Proteins
... Although proteins are more important as a source of building blocks, amino acids may be used by the body as a source of energy (through the process of cellular respiration), but first they must be converted by the body to carbohydrates. This process does not happen as long as there is a carbohydrate ...
... Although proteins are more important as a source of building blocks, amino acids may be used by the body as a source of energy (through the process of cellular respiration), but first they must be converted by the body to carbohydrates. This process does not happen as long as there is a carbohydrate ...
Microarray Pitfalls
... • Affymetrix provided probeset annotations change over time • The gene symbol associated with a given probeset is not necessarily stable • This is due to changes in gene prediction as new information becomes available. ...
... • Affymetrix provided probeset annotations change over time • The gene symbol associated with a given probeset is not necessarily stable • This is due to changes in gene prediction as new information becomes available. ...
Gene Section ABL2 (Abelson homolog 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... coding sequence of arg defines the Abelson subfamily of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5802-6 ...
... coding sequence of arg defines the Abelson subfamily of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5802-6 ...
FlexWeb
... Proteins • The ability of proteins to change their conformation is important to their function as biological machines. ...
... Proteins • The ability of proteins to change their conformation is important to their function as biological machines. ...
Biology 3A Lab Protein Fingerprinting Page 1 of 6 Biology 3A
... Charles Darwin proposed the revolutionary idea that varieties of forms and species are derived from a common ancestor – descent with modification. When a population of similar, related individuals acquires new characteristics over many generations, we refer to that process of modification over time ...
... Charles Darwin proposed the revolutionary idea that varieties of forms and species are derived from a common ancestor – descent with modification. When a population of similar, related individuals acquires new characteristics over many generations, we refer to that process of modification over time ...
HLFinalcell
... Small structures in the cytoplasm of a cell that all have more than one function. ...
... Small structures in the cytoplasm of a cell that all have more than one function. ...
“Algorithms for genomes” 2b Central Dogma Transcription start and
... Protein domains: Modular structure of proteins, exon-shuffling ...
... Protein domains: Modular structure of proteins, exon-shuffling ...
Chemistry of Life
... Hydrocarbons undergo reactions that release relatively large amounts of energy Replace a H with a C and the backbone grows, keep going and you get long chains, branched chains, and ring structures No polarity to bonds, not soluble in water ...
... Hydrocarbons undergo reactions that release relatively large amounts of energy Replace a H with a C and the backbone grows, keep going and you get long chains, branched chains, and ring structures No polarity to bonds, not soluble in water ...
From Gene to Protein
... Alternative RNA Splicing: produce different combinations of exons One gene can make more than one polypeptide! 20,000 genes 100,000 ...
... Alternative RNA Splicing: produce different combinations of exons One gene can make more than one polypeptide! 20,000 genes 100,000 ...
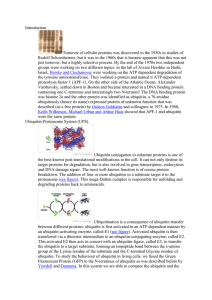
Introduction
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
... Turnover of cellular proteins was discovered in the 1930s in studies of Rudolf Schoenheimer, but it was in the 1960s that is became apparent that this was not just turnover, but a highly selective process. By the end of the 1970s two independent groups were working on two different topics: in the la ...
Primary Structure - LaurensAPBiology
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
Chapter 2 bio
... These bonding interactions may be stronger than the hydrogen bonds between amide groups holding the helical structure. As a result, bonding interactions between "side chains" may cause a number of folds, bends, and loops in the protein chain. Different fragments of the same chain may ...
... These bonding interactions may be stronger than the hydrogen bonds between amide groups holding the helical structure. As a result, bonding interactions between "side chains" may cause a number of folds, bends, and loops in the protein chain. Different fragments of the same chain may ...
Gene regulation
... a system that produces a second messenger – in the case of glucagon, adenylate cyclase brings about the production of cyclic AMP from ATP. The cyclic AMP then activates intracellular enzymes like protein kinase A (PKA) by altering their three dimensional structure. The activated enzyme then catalyse ...
... a system that produces a second messenger – in the case of glucagon, adenylate cyclase brings about the production of cyclic AMP from ATP. The cyclic AMP then activates intracellular enzymes like protein kinase A (PKA) by altering their three dimensional structure. The activated enzyme then catalyse ...
Experiment 9: The Widely Varying Colors of d
... precipitate has formed, if a color change is observed or if heat is noted in the reaction. We have seen examples of all of these throughout the term. Sometimes a color change can be subtle and you need instrumentation to notice what is happening (e.g., myoglobin vs. reduced myoglobin). You have now ...
... precipitate has formed, if a color change is observed or if heat is noted in the reaction. We have seen examples of all of these throughout the term. Sometimes a color change can be subtle and you need instrumentation to notice what is happening (e.g., myoglobin vs. reduced myoglobin). You have now ...
