Ancient Greece The Golden Age Notes
... Ancient Greece – The Golden Age What is a Golden Age? _____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________. Greek city-states united to form a group of allies, or ____________________________________, against Persia, a common enemy. _ ...
... Ancient Greece – The Golden Age What is a Golden Age? _____________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________. Greek city-states united to form a group of allies, or ____________________________________, against Persia, a common enemy. _ ...
Athens and Sparta - Jacqueline Firestone
... who seems to be lacking integrity, but is fighting to make his name great. It is not only clear through Homer’s projection of the differing ideologies on both Achilles and Hector that he found these polis’ mindsets intriguing, but also his pull toward the Spartan outlook above the Athenian understan ...
... who seems to be lacking integrity, but is fighting to make his name great. It is not only clear through Homer’s projection of the differing ideologies on both Achilles and Hector that he found these polis’ mindsets intriguing, but also his pull toward the Spartan outlook above the Athenian understan ...
The Peloponnesian War
... Athenians did not want to hide. PRIDE!!! Plague struck. Lasted 4 years. Killed 1/4-1/3 of all Athenians. Athenians came out to fight. Both won and lost battles. Peace treaty in 421, but did not last long. Athens just bought time to regroup. Spartans eventually won. War ended around 404 BCE. Lasted a ...
... Athenians did not want to hide. PRIDE!!! Plague struck. Lasted 4 years. Killed 1/4-1/3 of all Athenians. Athenians came out to fight. Both won and lost battles. Peace treaty in 421, but did not last long. Athens just bought time to regroup. Spartans eventually won. War ended around 404 BCE. Lasted a ...
2008 SAN ANTONIO CLASSICAL SOCIETY
... a) Leonidas b) Themistocles c) Callimachus d) Miltiades. 33) Name the Spartan king who went over to the Persians or medized in 490 BCE. a) Demaratus b) Cleomenes c) Leonidas d) Agis. 34) In 484 BCE the Great King who decided to invade Greece was a) Darius b) Xerxes c) Cyrus d) Mardonius 35) Which of ...
... a) Leonidas b) Themistocles c) Callimachus d) Miltiades. 33) Name the Spartan king who went over to the Persians or medized in 490 BCE. a) Demaratus b) Cleomenes c) Leonidas d) Agis. 34) In 484 BCE the Great King who decided to invade Greece was a) Darius b) Xerxes c) Cyrus d) Mardonius 35) Which of ...
20130411164052
... Athens – post war • Because of war and a plague that struck during war, Athens lost more than ¼ of its people • Many left Athens to become Mercenaries (hired soldiers) for the Persians ...
... Athens – post war • Because of war and a plague that struck during war, Athens lost more than ¼ of its people • Many left Athens to become Mercenaries (hired soldiers) for the Persians ...
Chapter Two - GEOCITIES.ws
... •Wrote little, therefore, known through the writings of “foreigners” •Poor ...
... •Wrote little, therefore, known through the writings of “foreigners” •Poor ...
Olympic Games Assembly
... women were allowed to take part in as they were allowed to own horses that raced. I call all those for the chariot racing! Take your positions please! (Competitors take their places and jostle for starting position) On your marks! Go! And they’re off! And look at them go! Oh no – the horse from Argo ...
... women were allowed to take part in as they were allowed to own horses that raced. I call all those for the chariot racing! Take your positions please! (Competitors take their places and jostle for starting position) On your marks! Go! And they’re off! And look at them go! Oh no – the horse from Argo ...
Athenian Government Rocks - wwpk-3
... Athens, you voted on laws yourselves. This is what we call a direct democracy. A direct democracy was better than an oligarchy because in an oligarchy, although you get certain protections, you get very little political rights such as voting. Therfore, you have a very little say in how the city-stat ...
... Athens, you voted on laws yourselves. This is what we call a direct democracy. A direct democracy was better than an oligarchy because in an oligarchy, although you get certain protections, you get very little political rights such as voting. Therfore, you have a very little say in how the city-stat ...
Chapter 5 Classical Greece
... • Spartan Daily Life Con’t 2. – Girls: • Received military training, put love for Sparta above all (even family) – “Come back with your shield or on it.” ...
... • Spartan Daily Life Con’t 2. – Girls: • Received military training, put love for Sparta above all (even family) – “Come back with your shield or on it.” ...
Chapter 5 Classical Greece
... • Spartan Daily Life Con’t 2. – Girls: • Received military training, put love for Sparta above all (even family) – “Come back with your shield or on it.” ...
... • Spartan Daily Life Con’t 2. – Girls: • Received military training, put love for Sparta above all (even family) – “Come back with your shield or on it.” ...
