AORTIC STENOSIS - Ravenwood-PA
... obstruction to LV outflow may not be at the aortic valve but rather in the sub or supra-valvular regions Also indicated to evaluate the coronaries in AS patients at risk for coronary artery disease ...
... obstruction to LV outflow may not be at the aortic valve but rather in the sub or supra-valvular regions Also indicated to evaluate the coronaries in AS patients at risk for coronary artery disease ...
Shone`s complex – a rare case report
... SHONE’S COMPLEX is a rare cardiac anomaly consisting of four obstructive lesions of the left heart: supra mitral membrane, parachute mitral valve, subaortic stenosis, coarctation of aorta. We report a 2 year old female child who was initially diagnosed as having aortic stenosis but continued having ...
... SHONE’S COMPLEX is a rare cardiac anomaly consisting of four obstructive lesions of the left heart: supra mitral membrane, parachute mitral valve, subaortic stenosis, coarctation of aorta. We report a 2 year old female child who was initially diagnosed as having aortic stenosis but continued having ...
Mitral valve replacement
... - fibrosis & deformity of valve leaflets. - shortening of chordae tendinae . 2. Dilatation of the LV & mitral valve ring (functional) 3. Dysfunction of papillary muscles: due to ischemia , ...
... - fibrosis & deformity of valve leaflets. - shortening of chordae tendinae . 2. Dilatation of the LV & mitral valve ring (functional) 3. Dysfunction of papillary muscles: due to ischemia , ...
Bacterial Endocarditis of Systemic Atrioventricular Valve
... In cases without additional defects, cardiac complications that affect the survival and life quality are complete atrioventricular heart block, systemic (tricuspid) atrioventricular valve regurgitation, infective endocarditis, supraventricular tachycardia and congestive heart failure. The most commo ...
... In cases without additional defects, cardiac complications that affect the survival and life quality are complete atrioventricular heart block, systemic (tricuspid) atrioventricular valve regurgitation, infective endocarditis, supraventricular tachycardia and congestive heart failure. The most commo ...
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement icd 10
... Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR) is a new therapy for patients with severe aortic stenosis who are not candidates for surgery 1,2 or who are at high risk. The CoreValve Platform features an advanced TAVR design to meet your transcatheter aortic valve replacement patient's specific clini ...
... Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR) is a new therapy for patients with severe aortic stenosis who are not candidates for surgery 1,2 or who are at high risk. The CoreValve Platform features an advanced TAVR design to meet your transcatheter aortic valve replacement patient's specific clini ...
Seven and one-half years` experience with the Medtronic
... compared with more than 6% per year for our aortic ball valves, although the latter were implanted during a previous time frame, which may have affected the results (5). There were no cases of mechanical failure with either of these tilting disc valve models, whereas we experienced fabric disruption ...
... compared with more than 6% per year for our aortic ball valves, although the latter were implanted during a previous time frame, which may have affected the results (5). There were no cases of mechanical failure with either of these tilting disc valve models, whereas we experienced fabric disruption ...
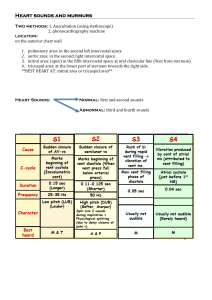
Heart sounds and murmurs
... 2. aortic area: in the second right intercostal space 3. mitral area: (apex) in the fifth intercostal space at mid clavicular line (9cm from sternum) 4. tricuspid area: at the lower part of sternum towards the right side. **BEST HEART AT: mitral area or tricuspid area** ...
... 2. aortic area: in the second right intercostal space 3. mitral area: (apex) in the fifth intercostal space at mid clavicular line (9cm from sternum) 4. tricuspid area: at the lower part of sternum towards the right side. **BEST HEART AT: mitral area or tricuspid area** ...
Mitral Systolic Anterior Motion (SAM) with Dynamic Left Ventricular
... to be aware of this uncommon potential postoperative occurrence, as therapy requires fluids, beta-blocker therapy, and removal of inotropes.13 Phenylephrine has been used to “splint open the LVOT” in hemodynamically compromised patients.11 It appears that “risk factors” for development of post-AVR S ...