SCI 241 Protein Article research wk 5 version 6 Protein and the
... thinness, and shades of color, a protruded stomach, rashes and edema are symptoms of a lack or shortage of protein. The experienced feeling of forgetfulness, weariness, annoyance, and lack of concern are also symptoms of protein loss. A loss in weight, height, and a stimulation of growth give a chil ...
... thinness, and shades of color, a protruded stomach, rashes and edema are symptoms of a lack or shortage of protein. The experienced feeling of forgetfulness, weariness, annoyance, and lack of concern are also symptoms of protein loss. A loss in weight, height, and a stimulation of growth give a chil ...
SUZ12 antibody - middle region (ARP32515_P050)
... A chromosomal aberration involving SUZ12 may be a cause of endometrial stromal tumors. Translocation t (7;17)(p15;q21) with JAZF1 generates the JAZF1-SUZ12 oncogene consisting of the N-terminus part of JAZF1 and the C-terminus part of SUZ12. It is frequently found in all cases of endometrial stromal ...
... A chromosomal aberration involving SUZ12 may be a cause of endometrial stromal tumors. Translocation t (7;17)(p15;q21) with JAZF1 generates the JAZF1-SUZ12 oncogene consisting of the N-terminus part of JAZF1 and the C-terminus part of SUZ12. It is frequently found in all cases of endometrial stromal ...
gene expression
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
... Noncoding RNAs and gene expression • Discovering more about RNA’S that do not make protein • MicroRNAs (miRNA) – small, single stranded RNA generated from a hairpin on precursor RNA; associates with proteins that can degrade or prevent translation of mRNA with complementary sequence • Small interfe ...
Cells - Seattle Central College
... • Have skeletons for protection and support (proteins) • Move (via proteins) ...
... • Have skeletons for protection and support (proteins) • Move (via proteins) ...
Master Dissertation Project
... Tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb), despite being completely curable, has reemerged as a global pandemic. The failure of effective vaccine protection, lack of early detection of the disease, emergence of drug resistance and the deadly synergism with HIV infection have lim ...
... Tuberculosis (TB), caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb), despite being completely curable, has reemerged as a global pandemic. The failure of effective vaccine protection, lack of early detection of the disease, emergence of drug resistance and the deadly synergism with HIV infection have lim ...
Solid Tumour Section Soft tissue tumors: Pericytoma with t(7;12)
... DNA in the centromere-to-telomere orientation. The translation initiation codon is located in exon 2, and the stop codon in exon 12. The GLI1 mRNA transcript is 3.6 kb. GLI proteins function as direct effectors of sonic hedgehog-signaling during embryogenesis. GLI1 (also GLI2 and GLI3) are therefore ...
... DNA in the centromere-to-telomere orientation. The translation initiation codon is located in exon 2, and the stop codon in exon 12. The GLI1 mRNA transcript is 3.6 kb. GLI proteins function as direct effectors of sonic hedgehog-signaling during embryogenesis. GLI1 (also GLI2 and GLI3) are therefore ...
Toward structural characterization of novel mechanism of inhibition
... positive for agriculture, the net global effect is predicted to severely degrade conditions for plant growth and development, resulting in significant expansion of non-arable land areas. All plants possess facilities to sense changes of environmental conditions and respond with the initiation of var ...
... positive for agriculture, the net global effect is predicted to severely degrade conditions for plant growth and development, resulting in significant expansion of non-arable land areas. All plants possess facilities to sense changes of environmental conditions and respond with the initiation of var ...
Chapter Two Mineral Nutrition of Plant
... entire width of the phospholipid bilayer. They serve as ion channels and certain receptors etc. peripheral protein are bound to membrane surface by noncovalent bonds, such as ionic bonds or hydrogen bonds. Peripheral proteins serve a variety of functions in the cell. Anchored protein are bound to th ...
... entire width of the phospholipid bilayer. They serve as ion channels and certain receptors etc. peripheral protein are bound to membrane surface by noncovalent bonds, such as ionic bonds or hydrogen bonds. Peripheral proteins serve a variety of functions in the cell. Anchored protein are bound to th ...
2013 version with answers.
... Describe which bioinformatics tools are needed in the process. BLAST against PDB to find homolog (or its own structure if Murphy is on vacation). Use homology modelling to get structure. Find nice stretchy at surface that is a bit extended. Use software that predicts antigenicity for aa types to fin ...
... Describe which bioinformatics tools are needed in the process. BLAST against PDB to find homolog (or its own structure if Murphy is on vacation). Use homology modelling to get structure. Find nice stretchy at surface that is a bit extended. Use software that predicts antigenicity for aa types to fin ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.