Lecture 6 The connection between genes, proteins and metabolism
... - Will grow if supplied with either ornithine or citrulline or arginine - Therefore the metabolic block must lie upstream of ornithine ...
... - Will grow if supplied with either ornithine or citrulline or arginine - Therefore the metabolic block must lie upstream of ornithine ...
PowerPoint 0.8MB - The Biomolecular Modeling & Computational
... • Quality of prediction is given by E Eij ij ...
... • Quality of prediction is given by E Eij ij ...
[] Protein Splicing i) inteins and ext...,
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Design of Genetic Sequences Encoding MMP-2-degradable
... glioblastoma multiforme. The repeating units of target recombinant protein polymers contain a binding and cleavage site for metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are excreted by tumor cells for tissue remodeling and angiogenesis. Polymer protein contact with MMPs will result in the degradation of the pro ...
... glioblastoma multiforme. The repeating units of target recombinant protein polymers contain a binding and cleavage site for metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are excreted by tumor cells for tissue remodeling and angiogenesis. Polymer protein contact with MMPs will result in the degradation of the pro ...
Lecture 6
... • Rates vary widely for different proteins but scale with time • Local clock vs global clock • Rates can vary over branches and over time • Selection • Generation time effect • Efficiency of DNA repair • Some evidence ...
... • Rates vary widely for different proteins but scale with time • Local clock vs global clock • Rates can vary over branches and over time • Selection • Generation time effect • Efficiency of DNA repair • Some evidence ...
Familial Pawpad Hyperkeratosis in a Mixed
... – Formed inside the cytoplasmic membrane of differentiating keratinocytes – Eventually resides on exterior of cornified cells • Mechanical & chemical barrier ...
... – Formed inside the cytoplasmic membrane of differentiating keratinocytes – Eventually resides on exterior of cornified cells • Mechanical & chemical barrier ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... monomers because we are making _____________________. Now that we have the place to build the protein and the copied instructions on how to make the protein, the parts (amino acids) need to be brought over to the workbench and placed in the correct order. The job of ______ is to transfer these amino ...
... monomers because we are making _____________________. Now that we have the place to build the protein and the copied instructions on how to make the protein, the parts (amino acids) need to be brought over to the workbench and placed in the correct order. The job of ______ is to transfer these amino ...
Mr. Tuan Hoang - Molecular and Cellular Biology
... ion transport assays (both proton and chloride) were developed for reconstituted UCPs using the anion-sensitive fluorescent probe SPQ. Three specific objectives, in the form of three separate but interrelated research projects, were targeted in this study. In the first project, the ion transport act ...
... ion transport assays (both proton and chloride) were developed for reconstituted UCPs using the anion-sensitive fluorescent probe SPQ. Three specific objectives, in the form of three separate but interrelated research projects, were targeted in this study. In the first project, the ion transport act ...
Handout
... and how they are controlled What binds to the operator & when does this occur High levels of what substance affects how this operon how? 2. Why are genes under regulation? ...
... and how they are controlled What binds to the operator & when does this occur High levels of what substance affects how this operon how? 2. Why are genes under regulation? ...
ANTIBIOTICS
... Ampicillin is a penicillin derivative that inhibits crosslinking of peptidoglycan chains in the cell wall of eubacteria. Cells growing in the presence of ampicillin synthesize weak cell walls, causing them to burst due to the high internal osmotic pressure. AmpR encoded by Mu derivatives and pBR pla ...
... Ampicillin is a penicillin derivative that inhibits crosslinking of peptidoglycan chains in the cell wall of eubacteria. Cells growing in the presence of ampicillin synthesize weak cell walls, causing them to burst due to the high internal osmotic pressure. AmpR encoded by Mu derivatives and pBR pla ...
TheraGest - ProThera
... down fat, carbohydrate, and protein. Digestive enzymes assist the body in breaking down large food particles into smaller particles that can be efficiently absorbed by the intestinal tract. Improper digestion can lead to abdominal discomfort such as bloating, feeling of fullness and constipation as ...
... down fat, carbohydrate, and protein. Digestive enzymes assist the body in breaking down large food particles into smaller particles that can be efficiently absorbed by the intestinal tract. Improper digestion can lead to abdominal discomfort such as bloating, feeling of fullness and constipation as ...
From differential transcription of ribosomal proteins to differential
... to the decades-old model of the ribosomes, each ribosome has exactly one copy of each core RP. Thus, the simplest mechanism for making more ribosomes is to induce the transcription of each RP by the same amount, not to induce some RPs and repress others. Still, biology often defies simplistic expect ...
... to the decades-old model of the ribosomes, each ribosome has exactly one copy of each core RP. Thus, the simplest mechanism for making more ribosomes is to induce the transcription of each RP by the same amount, not to induce some RPs and repress others. Still, biology often defies simplistic expect ...