... to be aware of this uncommon potential postoperative occurrence, as therapy requires fluids, beta-blocker therapy, and removal of inotropes.13 Phenylephrine has been used to “splint open the LVOT” in hemodynamically compromised patients.11 It appears that “risk factors” for development of post-AVR S ...
MVRepair Fact Sheet
... for this volume overload for many months or years (provided the leakage came on slowly and progressively), but it eventually begins to fail producing symptoms of shortness of breath or fatigue. ...
... for this volume overload for many months or years (provided the leakage came on slowly and progressively), but it eventually begins to fail producing symptoms of shortness of breath or fatigue. ...
MVRepair Fact Sheet
... for this volume overload for many months or years (provided the leakage came on slowly and progressively), but it eventually begins to fail producing symptoms of shortness of breath or fatigue. ...
... for this volume overload for many months or years (provided the leakage came on slowly and progressively), but it eventually begins to fail producing symptoms of shortness of breath or fatigue. ...
- British Heart Valve Society
... pumps blood to the head and body. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium. The mitral valve is placed at the junction between the left atrium and left ventricle and is the inlet valve to the left ventricle. It is open in diastole to allow blood to flow between the left atrium ...
... pumps blood to the head and body. It receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium. The mitral valve is placed at the junction between the left atrium and left ventricle and is the inlet valve to the left ventricle. It is open in diastole to allow blood to flow between the left atrium ...
Surgical Repair Is the Treatment of Choice for Native Aortic
... Immediate postnatal LV growth? The dramatic acute dimensional changes following repair of borderline LV lesions are the result of normalization of loading conditions that permit full expression of left ventricular phenotype This not evidence of growth but simple unmasking of the left ...
... Immediate postnatal LV growth? The dramatic acute dimensional changes following repair of borderline LV lesions are the result of normalization of loading conditions that permit full expression of left ventricular phenotype This not evidence of growth but simple unmasking of the left ...
CARDIAC ASSESSMENT - University of Manitoba
... dub sound more easily than the tub at the aortic and pulmonic valve areas. galloping. Si is considered a ventricIf you have difficulty distinguishing ular gallop; S.,, an atrial gallop. S| from S,, try palpating the carotid pulse as you auscultate. The ¡ub sound Describing your findings of S, will o ...
... dub sound more easily than the tub at the aortic and pulmonic valve areas. galloping. Si is considered a ventricIf you have difficulty distinguishing ular gallop; S.,, an atrial gallop. S| from S,, try palpating the carotid pulse as you auscultate. The ¡ub sound Describing your findings of S, will o ...
Anesthesia for Patients with Valvular Heart Disease for Non
... Mitral stenosis is a narrowing of the mitral valve orifice that results in left atrial hypertension, limited filling of the LV, pulmonary congestion, and in moderate to severe cases, pulmonary arterial hypertension and right ventricular pressure overload. Dyspnea is the most common presenting sympto ...
... Mitral stenosis is a narrowing of the mitral valve orifice that results in left atrial hypertension, limited filling of the LV, pulmonary congestion, and in moderate to severe cases, pulmonary arterial hypertension and right ventricular pressure overload. Dyspnea is the most common presenting sympto ...
COR - IS MU
... The valves are grouped so closely that when they are listened to at their real sites, it is not possible to distinguish clearly the sounds produced at each valve. The blood tends to carry the sound in the direction of its flow, consequently the valve sounds are listened to at specified auscultatory ...
... The valves are grouped so closely that when they are listened to at their real sites, it is not possible to distinguish clearly the sounds produced at each valve. The blood tends to carry the sound in the direction of its flow, consequently the valve sounds are listened to at specified auscultatory ...
right atrial thrombus, aortic regurgitation, coronary artery stenosis
... structures or on endothelial cells of intravalvularcapillaries, and subsequent binding, of auto antibodies to the phospholipids -antigen complexes causing a endocardial cell activation and microscopicspots of thrombosis(9). These micro clots by natural healing mechanism switching into fibrotic tissu ...
