* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gravity in Einstein`s Universe
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
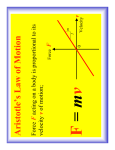
Einstein’s Universe Dr Martin Hendry Dept of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow Isaac Newton Albert Einstein Isaac Newton Albert Einstein Isaac Newton Galileo Galilei How do things move?…. Aristotle’s Theory: 1. Objects move only as long as we apply a force to them 2. Falling bodies fall at a constant rate 3. Heavy bodies fall faster than light ones How do things move?…. v Aristotle’s Theory: Galileo’s Experiment: 1. Objects move only as long as we apply a force to them 2. Falling bodies fall at a constant rate 3. Heavy bodies fall faster than light ones 1. Objects keep moving after we stop applying a force (if no friction) 2. Falling bodies accelerate as they fall 3. Heavy bodies fall at the same rate as light ones How do things move?…. Aristotle’s Theory: Galileo’s Experiment: 1. Objects move only as long as we apply a force to them 2. Falling bodies fall at a constant rate 3. Heavy bodies fall faster than light ones 1. Objects keep moving after we stop applying a force (if no friction) 2. Falling bodies accelerate as they fall 3. Heavy bodies fall at the same rate as light ones How do things move?…. v Aristotle’s Theory: Galileo’s Experiment: 1. Objects move only as long as we apply a force to them 2. Falling bodies fall at a constant rate 3. Heavy bodies fall faster than light ones 1. Objects keep moving after we stop applying a force (if no friction) 2. Falling bodies accelerate as they fall 3. Heavy bodies fall at the same rate as light ones Apollo 15 astronaut David Scott How do things move?…. Newton built on Galileo’s work and proposed 3 laws of motion: 1. A body moves in a straight line unless acted on by some force How do things move?…. Newton built on Galileo’s work and proposed 3 laws of motion: 1. A body moves in a straight line unless acted on by some force 2. The acceleration of a body is proportional to the force on it F = ma How do things move?…. Newton built on Galileo’s work and proposed 3 laws of motion: 1. A body moves in a straight line unless acted on by some force 2. The acceleration of a body is proportional to the force on it F = ma 3. To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction Isaac Newton: 1642 – 1727 AD The Principia: 1684 - 1686 Moon’s orbit Newton worked out that the Moon feels a ‘circular’ force which balances gravity Earth Classical Physics: “All the World’s A Stage” Newton’s physics assumes absolute space and time. Working out how things look to different observers follows simple rules, in different reference frames Classical Physics: “All the World’s A Stage” Newton’s physics assumes absolute space and time. Working out how things look to different observers follows simple rules, in different reference frames Classical Physics: “All the World’s A Stage” Newton’s physics assumes absolute space and time. Working out how things look to different observers follows simple rules, in different reference frames Classical Physics: “All the World’s A Stage” Newton’s physics assumes absolute space and time. Working out how things look to different observers follows simple rules, in different reference frames The laws of physics are the same for everyone, everywhere! Classical Physics: Maxwell’s theory of light Light is a wave – electromagnetic radiation Classical Physics: Maxwell’s theory of light Light is a wave – electromagnetic radiation Maxwell’s Equations imply Speed of light = 300,000 km/s Classical Physics: Maxwell’s theory of light Light is a wave – electromagnetic radiation Maxwell’s Equations imply Speed of light = 300,000 km/s But how did light propagate?…… Through the Ether?… Earth in January Light from a distant star Sun Earth in July 50mph In Newton’s picture, the relative speed of the two trains is 50 + 50 = 100mph 50mph 50mph 50mph Speed of light relative to the ground faster than speed of light relative to the train Through the Ether?… Light from distant stars Ether drift Michelson and Morley devised an experiment to measure the speed of light coming from different directions The Michelson and Morley Experiment would try to measure the “Ether Drift” by timing different light beams – like swimmers on a fast-flowing river River flow The Michelson and Morley Experiment would try to measure the “Ether Drift” by timing different light beams – like swimmers on a fast-flowing river C . River flow . A . B The Michelson and Morley Experiment would try to measure the “Ether Drift” by timing different light beams – like swimmers on a fast-flowing river C . River flow They detected absolutely no Ether Drift. Something weird was going on. Light was not following Newton’s rules . A . B Special Relativity: 1905 “Maxwell’s Equations of Electromagnetism are the same for all observers, regardless of their relative motion” Special Relativity: 1905 Implies the speed of light must be constant, measured to be the same by any two observers, regardless of their relative motion” There must be no ether, and so no ether drift Special Relativity: 1905 Implies the speed of light must be constant, measured to be the same by