IT`S UNIVERSAL GRAVITY CONCEPTS
... quantities from the other two. For instance, you can figure out the mass of a planet simply by observing how its moons orbit around it. The mass of Jupiter was calculated this way hundreds of years ago. Calculating gravitational forces also helps astronomers find planets. In the 1840s, the planet Ur ...
... quantities from the other two. For instance, you can figure out the mass of a planet simply by observing how its moons orbit around it. The mass of Jupiter was calculated this way hundreds of years ago. Calculating gravitational forces also helps astronomers find planets. In the 1840s, the planet Ur ...
Relativistic Mass and Virtual Objects
... the resultant speed of the entangled Einstein-spacetime components must be equal to c so the spin speed of the particle/vortex must decrease. But due to the law of conservation of spin of the particle/vortex (spin = Mrelativistic vspin r), its mass must increase so there appear the inflows of the ad ...
... the resultant speed of the entangled Einstein-spacetime components must be equal to c so the spin speed of the particle/vortex must decrease. But due to the law of conservation of spin of the particle/vortex (spin = Mrelativistic vspin r), its mass must increase so there appear the inflows of the ad ...
Physics - Content by Unit
... Fritz Zwicky, an astronomer at the California Institute of Technology, stumbled across the gravitational effects of dark matter in the early 1930s while studying how galaxies move within the Coma Cluster. The Coma Cluster consists of approximately 1,000 galaxies spread over about two degrees on the ...
... Fritz Zwicky, an astronomer at the California Institute of Technology, stumbled across the gravitational effects of dark matter in the early 1930s while studying how galaxies move within the Coma Cluster. The Coma Cluster consists of approximately 1,000 galaxies spread over about two degrees on the ...
GENERAL RELATIVITY - Raman Research Institute
... The above statement is called the “Equivalence Principle” given by Einstein. For example let us assume two closed laboratories „A‟ and „B‟. The laboratory A is on the earth and the laboratory B is in deep space accelerating with the same acceleration as that of the „g‟ of earth. Now the observer in ...
... The above statement is called the “Equivalence Principle” given by Einstein. For example let us assume two closed laboratories „A‟ and „B‟. The laboratory A is on the earth and the laboratory B is in deep space accelerating with the same acceleration as that of the „g‟ of earth. Now the observer in ...
Definitions
... obey this law. Any force not obeying this law would cause big problems in physics, like getting free mechanical energy from nothing. However, the Second Law in the form we learn it in Physics I is not exactly correct. Where did Newton go wrong? ...
... obey this law. Any force not obeying this law would cause big problems in physics, like getting free mechanical energy from nothing. However, the Second Law in the form we learn it in Physics I is not exactly correct. Where did Newton go wrong? ...
chapter9_PC
... This is a sweeping generalization of the principle of Newtonian relativity, which refers only to the laws of mechanics The results of any kind of experiment performed in a laboratory at rest must be the same as when performed in a laboratory moving at a constant velocity relative to the first one No ...
... This is a sweeping generalization of the principle of Newtonian relativity, which refers only to the laws of mechanics The results of any kind of experiment performed in a laboratory at rest must be the same as when performed in a laboratory moving at a constant velocity relative to the first one No ...
Gravitational Force is
... 2. - directed along the line joining the two particles. 3. - for a sphere of uniform density, the force that it exerts on other objects can be obtained by treating the sphere as a point mass at the centre of the sphere. ...
... 2. - directed along the line joining the two particles. 3. - for a sphere of uniform density, the force that it exerts on other objects can be obtained by treating the sphere as a point mass at the centre of the sphere. ...
Types of Forces with Newton`s Laws
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
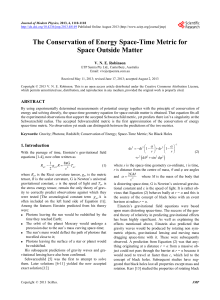
The Conservation of Energy Space-Time Metric for Space Outside
... holes and was able to predict a spreading of photon wavelengths when seen by outside observers. The developments of the general theory of relativity have been very good at explaining most planetary and stellar gravitational effects as well as many galactic phenomena and some inter galactic effects. ...
... holes and was able to predict a spreading of photon wavelengths when seen by outside observers. The developments of the general theory of relativity have been very good at explaining most planetary and stellar gravitational effects as well as many galactic phenomena and some inter galactic effects. ...
Gravity - Glow Blogs
... is its _____, which is measured in __________ (__). The force of gravity acting on an object is its ________. This is measured in _________ (_). The bigger the mass, the _____ its weight will be. Each planet has its own force fo gravity. The ______ the planet, the bigger its force of gravity. On the ...
... is its _____, which is measured in __________ (__). The force of gravity acting on an object is its ________. This is measured in _________ (_). The bigger the mass, the _____ its weight will be. Each planet has its own force fo gravity. The ______ the planet, the bigger its force of gravity. On the ...
Gravity in Einstein`s Universe
... Newton built on Galileo’s work and proposed 3 laws of motion: ...
... Newton built on Galileo’s work and proposed 3 laws of motion: ...