1.7 what is the distance between the town of Johar Bahuru and Singapore's airport? 3. In Fig 1.19 what is the distance between the home of the Atlanta Braves and the Kansas City Royals? 4. In Fig 1.15 ...
Basic Tools and Methods of Human Geographers
... • Focuses on equator • Does not show equal area • Poles appear as “lines;” not points • Good “visual” (not navigational) representation ...
... • Focuses on equator • Does not show equal area • Poles appear as “lines;” not points • Good “visual” (not navigational) representation ...
The 5 Themes of Geography - Chandler Unified School District
... the best World map’s available • However, even a Robinson projection has distortions (in areas around the edges of the map). ...
... the best World map’s available • However, even a Robinson projection has distortions (in areas around the edges of the map). ...
CGC 1D Wusssuuuupppp with Maps??? An Intro to mapping skills
... probably the easiest to understand ...
... probably the easiest to understand ...
The Where, Why, How and Who of Geography
... – Geography is the science of place and space. Geographers ask where things are located on the surface of the earth, why they are located where they are, how places differ from one another, and how people interact with the environment—AAG – Geography is all about trying to make sense of the ...
... – Geography is the science of place and space. Geographers ask where things are located on the surface of the earth, why they are located where they are, how places differ from one another, and how people interact with the environment—AAG – Geography is all about trying to make sense of the ...
2 b Map Skills PP KEY
... Small Scale maps • Show a small amount of detail of a large area • Used for political maps, physical maps, world maps… – Examine figure 3.11 (page 60) – Examine figure 11.9 (page 195) ...
... Small Scale maps • Show a small amount of detail of a large area • Used for political maps, physical maps, world maps… – Examine figure 3.11 (page 60) – Examine figure 11.9 (page 195) ...
Map - TeacherWeb
... longitude. On a map, all lines to the right of the Prime Meridian are east longitude; to the left is west longitude. It runs through Greenwich, Eng. International Date Line - Line at 180° longitude. It lies opposite the Prime Meridian. The date changes by one day when you cross this line. ...
... longitude. On a map, all lines to the right of the Prime Meridian are east longitude; to the left is west longitude. It runs through Greenwich, Eng. International Date Line - Line at 180° longitude. It lies opposite the Prime Meridian. The date changes by one day when you cross this line. ...
Name
... 10. How many contour lines would be needed to show an island 250 feet high on a map with a contour interval of 50 feet? ____________________________________ 11. What is the name of the contour lines which show craters of volcanoes? __________________________ 12. What landform is shown when many cont ...
... 10. How many contour lines would be needed to show an island 250 feet high on a map with a contour interval of 50 feet? ____________________________________ 11. What is the name of the contour lines which show craters of volcanoes? __________________________ 12. What landform is shown when many cont ...
Unit 1: An Overview of Geography
... – Mapmakers wanted to present this information correctly. – The best way was to put it on a globe, a round ball that represented the Earth. ...
... – Mapmakers wanted to present this information correctly. – The best way was to put it on a globe, a round ball that represented the Earth. ...
You are responsible for pages 3 – 13 in the text
... Conic projection - Conic – most accurate where the cone touches the globe. It is least accurate at the tip of the cone and where the cone does not touch the globe. It is used for maps that run from east to west in the middle latitudes (30 – 60 degrees N. & S.) US maps are usually conic. Cylindrical ...
... Conic projection - Conic – most accurate where the cone touches the globe. It is least accurate at the tip of the cone and where the cone does not touch the globe. It is used for maps that run from east to west in the middle latitudes (30 – 60 degrees N. & S.) US maps are usually conic. Cylindrical ...
Small Scale Maps
... Projection- True size and shape of land, but distances are distorted Mercator ProjectionAccurate at equator, but distorts size and distance as you move away from equator. Accurately shows true direction, good for sea travel and navigation. ...
... Projection- True size and shape of land, but distances are distorted Mercator ProjectionAccurate at equator, but distorts size and distance as you move away from equator. Accurately shows true direction, good for sea travel and navigation. ...
file_n_2
... Richter Scale: Open scale designed to measure the energy developed by a seism, i.e. its magnitude. Measure of the maximum amplitude of the seismic waves recorded by a standard seismograph at a distance of 100 km of the epicentre Epicentre: Point on the Earth surface located vertically to the focus. ...
... Richter Scale: Open scale designed to measure the energy developed by a seism, i.e. its magnitude. Measure of the maximum amplitude of the seismic waves recorded by a standard seismograph at a distance of 100 km of the epicentre Epicentre: Point on the Earth surface located vertically to the focus. ...