... structures or on endothelial cells of intravalvularcapillaries, and subsequent binding, of auto antibodies to the phospholipids -antigen complexes causing a endocardial cell activation and microscopicspots of thrombosis(9). These micro clots by natural healing mechanism switching into fibrotic tissu ...
Auscultation of the heart
... at the beginning of diastole the rush of blood into the left ventricle causes vibration of the valve leaflets and the chordae tendinae. • It is heard best at the apex in the left lateral position. It is louder on inspiration. Dull, low – pitched. ...
... at the beginning of diastole the rush of blood into the left ventricle causes vibration of the valve leaflets and the chordae tendinae. • It is heard best at the apex in the left lateral position. It is louder on inspiration. Dull, low – pitched. ...
Heart Sounds Worksheet
... Explain the hypertrophy associated with each valvular disorder listed in the previous question. ...
... Explain the hypertrophy associated with each valvular disorder listed in the previous question. ...
Mitral Valve Stenosis
... removing tissues that obstruct the valve or making adjustments to the fibers, or cords, which hold the base of the valve’s flaps to the heart. A valve repair may not last or be successful and may need to be repeated. ...
... removing tissues that obstruct the valve or making adjustments to the fibers, or cords, which hold the base of the valve’s flaps to the heart. A valve repair may not last or be successful and may need to be repeated. ...
Functional Anatomy of Heart
... • Heart is muscular organ. It is involuntary, present in the middle of the thoracic cavity, about the size of fist [14cm long, 9cm wide]. • Sternum lies anteriorly and vertebral column [backbone] lies posteriorly and lungs laterally. • Heart has base and apex. - Base is at the top, behind the 2nd in ...
... • Heart is muscular organ. It is involuntary, present in the middle of the thoracic cavity, about the size of fist [14cm long, 9cm wide]. • Sternum lies anteriorly and vertebral column [backbone] lies posteriorly and lungs laterally. • Heart has base and apex. - Base is at the top, behind the 2nd in ...
Rheumatic heart disease
... • In chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) the inflammatory lesions in the heart undergo organisation and fibrosis. • Recurrent episodes of rheumatic fever cause cumulative damage. • In particular, the valves become scarred and distorted, affecting their function. • Clinical signs of the valvu ...
... • In chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) the inflammatory lesions in the heart undergo organisation and fibrosis. • Recurrent episodes of rheumatic fever cause cumulative damage. • In particular, the valves become scarred and distorted, affecting their function. • Clinical signs of the valvu ...
Rembert Pogge von Strandmann PhD
... • Baseline and post-BAV AS severity, as assessed by several echocardiographic indices, were similar between the groups. However, at one month after BAV the AVA was significantly larger, but the SWL loss and aortic valve resistance were significantly lower, in the paclitaxel-BAV group. • At follow up ...
... • Baseline and post-BAV AS severity, as assessed by several echocardiographic indices, were similar between the groups. However, at one month after BAV the AVA was significantly larger, but the SWL loss and aortic valve resistance were significantly lower, in the paclitaxel-BAV group. • At follow up ...
Mitral Valve Regurgitation
... work very well. These valves last longer without wearing out, but blood thinners must be taken for the rest of your life. Other than surgery, drugs that expand (dilate) blood vessels and slightly lower blood pressure are the only medicines helpful in treating mitral regurgitation. They work best if ...
... work very well. These valves last longer without wearing out, but blood thinners must be taken for the rest of your life. Other than surgery, drugs that expand (dilate) blood vessels and slightly lower blood pressure are the only medicines helpful in treating mitral regurgitation. They work best if ...
contact line
... • In chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) the inflammatory lesions in the heart undergo organisation and fibrosis. • Recurrent episodes of rheumatic fever cause cumulative damage. • In particular, the valves become scarred and distorted, affecting their function. • Clinical signs of the valvular an ...
... • In chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD) the inflammatory lesions in the heart undergo organisation and fibrosis. • Recurrent episodes of rheumatic fever cause cumulative damage. • In particular, the valves become scarred and distorted, affecting their function. • Clinical signs of the valvular an ...