Expression and identification of the RfbE protein from Vibrio
... [(M + Na)+] 611.13 amu) and the TLC analysis of the D-perosamine component proved the structure of the product to be in accord with GDP-α-D-perosamine. Discussion The intention of this work was to identify the function of the RfbE protein by an overexpression of the rfbE gene and an in vitro product ...
... [(M + Na)+] 611.13 amu) and the TLC analysis of the D-perosamine component proved the structure of the product to be in accord with GDP-α-D-perosamine. Discussion The intention of this work was to identify the function of the RfbE protein by an overexpression of the rfbE gene and an in vitro product ...
This presentation follows on from the talk presented
... sequence homology search has been tailored to de novo solution data, and allows for Q>K and F->M* in the alignment without penalty for example. Out of the de novo results we took the 156 spectra with 1 or more solutions and a De novo score >= 40, that is the good quality de novo matches. These 156 s ...
... sequence homology search has been tailored to de novo solution data, and allows for Q>K and F->M* in the alignment without penalty for example. Out of the de novo results we took the 156 spectra with 1 or more solutions and a De novo score >= 40, that is the good quality de novo matches. These 156 s ...
Passive transport
... -the hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration -the hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration Osmosis moves water through aquaporins toward the hypertonic solution. ...
... -the hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration -the hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration Osmosis moves water through aquaporins toward the hypertonic solution. ...
Protein Purification 2003
... – What kind of cell is it coming from – What part of cell – What does it do ...
... – What kind of cell is it coming from – What part of cell – What does it do ...
Lecture 32: Spectroscopy (continued)
... introduced. Binding event only occurs when the sequence introduced is complementary to the structure present on the chip. In this way, today genes are detected. ...
... introduced. Binding event only occurs when the sequence introduced is complementary to the structure present on the chip. In this way, today genes are detected. ...
Analysis of Gene Expression
... with the matrix molecules, which efficiently absorb the UV laser energy and encourage ionization of the proteins. When irradiated with the laser, they vaporize along with the protein, but their small size makes them easy to detect and ignore. Time-of-flight mass spectrometry is generally used (so th ...
... with the matrix molecules, which efficiently absorb the UV laser energy and encourage ionization of the proteins. When irradiated with the laser, they vaporize along with the protein, but their small size makes them easy to detect and ignore. Time-of-flight mass spectrometry is generally used (so th ...
Tryptophan regulation by the formation of
... Tryptophan is one of the 20 amino acids that are essential for life. Regulation of the gene that is responsible for the synthesis of Tryptophan is key for living organisms. Over, under, or absence of this amino acid could cause the death of the organism. Bacteria have an interesting way of regulatin ...
... Tryptophan is one of the 20 amino acids that are essential for life. Regulation of the gene that is responsible for the synthesis of Tryptophan is key for living organisms. Over, under, or absence of this amino acid could cause the death of the organism. Bacteria have an interesting way of regulatin ...
Atomistic modeling of the structural components of the
... Blood-brain barrier, which is a barrage system between the brain and blood vessels, plays a key role in the "isolation" of the brain of unnecessary information, and reduce the "noise" in the interneuron communication. It is known that the barrier function of the BBB strictly depends on the initial s ...
... Blood-brain barrier, which is a barrage system between the brain and blood vessels, plays a key role in the "isolation" of the brain of unnecessary information, and reduce the "noise" in the interneuron communication. It is known that the barrier function of the BBB strictly depends on the initial s ...
Parkinson’s Disease Genetics
... epidemiological data suggesting a positive correlation between pesticide exposure and incidence of PD led to many studies of the effects of pesticides on DA neurons in animal models. Paraquat and rotenone, a broad spectrum pesticide which is a mitochondrial toxin like MPP+, were eventually found to ...
... epidemiological data suggesting a positive correlation between pesticide exposure and incidence of PD led to many studies of the effects of pesticides on DA neurons in animal models. Paraquat and rotenone, a broad spectrum pesticide which is a mitochondrial toxin like MPP+, were eventually found to ...