The Peloponnesian War
... Sparta called on the other Greek poli for assistance to quell a helot uprising. The helots were slaves forced to farm the land that fed the Spartans. Athens sent a force of 4000 soldiers, but the Spartans rejected the Athenian support. Thucydides later suggested that the Spartans feared the Athenian ...
... Sparta called on the other Greek poli for assistance to quell a helot uprising. The helots were slaves forced to farm the land that fed the Spartans. Athens sent a force of 4000 soldiers, but the Spartans rejected the Athenian support. Thucydides later suggested that the Spartans feared the Athenian ...
Chapter 16: The Americas
... a. Pericles and the city-state of Sparta surrounded Athens. The powerful Athenian navy would bring supplies to the city from its colonies and allies. However, Sparta lacked a and could not stop the Athenian ships. b. After two years of remaining safe, a broke out in the overcrowded city of Athens. M ...
... a. Pericles and the city-state of Sparta surrounded Athens. The powerful Athenian navy would bring supplies to the city from its colonies and allies. However, Sparta lacked a and could not stop the Athenian ships. b. After two years of remaining safe, a broke out in the overcrowded city of Athens. M ...
An Introduction to Ancient Greece
... and Aristotle studied and taught in and around Athens. Many of the famous buildings that are only ruins today were in Athens. An example is the Parthenon. Athens was the home of the Greeks' great fleet, which beat back the invading Persians several times during the Persian Wars. Athens also used thi ...
... and Aristotle studied and taught in and around Athens. Many of the famous buildings that are only ruins today were in Athens. An example is the Parthenon. Athens was the home of the Greeks' great fleet, which beat back the invading Persians several times during the Persian Wars. Athens also used thi ...
Peloponnesian Wars ppt.
... Greece became weak because of the wars Many people died in battle and because of disease Many young Greeks left and joined the Persian army Sparta ruled Greece and was very harsh Many city-states rebelled against Sparta In 338 BC, Macedonia conquered Greece ...
... Greece became weak because of the wars Many people died in battle and because of disease Many young Greeks left and joined the Persian army Sparta ruled Greece and was very harsh Many city-states rebelled against Sparta In 338 BC, Macedonia conquered Greece ...
Athens and Sparta - Greek Worlds Apart Athenian Art What
... projects occurred in the 7th century BC and were usually to supply communal drinking fountains. Modernday comparisons Both Samos and Athens were supplied by longdistance aqueducts from the 6th century BCE. aqueducts were a means to transport water from one place to another, achieving a r ...
... projects occurred in the 7th century BC and were usually to supply communal drinking fountains. Modernday comparisons Both Samos and Athens were supplied by longdistance aqueducts from the 6th century BCE. aqueducts were a means to transport water from one place to another, achieving a r ...
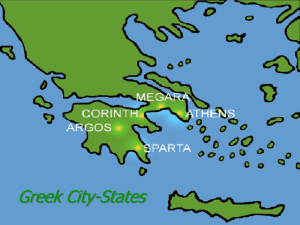
Greek City - States
... and hardship to become a superior Spartan soldier and citizen! • Sparta's government was an oligarchy. The people were ruled by a small group of warriors. The Spartans spoke Greek, wrote Greek, thought of themselves as Greeks, but they were very different from the other Greek city-states, and proud ...
... and hardship to become a superior Spartan soldier and citizen! • Sparta's government was an oligarchy. The people were ruled by a small group of warriors. The Spartans spoke Greek, wrote Greek, thought of themselves as Greeks, but they were very different from the other Greek city-states, and proud ...
chris-manassa
... the Spartan city which was their rival for so many years and they would rather let Sparta’s pride be trampled underfoot. Cimon, on the other hand, put Sparta’s interest before his own country’s aggrandisement and persuaded the Athenians to send a large force of hoplites to her aid. When a nation is ...
... the Spartan city which was their rival for so many years and they would rather let Sparta’s pride be trampled underfoot. Cimon, on the other hand, put Sparta’s interest before his own country’s aggrandisement and persuaded the Athenians to send a large force of hoplites to her aid. When a nation is ...
golden age - athens - Missouri State University
... States divided generally between eastern coastal & island cities worried about Persian revenge and mainland, western cities dependent on Sparta’s infantry ...
... States divided generally between eastern coastal & island cities worried about Persian revenge and mainland, western cities dependent on Sparta’s infantry ...
Concise Timeline for The Golden Age of Athens
... Xerxes’ Invasion of Greece; Battles of Thermopylae and Salamis Death of Xenophanes ...
