
What can be done to reduce overconsumption?
... Characterizing the problem of overconsumption as an overutilization by society members of a shared basket of resources leads us to consider the fundamental dilemma associated with the use of common pool resources: If individuals follow selfinterested motives and consume more than their ‘fair shares’ ...
... Characterizing the problem of overconsumption as an overutilization by society members of a shared basket of resources leads us to consider the fundamental dilemma associated with the use of common pool resources: If individuals follow selfinterested motives and consume more than their ‘fair shares’ ...
Sustainable Buildings: An Ever Evolving Target
... Hernandez and Kenny [58] extended the idea of a net-zero energy building to the life cycle zero-energy building (LC-ZEB). As defined by the European Parliament, a net-zero-energy building is ―a building where, as a result of the very high level of energy efficiency of the building, the overall annua ...
... Hernandez and Kenny [58] extended the idea of a net-zero energy building to the life cycle zero-energy building (LC-ZEB). As defined by the European Parliament, a net-zero-energy building is ―a building where, as a result of the very high level of energy efficiency of the building, the overall annua ...
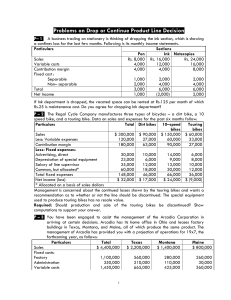
ProblemsonDropOrContinueProductLineDecision
... Under this proposal variable costs would be $8 per unit sold. b. Enter into a long–term contract with a competitor who will serve that area’s customers. This competitor would pay Arcadia a royalty of $4 per unit based upon an estimate of 30,000 units being sold. c. Close the Maine factory and not ex ...
... Under this proposal variable costs would be $8 per unit sold. b. Enter into a long–term contract with a competitor who will serve that area’s customers. This competitor would pay Arcadia a royalty of $4 per unit based upon an estimate of 30,000 units being sold. c. Close the Maine factory and not ex ...
The little Book of GRIHA rating
... fashionable trends that are short-lived often lead us to provide ‘international’ comfort conditions in our buildings, at the cost of very high energy consumption. It should be our endeavour to help secure the energy and resource future of our country through green buildings and habitats suitable to ...
... fashionable trends that are short-lived often lead us to provide ‘international’ comfort conditions in our buildings, at the cost of very high energy consumption. It should be our endeavour to help secure the energy and resource future of our country through green buildings and habitats suitable to ...
File
... The price has to be reduced for you to keep consuming at a given time. • The Income Effect: A change in the price of a product changes a consumer’s real income (purchasing power) and thus the quantity of the product purchased. In other words, you are richer if a price drops and vice versa. • The Sub ...
... The price has to be reduced for you to keep consuming at a given time. • The Income Effect: A change in the price of a product changes a consumer’s real income (purchasing power) and thus the quantity of the product purchased. In other words, you are richer if a price drops and vice versa. • The Sub ...
A) C(x)
... Example – Demand: Private Schools The demand for a commodity usually goes down as its price goes up. It is traditional to use the letter q for the (quantity of) demand, as measured, for example, in sales. The demand for private schools in Michigan depends on the tuition cost and can be approximated ...
... Example – Demand: Private Schools The demand for a commodity usually goes down as its price goes up. It is traditional to use the letter q for the (quantity of) demand, as measured, for example, in sales. The demand for private schools in Michigan depends on the tuition cost and can be approximated ...
Production and Cost Analysis: Part II
... • Moore's law states that the cost of computing will fall by half every 18 months. – As the price of computer chips falls, other industries are affected as well. ...
... • Moore's law states that the cost of computing will fall by half every 18 months. – As the price of computer chips falls, other industries are affected as well. ...
1. Consumer Theory (Cont.) 1.5- Consumer Choice 1.6
... • We could think that the responsiveness of the demand of a good to its price can be given by the slope of the demand curve, since it gives the magnitude of the variation in the quantity demanded that follows a price change. However, that measure is dependent on the units in which quantities and pr ...
... • We could think that the responsiveness of the demand of a good to its price can be given by the slope of the demand curve, since it gives the magnitude of the variation in the quantity demanded that follows a price change. However, that measure is dependent on the units in which quantities and pr ...
Consumption, Environmental Sustainability and - RegNet
... recourse has been to look to environmental groups or deep ecology protagonists to campaign for and point out the environmental imperatives. Yet, it is argued here, geographers have the capacity to enter this debate from a different perspective. That is, by understanding more about how and why Austra ...
... recourse has been to look to environmental groups or deep ecology protagonists to campaign for and point out the environmental imperatives. Yet, it is argued here, geographers have the capacity to enter this debate from a different perspective. That is, by understanding more about how and why Austra ...
section1powerpoint
... which the percentage change in quantity demanded is larger in absolute value than the percentage change in price. • The demand elasticity has an absolute value greater than one. • An example could be the demand for bananas or any other product for which there are close substitutes. ...
... which the percentage change in quantity demanded is larger in absolute value than the percentage change in price. • The demand elasticity has an absolute value greater than one. • An example could be the demand for bananas or any other product for which there are close substitutes. ...
RIGHT_SIDE[1]
... emerged organs at the same time (SD=0). Preliminary results suggest 1,000 ppm caffeine marginally promotes leaf emergence. ...
... emerged organs at the same time (SD=0). Preliminary results suggest 1,000 ppm caffeine marginally promotes leaf emergence. ...
The Direct Trade-Induced Composition Effect and Its Environmental
... new land research. Using this approach, these authors are able to distinguish empirically between the negative environment consequences of scalar increases in economic activity (scale effect), the positive environment consequences of a greater real income on the cleaner production technique (techniq ...
... new land research. Using this approach, these authors are able to distinguish empirically between the negative environment consequences of scalar increases in economic activity (scale effect), the positive environment consequences of a greater real income on the cleaner production technique (techniq ...