Chapter 21 (Part 2)
... tRNA Processing •tRNA is first transcribed by RNA •Polymerase III, is then processed •tRNAs are further processed in the chemical modification of bases ...
... tRNA Processing •tRNA is first transcribed by RNA •Polymerase III, is then processed •tRNAs are further processed in the chemical modification of bases ...
Gene Section YBX1 (Y box binding protein 1)
... boxes located between -1855 and -422 nucleotides (relative to the start of exon 1) and several GT and GC boxes. The gene also contains a large and highly conserved CpG island at the immediate 5' promoter region which extends to the first exon encoding 5' UTR of YBX1 mRNA. The region between nucleoti ...
... boxes located between -1855 and -422 nucleotides (relative to the start of exon 1) and several GT and GC boxes. The gene also contains a large and highly conserved CpG island at the immediate 5' promoter region which extends to the first exon encoding 5' UTR of YBX1 mRNA. The region between nucleoti ...
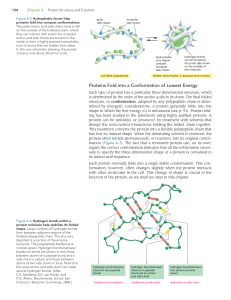
100 - A Primer on Calf Nutition
... and many other components of the body. They are involved in almost every biochemical reaction in the body and are indispensable for growth and survival. Proteins are produced in the body by absorption of amino acids from the diet and formation of the amino acids into the proteins required by the bod ...
... and many other components of the body. They are involved in almost every biochemical reaction in the body and are indispensable for growth and survival. Proteins are produced in the body by absorption of amino acids from the diet and formation of the amino acids into the proteins required by the bod ...
Who needs an artificial cornea?
... • Determine diffusion coefficients for other proteins through human cornea • Apply principles to development of artificial cornea • Modify refractive index for inlay application (presbyopia) DEVICE Protein tethering • Optimize the ECM content tethered to the hydrogel • Use time-lapse microscopy to s ...
... • Determine diffusion coefficients for other proteins through human cornea • Apply principles to development of artificial cornea • Modify refractive index for inlay application (presbyopia) DEVICE Protein tethering • Optimize the ECM content tethered to the hydrogel • Use time-lapse microscopy to s ...
Powerpoint for chapters 17-20 of Campbell Biology by Emily Diamond
... oncogenes and proto-oncogenes ...
... oncogenes and proto-oncogenes ...
Biosynthesis of a Secretory Protein
... Within the RER, the polypeptide is cleaved, sugar added, and polypeptide folds to take a specific shape. Soluble proteins are transported in a transport vesicle to the Golgi Body by exocytosis. Transport vesicle with protein are moved from one area of the Golgi Body to another by endocytosis and exo ...
... Within the RER, the polypeptide is cleaved, sugar added, and polypeptide folds to take a specific shape. Soluble proteins are transported in a transport vesicle to the Golgi Body by exocytosis. Transport vesicle with protein are moved from one area of the Golgi Body to another by endocytosis and exo ...
PPT
... Only main-chain heavy atoms and Cbeta-atom of sidechains are taken into account, Bond lengths and bond angles are held constant and correspond to the alanine geometry. The only remaining geometrical variables are the backbone torsion angles. ...
... Only main-chain heavy atoms and Cbeta-atom of sidechains are taken into account, Bond lengths and bond angles are held constant and correspond to the alanine geometry. The only remaining geometrical variables are the backbone torsion angles. ...
The use of isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT)
... thus is not suitable for the quantitative comparison of membrane proteins. ICAT and SILAC, on the other hand, are not based on 2D-PAGE and rely on MS for protein quantification. Therefore ICAT and SILAC can be used to compare membrane proteomes. Foster et al. [19] used SILAC to identify lipid-raft-l ...
... thus is not suitable for the quantitative comparison of membrane proteins. ICAT and SILAC, on the other hand, are not based on 2D-PAGE and rely on MS for protein quantification. Therefore ICAT and SILAC can be used to compare membrane proteomes. Foster et al. [19] used SILAC to identify lipid-raft-l ...