any two observers, regardless of their relative motion” This abolished completely Newton’s idea that space and time were absolute h Train carriage Let’s try to see why! Torch beam reflected off roof of carriage Train carriage Let’s try to see why! h Distance = speed x time Torch beam reflected off roof of carriage Train carriage h Distance = speed x time Torch beam reflected off roof of carriage Train carriage 2h = c x tc h Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… v Now viewed from the platform… v Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… Now viewed from the platform… Let’s call the time measured on the platform tP Now viewed from the platform… Let’s call the time measured on the platform tP Now viewed from the platform… Let’s call the time measured on the platform tP Now viewed from the platform… v tP The base of this triangle is v tP Now viewed from the platform… v tP This is an isosceles triangle, so it’s made up of two equal right angled triangles Now viewed from the platform… This is an isosceles triangle, so it’s made up of two equal right angled triangles Now viewed from the platform… This is an isosceles triangle, so it’s made up of two equal right angled triangles Let’s look at this triangle. What’s the length of its base? 1 2 v tP Let’s look at this triangle. What’s the length of its base? 1 2 v tP What about its height? h Train carriage h 1 2 v tP What about its height? h 1 Remember: 2 v tP 2h = c x tc Distance = speed x time Torch beam reflected off roof of carriage Train carriage 2h = c x tc h 1 2 c tc 1 Remember: 2 v tP 2h = c x tc 1 2 c tc 1 2 v tP If both observers measure the same speed of light, c… Total distance = c x tP 1 2 ctS 1 2 vtm If both observers measure the same speed of light, c… 1 1 c tc 2 1 c t P 2 2 v tP If both observers measure the same speed of light, c… 1 1 c tc 2 1 c t P 2 2 v tP Using Pythagoras’ theorem, (ctP)2 = (vtP)2 + (ctc)2 1 1 c tc 2 1 c t P 2 2 v tP tc = tP ( 1 2 v 2 c) It appears that time is running more slowly on the moving train!! We need to think about a unified spacetime tc = tP ( 1 2 v 2 c) Cosmic Ray Muons 60km Evidence for Time Dilation Slow moving muons, would never reach sea level… but v = 0.999c, so muon lifetime appears to us to be greatly extended Sea level Einstein’s Relativity 300,000 1 kms The speed of light is the ultimate speed limit in the Universe Just as special relativity shows that space and time are inextricably connected, so too are energy and momentum Just as special relativity shows that space and time are inextricably connected, so too are energy and momentum Particles have a particular rest mass, which is the mass you would measure if the particle is at rest Just as special relativity shows that space and time are inextricably connected, so too are energy and momentum Particles have a particular rest mass, which is the mass you would measure if the particle is at rest Mass and energy are equivalent E= 2 mc Hydrogen fusion – fuelling a star’s nuclear furnace H = Hydrogen He = Helium 2 E = mc Einstein’s Relativity What about accelerated observers? How does gravity fit into this? General Relativity: 1916 Isaac Newton: 1642 – 1727 AD The Principia: 1684 - 1686 Moon’s orbit But how does the Moon know to orbit the Earth? How does gravity act at a distance across space? Earth Gravity in Einstein’s Universe Gravity and acceleration are equivalent Gravity is not a force acting through space and time, but the result of mass (and energy) warping spacetime itself Einstein’s Relativity Gravity in Einstein’s Universe Matter causes space “Spacetime tells matter how move, to to curve orand warp matter tells spacetime how to curve” Gravity in Einstein’s Universe v Differences between Newton’s and Einstein’s gravity predictions are tiny, but can be detected in the Solar System – and Einstein always wins! Gravity in Einstein’s Universe v 1. Precession of orbits – observed for Mercury, matching GR prediction Gravity in Einstein’s Matter causes space to curve or warp Universe v 1. Precession of orbits – observed for Mercury, matching GR prediction 2. Bending of light close to the Sun – visible during total eclipse, measured in 1919 Gravity in Einstein’s Universe v 1. Precession of orbits – observed for Mercury, matching GR prediction 2. Bending of light close to the Sun – visible during total eclipse, measured in 1919 Gravity in Einstein’s Universe v 1. Precession of orbits – observed for Mercury, matching GR prediction 2. Bending of light close to the Sun – visible during total eclipse, measured in 1919 Gravity in Einstein’s Universe A ‘Black Hole’ warps spacetime so much that even light can’t escape Gravity in Einstein’s Universe Close to a rotating black hole, spacetime does very strange things: Closed timelike loops are possible Inside a black hole there may be a wormhole which could allow Faster than Light travel and communication (but how do we open a wormhole?…) Gravity in Einstein’s Universe What is driving the cosmic acceleration?… Einstein’s Greatest Blunder?… Could we use To hold open wormholes?… Well, it works in Star Trek DS9!! Grand Unification Theories “The generalisation of the theory of gravitation has occupied me unceasingly since 1916” Einstein, 1952