File
... (probably because I studied plants, not flies). So, I Googled it and found a great image explaining what the system actually does. It’s a really interesting way of controlling the expression of genes in a tissue that you care about studying – this way a scientist can target gene expression to specif ...
... (probably because I studied plants, not flies). So, I Googled it and found a great image explaining what the system actually does. It’s a really interesting way of controlling the expression of genes in a tissue that you care about studying – this way a scientist can target gene expression to specif ...
Digestive System
... Used to make our own enzymes and other body proteins. Used for cellular energy and energy storage; used to make cell membranes, steroid hormones. Store and transmit hereditary information ...
... Used to make our own enzymes and other body proteins. Used for cellular energy and energy storage; used to make cell membranes, steroid hormones. Store and transmit hereditary information ...
Definition of a RACK1 Interaction Network in Drosophila
... cellular proteins are hijacked by viruses to complete their replication cycle and represent putative targets for host-targeted antiviral drugs. Using the model organism Drosophila melanogaster, we recently showed that Receptor for Activated protein C Kinase 1 (RACK1) is an essential host factor for ...
... cellular proteins are hijacked by viruses to complete their replication cycle and represent putative targets for host-targeted antiviral drugs. Using the model organism Drosophila melanogaster, we recently showed that Receptor for Activated protein C Kinase 1 (RACK1) is an essential host factor for ...
Summary Chemical biology Index
... Chemical induced dimerization is a simple way to bring specific proteins together. FRAPFRB can be connected to a specific protein or to the cellmembrane or an organell. If rapamycin glues FKBP12 and FRAP-FRB together FKBP12 will also be connected to the specific protein. When a protein of interest ( ...
... Chemical induced dimerization is a simple way to bring specific proteins together. FRAPFRB can be connected to a specific protein or to the cellmembrane or an organell. If rapamycin glues FKBP12 and FRAP-FRB together FKBP12 will also be connected to the specific protein. When a protein of interest ( ...
Tutorial_13 (2014)
... are the three archetypes. In this case, because a triangle defines a plane, even high dimensional data on many traits are expected to collapse onto two dimensions. The closer a point is to one of the vertices of the triangle, the more important the corresponding task is to fitness in the organism’s ...
... are the three archetypes. In this case, because a triangle defines a plane, even high dimensional data on many traits are expected to collapse onto two dimensions. The closer a point is to one of the vertices of the triangle, the more important the corresponding task is to fitness in the organism’s ...
File
... Evolution of gene regulation • Eukaryotes – Multicellular = only expresses a fraction of its genes – evolved to maintain constant internal conditions even with changing conditions • (?) Homeostasis • must REGULATE the body as a whole rather than serve the needs of individual cells ...
... Evolution of gene regulation • Eukaryotes – Multicellular = only expresses a fraction of its genes – evolved to maintain constant internal conditions even with changing conditions • (?) Homeostasis • must REGULATE the body as a whole rather than serve the needs of individual cells ...
Text S1.
... bp from both transposon termini. Each tRNALys gene can be transcribed but does not encode a functional product. Upon insertion, the element generates a 9-bp target site duplication (TSD), which is characteristic for Mu-like elements. Based on EST evidence, two transcripts stem from the presumptive a ...
... bp from both transposon termini. Each tRNALys gene can be transcribed but does not encode a functional product. Upon insertion, the element generates a 9-bp target site duplication (TSD), which is characteristic for Mu-like elements. Based on EST evidence, two transcripts stem from the presumptive a ...
As Powerpoint Slide
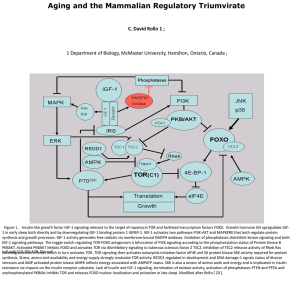
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
... 1 Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada ; ...
Abstract
... Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzyme activity, protein-protein interaction, subcel ...
... Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzyme activity, protein-protein interaction, subcel ...
UCLA Bioinformatics - Cal State LA
... • Most of the hyperthermophiles have 2 CXXC motifs in order to have abundant disulfide bonds. • The abundance of disulfide bonds appear to play a key role in stabilizing protein at high temperature. • Intracellular disulfide bond is a characteristic of all archaea or an adaptation to high temperatur ...
... • Most of the hyperthermophiles have 2 CXXC motifs in order to have abundant disulfide bonds. • The abundance of disulfide bonds appear to play a key role in stabilizing protein at high temperature. • Intracellular disulfide bond is a characteristic of all archaea or an adaptation to high temperatur ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.


![[] Protein Splicing i) inteins and ext...,](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008277893_1-250b6a85b20526696d229e05c4a3b4d7-300x300.png)