Essential Cell Biology Chapter 4 excerpt
... proteins come in a wide Variety of complicated Shapes Proteins are the most structurally diverse macromolecules in the cell. Although they range in size from about 30 amino acids to more than 10,000, the vast majority of proteins are between 50 and 2000 amino acids long. Proteins can be globular or ...
... proteins come in a wide Variety of complicated Shapes Proteins are the most structurally diverse macromolecules in the cell. Although they range in size from about 30 amino acids to more than 10,000, the vast majority of proteins are between 50 and 2000 amino acids long. Proteins can be globular or ...
Viral Mediated Gene Delivery
... sequence insertions. E1 is required, and its removal renders the virus incapable of replication; it must therefore be supplied either by a packaging cell line (such as HEK293) or a helper plasmid. Similarly, some lentiviral- and AAV-based systems have transferred structural and enzymatic genes from ...
... sequence insertions. E1 is required, and its removal renders the virus incapable of replication; it must therefore be supplied either by a packaging cell line (such as HEK293) or a helper plasmid. Similarly, some lentiviral- and AAV-based systems have transferred structural and enzymatic genes from ...
A defect in the CLIP1 gene (CLIP
... In neurons, most MTs lay along the length of axons and dendrites, where they are crucial for long range transport.5 The dynamic behavior of MTs is largely controlled by a group of proteins called MT plus-end tracking proteins ( þ TIPs), which specifically associate with the ends of growing MTs. CLIP ...
... In neurons, most MTs lay along the length of axons and dendrites, where they are crucial for long range transport.5 The dynamic behavior of MTs is largely controlled by a group of proteins called MT plus-end tracking proteins ( þ TIPs), which specifically associate with the ends of growing MTs. CLIP ...
Assignments 3 Problem 1 Below is the protein melting data for a pair
... Determine the following pieces of information. Note: While you are doing the plots and the calculations, make sure that you convert the temperatures from Celsius to Kelvin. a) Plot the melting curves (Fluorescence intensity vs. temp) for both the mutant and the wild-type protein. b) Determine your ...
... Determine the following pieces of information. Note: While you are doing the plots and the calculations, make sure that you convert the temperatures from Celsius to Kelvin. a) Plot the melting curves (Fluorescence intensity vs. temp) for both the mutant and the wild-type protein. b) Determine your ...
CELL MEMBRANES LEARNING OBJECTIVES • At the end
... Selective permeability: integral membrane proteins allow the cell to be selective about what passes through the membrane. Channel proteins have a polar interior allowing polar molecules to pass through. Carrier proteins bind to a specific molecule to facilitate its passage. PASSIVE TRANSPORT Channel ...
... Selective permeability: integral membrane proteins allow the cell to be selective about what passes through the membrane. Channel proteins have a polar interior allowing polar molecules to pass through. Carrier proteins bind to a specific molecule to facilitate its passage. PASSIVE TRANSPORT Channel ...
Labeling Proteins with Small Molecules by Site
... that were expressed as intein fusions. The intein domain was subsequently replaced by a small-molecule cysteine conjugate upon elution from a chitin column.3 Similarly, human O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (hGAT) has been used for site-specific protein labeling by irreversibly transferring the ...
... that were expressed as intein fusions. The intein domain was subsequently replaced by a small-molecule cysteine conjugate upon elution from a chitin column.3 Similarly, human O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (hGAT) has been used for site-specific protein labeling by irreversibly transferring the ...
Biological Membranes and Transport
... Strong attachment because of hydrophobic interactions between membrane lipids and hydrophobic domains of protein ...
... Strong attachment because of hydrophobic interactions between membrane lipids and hydrophobic domains of protein ...
December 2009
... b. The lac operon would be induced in medium containing lactose but no glucose. c. The CAP binding protein would bind to the CAP binding site when glucose was absent. d. In glucose and lactose, β-galactosidase levels would be higher than normal. e. RNA polymerase would not be able to bind to the lac ...
... b. The lac operon would be induced in medium containing lactose but no glucose. c. The CAP binding protein would bind to the CAP binding site when glucose was absent. d. In glucose and lactose, β-galactosidase levels would be higher than normal. e. RNA polymerase would not be able to bind to the lac ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.