... Xerxes’ Invasion of Greece; Battles of Thermopylae and Salamis Death of Xenophanes ...
2009 FJCL State Latin Forum Hellenic History
... 14. First mentioned in the Odyssey, which group of Greeks’ invasion marks the beginning of the Greek Dark Ages? a. Ionians b. Dorians c. Perians d. Dravidians 15. Which culture, found on Crete, was one of the earliest of Greek civilizations, lasting from 2700 – 1450 BC? a. Mycenaean b. Dorian c. Min ...
... 14. First mentioned in the Odyssey, which group of Greeks’ invasion marks the beginning of the Greek Dark Ages? a. Ionians b. Dorians c. Perians d. Dravidians 15. Which culture, found on Crete, was one of the earliest of Greek civilizations, lasting from 2700 – 1450 BC? a. Mycenaean b. Dorian c. Min ...
Classical Greece-2014
... rarely had to travel more than 85 miles in order to reach the coastline. – As a result the Greeks became skilled sailors, and linked them with other societies. – Due to the fact that Greece lacked natural resources trade became a vital part of Greek life. ...
... rarely had to travel more than 85 miles in order to reach the coastline. – As a result the Greeks became skilled sailors, and linked them with other societies. – Due to the fact that Greece lacked natural resources trade became a vital part of Greek life. ...
Comparing Sparta and Athens
... category. Award one point on the class Points Chart (100 accumulated points in 9 weeks = extra credit on tests) if they correctly place their word. Allow students to volunteer, but make sure each student goes. Have students copy the diagram as the activity moves along. Quiz (10 mins): pass out quiz ...
... category. Award one point on the class Points Chart (100 accumulated points in 9 weeks = extra credit on tests) if they correctly place their word. Allow students to volunteer, but make sure each student goes. Have students copy the diagram as the activity moves along. Quiz (10 mins): pass out quiz ...
Lsn 17 Map Quiz and Greece
... • What distinctions did exist in Spartan society were based not on wealth or social status, but on prowess, discipline, and military talent • Spartan educational system cultivated such attributes from an early age – Boys left their homes at age seven to live in military barracks under a rigorous reg ...
... • What distinctions did exist in Spartan society were based not on wealth or social status, but on prowess, discipline, and military talent • Spartan educational system cultivated such attributes from an early age – Boys left their homes at age seven to live in military barracks under a rigorous reg ...
Women of Athens and Sparta
... Sparta, a beautiful town near the river Evrotas, located in the center of the Peloponnese in southern Greece. Sparta was the Dorian Greek military state, considered as the protector of Greece as it was providing large army to Greece for many years. At present, Sparta is the administrative capital of ...
... Sparta, a beautiful town near the river Evrotas, located in the center of the Peloponnese in southern Greece. Sparta was the Dorian Greek military state, considered as the protector of Greece as it was providing large army to Greece for many years. At present, Sparta is the administrative capital of ...
Sparta

Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, Spártā; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, Spártē) or Lacedaemon (/ˌlæsəˈdiːmən/; Λακεδαίμων, Lakedaímōn) was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the overall leader of the combined Greek forces during the Greco-Persian Wars. Between 431 and 404 BC, Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War, from which it emerged victorious, though at great cost of lives lost. Sparta's defeat by Thebes in the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended Sparta's prominent role in Greece. However, it maintained its political independence until the Roman conquest of Greece in 146 BC. It then underwent a long period of decline, especially in the Middle Ages, when many Spartans moved to live in Mystras. Modern Sparta is the capital of the Greek regional unit of Laconia and a center for the processing of goods such as citrus and olives.Sparta was unique in ancient Greece for its social system and constitution, which completely focused on military training and excellence. Its inhabitants were classified as Spartiates (Spartan citizens, who enjoyed full rights), mothakes (non-Spartan free men raised as Spartans), perioikoi (freedmen), and helots (state-owned serfs, enslaved non-Spartan local population). Spartiates underwent the rigorous agoge training and education regimen, and Spartan phalanges were widely considered to be among the best in battle. Spartan women enjoyed considerably more rights and equality to men than elsewhere in the classical world.Sparta was the subject of fascination in its own day, as well as in the West following the revival of classical learning. This love or admiration of Sparta is known as Laconism or Laconophilia. At its peak around 500 BC the size of the city would have been some 20,000 – 35,000 free residents, plus numerous helots and perioikoi (“dwellers around”). At 40,000 – 50,000 it was one of the largest Greek cities; however, according to Thucydides, the population of Athens in 431 BC was 360,000 – 610,000, making it unlikely that Athens was smaller than Sparta in 5th century BC.