I Introduction
... sometimes used in conjunction with them for greater clarity. Map Projections For the representation of the entire surface of the earth without any kind of distortion, a map must have a spherical surface; a map of this kind is known as a globe. A flat map cannot accurately represent the rounded surfa ...
... sometimes used in conjunction with them for greater clarity. Map Projections For the representation of the entire surface of the earth without any kind of distortion, a map must have a spherical surface; a map of this kind is known as a globe. A flat map cannot accurately represent the rounded surfa ...
$doc.title
... 8. World GDP -‐ Use the map on page 4-‐5 in your textbook to prepare a sketch map which shows the per capita gross national income in 2009. Most geographers refer to GDP as a measurement ...
... 8. World GDP -‐ Use the map on page 4-‐5 in your textbook to prepare a sketch map which shows the per capita gross national income in 2009. Most geographers refer to GDP as a measurement ...
File - Boca Ciega AP Human Geography
... TRUE (A) FALSE (B) 42. Parallels converge at the North and South Poles. 43. The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians is called latitude. 44. For each 15° change in longitude, time changes by one hour. 45. Every map projection distorts the surface of Earth in some way. 46. A ma ...
... TRUE (A) FALSE (B) 42. Parallels converge at the North and South Poles. 43. The numbering system used to indicate the location of meridians is called latitude. 44. For each 15° change in longitude, time changes by one hour. 45. Every map projection distorts the surface of Earth in some way. 46. A ma ...
Relative distance - Winston-Salem/Forsyth County Schools
... maps written on clay tablets. Aristotle – 384-322 BC demonstrated earth was spherical through maps. Eratosthenes – 276-194 BC first person to use the word geography. Also the first person to correctly divide earth into 5 climatic regions. Ptolemy – 100-170 AD Guide to Geography Age of Exploration – ...
... maps written on clay tablets. Aristotle – 384-322 BC demonstrated earth was spherical through maps. Eratosthenes – 276-194 BC first person to use the word geography. Also the first person to correctly divide earth into 5 climatic regions. Ptolemy – 100-170 AD Guide to Geography Age of Exploration – ...
Metzel Qs 10-16 exam 1 109
... 13) A map projection may distort a continent, making it appear stretched in some areas and smashed in others in order to A) distort the shapes of other continents. B) distort the distances and relative sizes of countries and continents. C) depict a map that accurately represents a globe in every de ...
... 13) A map projection may distort a continent, making it appear stretched in some areas and smashed in others in order to A) distort the shapes of other continents. B) distort the distances and relative sizes of countries and continents. C) depict a map that accurately represents a globe in every de ...
Landforms Maps Study Guide
... map legend: tells what each map symbol means; also known as the map key map grid: a set of lines that divide a map into columns and rows of squares (example B2, C4) People use different kinds of maps to help them locate places. map scale: a part of a map that helps you find real distance, tells ...
... map legend: tells what each map symbol means; also known as the map key map grid: a set of lines that divide a map into columns and rows of squares (example B2, C4) People use different kinds of maps to help them locate places. map scale: a part of a map that helps you find real distance, tells ...
Geography Skills Pre Test
... 18. The Task: Writing Directions from a Map of Washington D.C. This map is a large-‐scale map of Washington D.C. It shows streets and landmarks that are found in our nation’s capital. Your task ...
... 18. The Task: Writing Directions from a Map of Washington D.C. This map is a large-‐scale map of Washington D.C. It shows streets and landmarks that are found in our nation’s capital. Your task ...
Unit 1 – Geography, Its Nature and Perspectives Practice Questions
... Give an example of a toponym from the following backgrounds; Spain, England, and France. Define each type of region and give an example of each. Locate the 10 (or so) major regions in the world. Explain the latitudinal effects of weather on the globe. (define in the important parallels) Use an examp ...
... Give an example of a toponym from the following backgrounds; Spain, England, and France. Define each type of region and give an example of each. Locate the 10 (or so) major regions in the world. Explain the latitudinal effects of weather on the globe. (define in the important parallels) Use an examp ...
5 Themes of Geography PowerPoint
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented flat maps. ...
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented flat maps. ...
What happens in an earthquake?
... earthquake occurs? • Watch the Boardworks animation (next 5 slides). Look carefully at what happens in an earthquake • Take notes using the key words • Now describe in a paragraph what happens when an earthquake occurs… EXTENSION - Make sure you use the following words: Tension Focus Epicentre Seism ...
... earthquake occurs? • Watch the Boardworks animation (next 5 slides). Look carefully at what happens in an earthquake • Take notes using the key words • Now describe in a paragraph what happens when an earthquake occurs… EXTENSION - Make sure you use the following words: Tension Focus Epicentre Seism ...
Map Master Skills Handbook
... Parallel lines, or Latitude lines, are lines that are drawn horizontally on a map. They are lines that are drawn from left to right. Latitude lines are numbered from 0 degrees to 90 degrees NORTH Latitude and from 0 degrees to 90 degrees SOUTH Latitude. 5. What is the most important line of Latitude ...
... Parallel lines, or Latitude lines, are lines that are drawn horizontally on a map. They are lines that are drawn from left to right. Latitude lines are numbered from 0 degrees to 90 degrees NORTH Latitude and from 0 degrees to 90 degrees SOUTH Latitude. 5. What is the most important line of Latitude ...
Introduction to Geography - University of Missouri
... • Longitude – angular distance measured east or west of the Prime Meridian through 180º of arc. Degree distance decreases poleward. – Meridians – not lines of longitude • All meridians have the same length ½ of Equator ...
