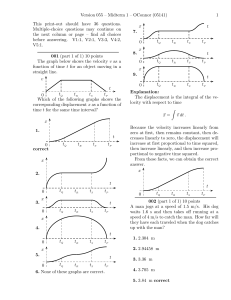
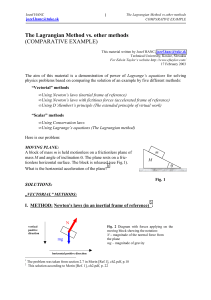
Biomechanics Student Exercise Book
... "I'd like to say my name is Benjamin Sinclair Johnson Jr, and this world record will last 50 years, maybe 100," he had told the room. Later he said: "A gold medal -- that's something no one can take away from you." But they could take it away from him. And they did. Just 24 hours later Johnson had f ...
... "I'd like to say my name is Benjamin Sinclair Johnson Jr, and this world record will last 50 years, maybe 100," he had told the room. Later he said: "A gold medal -- that's something no one can take away from you." But they could take it away from him. And they did. Just 24 hours later Johnson had f ...
Newton`s Third Law of Motion CHECK YOUR ANSWER
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
... Two people of equal mass on slippery ice push off from each other. Will both move at the same speed in opposite directions? A. B. C. D. ...
File - Mr. Downing Science 20
... Since uniform motion is rare in the natural world, there is often a necessity to use these new formulas. When you are not given a distance value in a question but you know: → ________________________________ ( ______________________________) and a time → an _______________________ (or the object s ...
... Since uniform motion is rare in the natural world, there is often a necessity to use these new formulas. When you are not given a distance value in a question but you know: → ________________________________ ( ______________________________) and a time → an _______________________ (or the object s ...
Honors Physics Unit 4 Notes
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...
... object is zero. • Objects that are either at rest or moving with constant velocity are said to be in equilibrium. • Newton’s first law describes objects in equilibrium. Tip: To determine whether a body is in equilibrium, find the net force. If the net force is zero, the body is in equilibrium. If th ...
Lecture 03 - Eunil Won
... Law of Inertia (mass) Any body will remain at rest of in motion in a straight line with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an outside force If the net force is zero, there is a reference frame with zero acceleration ...
... Law of Inertia (mass) Any body will remain at rest of in motion in a straight line with a constant velocity unless acted upon by an outside force If the net force is zero, there is a reference frame with zero acceleration ...
5, 6, 10, 13, 14, 18, 23 / 5, 7, 16, 23, 31, 34, 39, 43, 45
... rigid body, the two external forces that keep it in equilibrium are its weight, mg, located at the center of gravity, and the normal force, FN, exerted on the base by the table. ...
... rigid body, the two external forces that keep it in equilibrium are its weight, mg, located at the center of gravity, and the normal force, FN, exerted on the base by the table. ...
Worked solutions Chapter 2: Collisions and
... p = mv = 1.0 103 × 10 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east For the station wagon: p = mv = 2.0 103 × 5.0 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west Total momentum = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east + 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west = 0 p i = p f From Question 1c, p i = 0 so p f = 0 i.e. common velocity = 0 It hasn’t gone anywhere. The ...
... p = mv = 1.0 103 × 10 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east For the station wagon: p = mv = 2.0 103 × 5.0 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west Total momentum = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east + 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west = 0 p i = p f From Question 1c, p i = 0 so p f = 0 i.e. common velocity = 0 It hasn’t gone anywhere. The ...
Sample
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
... acceleration. The magnitude of the force that the cart exerts on the horse A) is zero newtons. B) equal to the magnitude of . C) less than the magnitude of . D) greater than the magnitude of . E) cannot be determined without knowing the mass of the horse. Answer: B Var: 1 24) An object of weight W i ...
Rotational Inertia and Angular Momentum
... Because the direction of something rotating is hard to determine, physicists say that the direction of angular momentum is in the plane of the rotation. If this wheel was rotating, we would say its angular momentum is pointed in this direction. So it would want to stay rotating in that direction. ...
... Because the direction of something rotating is hard to determine, physicists say that the direction of angular momentum is in the plane of the rotation. If this wheel was rotating, we would say its angular momentum is pointed in this direction. So it would want to stay rotating in that direction. ...
Efficiency
... The input work is the input force multiplied by the length of the ramp (10 meters). If you set the input work equal to the output work, you quickly find that the input force is 50 newtons (Fd = F × 10 m = 500 J). The input force is one-tenth of the output force. For a frictionless ramp, the mechanic ...
... The input work is the input force multiplied by the length of the ramp (10 meters). If you set the input work equal to the output work, you quickly find that the input force is 50 newtons (Fd = F × 10 m = 500 J). The input force is one-tenth of the output force. For a frictionless ramp, the mechanic ...
Rotary Homework #1
... rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. He does so by banking the road in such a way that the force causing the centripetal acceleration will be supplied by the component of the normal force toward the center of the circular path. (a) Show that, for a given speed v and a radius r, the ...
... rely on friction to round the curve without skidding. He does so by banking the road in such a way that the force causing the centripetal acceleration will be supplied by the component of the normal force toward the center of the circular path. (a) Show that, for a given speed v and a radius r, the ...
Contents
... A reference frame which is fixed with respect to a rotating rigid body is not inertial. The parade example of this is an observer fixed on the surface of the earth. Due to the rotation of the earth, such an observer is in a noninertial frame, and there are corresponding corrections to Newton’s laws ...
... A reference frame which is fixed with respect to a rotating rigid body is not inertial. The parade example of this is an observer fixed on the surface of the earth. Due to the rotation of the earth, such an observer is in a noninertial frame, and there are corresponding corrections to Newton’s laws ...
Density Significant Figures: Multiplication Significant Figures
... In the absence of external forces, when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a a straight line). When no force acts on an object, the ...
... In the absence of external forces, when viewed from an inertial reference frame, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity (that is, with a constant speed in a a straight line). When no force acts on an object, the ...
Bab 4
... Answer: (d). With twice the force, the object will experience twice the acceleration. Because the force is constant, the acceleration is constant, and the speed of the object (starting from rest) is given by v = at. With twice the acceleration, the object will arrive at speed v at half the time. ...
... Answer: (d). With twice the force, the object will experience twice the acceleration. Because the force is constant, the acceleration is constant, and the speed of the object (starting from rest) is given by v = at. With twice the acceleration, the object will arrive at speed v at half the time. ...
Chapter 7
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...
... and the length of the wire is 1.20 m. Find the velocity (magnitude and direction) of the ball (a) just before the collision, and (b) just after the collision. ...