Example 12.1 Minimizing Costs for a Cobb
... 2. Capital Costs: For accountants capital costs are the historical price of a machine, adjusted for depreciation. Here the economists cost notion is quite different. For economists the cost of machine is the implicit value of the machine – that is, economic cost is assessed in terms of alternative u ...
... 2. Capital Costs: For accountants capital costs are the historical price of a machine, adjusted for depreciation. Here the economists cost notion is quite different. For economists the cost of machine is the implicit value of the machine – that is, economic cost is assessed in terms of alternative u ...
Week 3
... their use accordingly. Since lubricating oil is a complement to fuel, less of it will be demanded as the usage of cars declines. Car engines present more complex problem. If they are complements, fewer of them will be demanded as the demand for cars decreases. On the other hand, if people substitute ...
... their use accordingly. Since lubricating oil is a complement to fuel, less of it will be demanded as the usage of cars declines. Car engines present more complex problem. If they are complements, fewer of them will be demanded as the demand for cars decreases. On the other hand, if people substitute ...
Comments
... to investment, leading to production inefficiency. It creates the space for bubbles. 2. Liquidity shortage and the investment effects of bubbles • Financial market imperfections lead to the shortage of asset supply (Holmstrom and Tirole, 1998, Caballero, 2006). Bubbles arise and serve as a vehicle f ...
... to investment, leading to production inefficiency. It creates the space for bubbles. 2. Liquidity shortage and the investment effects of bubbles • Financial market imperfections lead to the shortage of asset supply (Holmstrom and Tirole, 1998, Caballero, 2006). Bubbles arise and serve as a vehicle f ...
evaluation of the determinants of operational efficiency in
... because they suffer from under evaluation of credit risk and misallocation of resources. Therefore, it was denoted that the cost of the Tunisian banks increases with non performing loans. Employing Data Envelopment fixed effect regression analysis by Sarchez, Hassan and Bartkus (2013), efficient ban ...
... because they suffer from under evaluation of credit risk and misallocation of resources. Therefore, it was denoted that the cost of the Tunisian banks increases with non performing loans. Employing Data Envelopment fixed effect regression analysis by Sarchez, Hassan and Bartkus (2013), efficient ban ...
Chapter 26 - Lake Fenton Community Schools
... • How can energy efficiency be improved? – People can recycle old appliances and vehicles and purchase newer, more energy-efficient models as well as improve the energy efficiency of older homes. ...
... • How can energy efficiency be improved? – People can recycle old appliances and vehicles and purchase newer, more energy-efficient models as well as improve the energy efficiency of older homes. ...
Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... AP Vertical Teams, Pre-AP, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Entrance Examination Board. Admitted Class Evaluation Service, CollegeEd, Connect to college success, MyRoad, SAT Professional Development, SAT Readiness Program, and Setting the Cornerstones are trademarks o ...
... AP Vertical Teams, Pre-AP, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Entrance Examination Board. Admitted Class Evaluation Service, CollegeEd, Connect to college success, MyRoad, SAT Professional Development, SAT Readiness Program, and Setting the Cornerstones are trademarks o ...
Quantifying the effects of urban stormwater management – towards
... enhanced “landscape quality” (see above). For instance, Fuller et al. (2007) showed that species rich urban parks increase psychological wellbeing. Species and structurally rich vegetation along roadsides enhance air quality (e.g. Weber et al. 2014a) and increase attractiveness of open spaces (e.g. ...
... enhanced “landscape quality” (see above). For instance, Fuller et al. (2007) showed that species rich urban parks increase psychological wellbeing. Species and structurally rich vegetation along roadsides enhance air quality (e.g. Weber et al. 2014a) and increase attractiveness of open spaces (e.g. ...
Model answers
... the aim and responsibility of every worker in every activity at all times in a Kaizen Costing system. As a result of involving all workers significant overall cost reductions can be achieved over time. Both Standard Costs and Kaizen Costing may be used as part of a performance measurement process, h ...
... the aim and responsibility of every worker in every activity at all times in a Kaizen Costing system. As a result of involving all workers significant overall cost reductions can be achieved over time. Both Standard Costs and Kaizen Costing may be used as part of a performance measurement process, h ...
Chapter 2: Forces and Energy
... this period we examine the origins of forces and find that all known forces can be classified as one of four fundamental forces. Based on their properties, all of the currently known forces fall into four types: the gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. All forces ...
... this period we examine the origins of forces and find that all known forces can be classified as one of four fundamental forces. Based on their properties, all of the currently known forces fall into four types: the gravitational, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, and weak nuclear forces. All forces ...
Political and Economic Freedom and the Environment - S
... third reasons are simply due to competitive reasons; in order to survive firms have to react to changes in the market environment. Clearly, these two effects are only relevant if there are environmental regulations or a demand for cleaner production/goods from the consumers. (iii) The Stability Effe ...
... third reasons are simply due to competitive reasons; in order to survive firms have to react to changes in the market environment. Clearly, these two effects are only relevant if there are environmental regulations or a demand for cleaner production/goods from the consumers. (iii) The Stability Effe ...
Chap0132
... • The long-run average cost curve slopes upward because of diseconomies of scale • The envelope relationship between short-run and longrun average cost curves reflects that the short-run average cost curves are always above the long-run average cost curve, except at just one point • An entrepreneur ...
... • The long-run average cost curve slopes upward because of diseconomies of scale • The envelope relationship between short-run and longrun average cost curves reflects that the short-run average cost curves are always above the long-run average cost curve, except at just one point • An entrepreneur ...








![RIGHT_SIDE[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008151789_1-51a6c051d0de8160ad7e0898d1b0c2bc-300x300.png)