... • Longitude – angular distance measured east or west of the Prime Meridian through 180º of arc. Degree distance decreases poleward. – Meridians – not lines of longitude • All meridians have the same length ½ of Equator ...
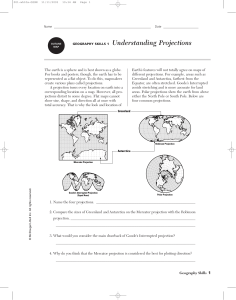
GEOGRAPHY SKILLS 1 Understanding Projections
... one, identified on the map, was not a point of origin for Vikings? ________________________ 2. Which of the cities on the map is farthest from the Vikings’ homeland? __________________ 3. What direction did the Vikings go to reach Greenland? ________________________________ 4. What is the region of ...
... one, identified on the map, was not a point of origin for Vikings? ________________________ 2. Which of the cities on the map is farthest from the Vikings’ homeland? __________________ 3. What direction did the Vikings go to reach Greenland? ________________________________ 4. What is the region of ...
Ch_ 1
... regions, that define an area of “sameness” or “connectedness.” e.g. the South the Mid-Atlantic the Middle East ...
... regions, that define an area of “sameness” or “connectedness.” e.g. the South the Mid-Atlantic the Middle East ...
File
... place is by describing places near it. Your home has a relative location. Where is it located in relation to schools, stores, and convenient transportation? OwlTeacher.com ...
... place is by describing places near it. Your home has a relative location. Where is it located in relation to schools, stores, and convenient transportation? OwlTeacher.com ...
Grade 9 Social Studies Exam
... 1. the exact coordinates of a place on the surface of the Earth 2 .the 0 degree line of longitude 3. a half of a shere ex the Northern hemisphere 4. the 0 degree line of latitude 5. the location of a place in terms of what is around it 6. the lines that measure directions east and west of the Prime ...
... 1. the exact coordinates of a place on the surface of the Earth 2 .the 0 degree line of longitude 3. a half of a shere ex the Northern hemisphere 4. the 0 degree line of latitude 5. the location of a place in terms of what is around it 6. the lines that measure directions east and west of the Prime ...
Week 7 - Geophile.net
... Types of maps: planimetric, topographic, bathymetric, geologic, and weather Map legends: North arrow, magnetic north, scale, location, and symbols Scale: statement/verbal, representative fraction, and scale bar Latitude and longitude Topography Contour lines, contour interval, index contour, bench m ...
... Types of maps: planimetric, topographic, bathymetric, geologic, and weather Map legends: North arrow, magnetic north, scale, location, and symbols Scale: statement/verbal, representative fraction, and scale bar Latitude and longitude Topography Contour lines, contour interval, index contour, bench m ...
Earthquakes October 15th, 2009
... Where do earthquakes occur? Most quakes occur in parts of the world that sit on top of fault-lines, or boundaries between the major tectonic plates The edges of the huge Pacific Plate, under the Pacific Ocean, are a particularly active area, which geologists have nicknamed ‘the ring of fire’ ...
... Where do earthquakes occur? Most quakes occur in parts of the world that sit on top of fault-lines, or boundaries between the major tectonic plates The edges of the huge Pacific Plate, under the Pacific Ocean, are a particularly active area, which geologists have nicknamed ‘the ring of fire’ ...
What is Geography?
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented flat maps. ...
... • Globes have a disadvantage: They cannot be complete enough to be useful and at the same time be small enough to be convenient. • Therefore, people invented flat maps. ...
Capital Connections - Indiana University Bloomington
... intermediate direction: points of the compass that fall between cardinal points (NE, SE, SW, NW) equator: latitude 0°; an imaginary line running east and west around the globe and dividing it into two equal parts known as the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere globe: small-scale model of th ...
... intermediate direction: points of the compass that fall between cardinal points (NE, SE, SW, NW) equator: latitude 0°; an imaginary line running east and west around the globe and dividing it into two equal parts known as the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere globe: small-scale model of th ...
geogch01
... • degree- a unit of measure used to determine absolute location; on globes and maps, latitude and longitude are measured in degrees • equator- an imaginary line that circles the globe at its widest point (halfway between the North and South poles), dividing the Earth into two halves called hemispher ...
... • degree- a unit of measure used to determine absolute location; on globes and maps, latitude and longitude are measured in degrees • equator- an imaginary line that circles the globe at its widest point (halfway between the North and South poles), dividing the Earth into two halves called hemispher ...
About Working with Maps, Globes
... All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale is the ratio between the representation and the thing it represents. A map may be drawn so that 1 inch equals 250 miles, or so that 1 inch equals 1 mile. Maps, as well as globes, almost always indicate the s ...
... All maps are drawn to scale; that is, they are smaller than the things they represent. Scale is the ratio between the representation and the thing it represents. A map may be drawn so that 1 inch equals 250 miles, or so that 1 inch equals 1 mile. Maps, as well as globes, almost always indicate the s ...
Exploring Regions of the United States Section 1
... in many ways. You might describe the location of your home by talking about what it is near. This is the relative location of your home. Or you might use your street address. This is the exact location of your home. Geographers use globes and maps to show the locations of places on Earth. Globes are ...
... in many ways. You might describe the location of your home by talking about what it is near. This is the relative location of your home. Or you might use your street address. This is the exact location of your home. Geographers use globes and maps to show the locations of places on Earth. Globes are ...
What is a Map? - WordPress.com
... – Grey should be used for areas not important to the map (e.g., other countries) – Blue should only be used for water bodies ...
... – Grey should be used for areas not important to the map (e.g., other countries) – Blue should only be used for water bodies ...