5. Universal Laws of Motion
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
Gravity
... On Earth, we have air. Air resistance will cause some objects to fall more slowly than others will. This works to our advantage when we want to fall more slowly, for example, when a skydiver jumps out of an airplane. He uses a parachute to create as much air resistance as possible to slow down his f ...
... On Earth, we have air. Air resistance will cause some objects to fall more slowly than others will. This works to our advantage when we want to fall more slowly, for example, when a skydiver jumps out of an airplane. He uses a parachute to create as much air resistance as possible to slow down his f ...
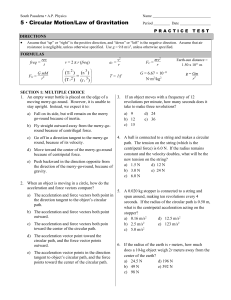
1. What is the weight of a 200 kg object? 2. A woman - IES Al
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
... is the acceleration of the basket? 3. A 20.0 kg mass is pulled by along a surface by a horizontal force of 100 N. Friction is 20.0 N. What is the acceleration of the mass? 4. A 49-N block is pulled by a horizontal force of 50.0 N along a rough horizontal surface at a constant acceleration of 6 m/s/s ...
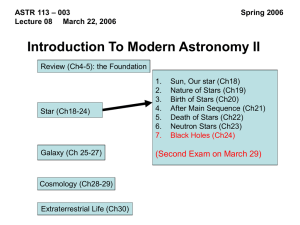
Black Holes - Solar Physics and Space Weather
... 4. In what sense is a black hole “black”? 5. In what way are black holes actually simpler than any other objects in astronomy? 6. What happens to an object that falls into a black hole? 7. Do black holes last forever? ...
... 4. In what sense is a black hole “black”? 5. In what way are black holes actually simpler than any other objects in astronomy? 6. What happens to an object that falls into a black hole? 7. Do black holes last forever? ...
Space #3
... Escape velocity: the initial velocity required by a projectile to rise vertically and just escape the gravitational field of a planet, so that it doesn’t return to that planet under the influence of their mutual gravitational attraction o It is the velocity which will result in zero mechanical energ ...
... Escape velocity: the initial velocity required by a projectile to rise vertically and just escape the gravitational field of a planet, so that it doesn’t return to that planet under the influence of their mutual gravitational attraction o It is the velocity which will result in zero mechanical energ ...
newtons 1st and 2nd law
... Standing here, my acceleration is zero and the net force on me is zero. The Earth is still pulling me down but the floor is pushing me up with the same force. I’ll try not to fall. Weight is the gravitational force on an object. Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity (W=mg) W = m x 9.8 m/s2 ( ...
... Standing here, my acceleration is zero and the net force on me is zero. The Earth is still pulling me down but the floor is pushing me up with the same force. I’ll try not to fall. Weight is the gravitational force on an object. Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity (W=mg) W = m x 9.8 m/s2 ( ...
1) If a blue whale has a mass of 1
... 7) A 5 kg projectile has a velocity of 255 m/s to the right. What force is required to stop this projectile in 1.45 s? ...
... 7) A 5 kg projectile has a velocity of 255 m/s to the right. What force is required to stop this projectile in 1.45 s? ...
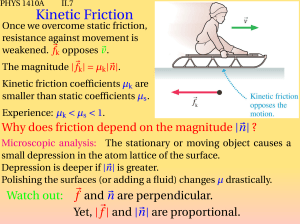
Kinetic Friction
... what does the scale read on the moon? what does the scale read in a freely falling elevator? AVOID ACCELERATED REFERENCE FRAMES ! ...
... what does the scale read on the moon? what does the scale read in a freely falling elevator? AVOID ACCELERATED REFERENCE FRAMES ! ...
PPT - LSU Physics
... of the Earth. In the film Farrell experiences normal gravity until he hits the core, then experiences a moment of weightlessness at the core, and then resumes normal gravity (in the opposite direction) as the train continues to the other side of the Earth. Decide if this is what really would happen ...
... of the Earth. In the film Farrell experiences normal gravity until he hits the core, then experiences a moment of weightlessness at the core, and then resumes normal gravity (in the opposite direction) as the train continues to the other side of the Earth. Decide if this is what really would happen ...